Gummel–Poon model
advertisement

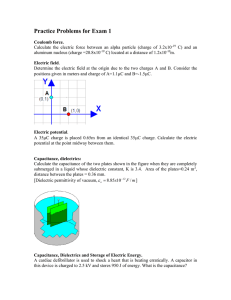
Gummel–Poon model From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Schematic of Spice Gummel-Poon Model NPN The Gummel–Poon model is a model of the bipolar junction transistor. It was first described in a paper published by Hermann Gummel and H. C. Poon at Bell Labs in 1970.[1] The Gummel–Poon model and modern variants of it are widely used via incorporation in the popular circuit simulators known as SPICE. A significant effect included in the Gummel–Poon model is the direct current variation of the transistor βF and βR. When certain parameters are omitted, the Gummel–Poon model reduces to the simpler Ebers–Moll model.[1] Model parameters Spice Gummel–Poon model parameters # Name 1 IS 2 BF 3 NF 4 VAF 5 IKF 6 ISE 7 NE 8 BR 9 NR 10 VAR 11 IKR Property Modeled current current current current current current current current current current current Parameter transport saturation current ideal max forward beta forward current emission coefficient forward Early voltage corner for forward beta high current roll-off B-E leakage saturation current B-E leakage emission coefficient ideal max reverse beta reverse current emission coefficient reverse Early voltage corner for reverse beta high current roll-off Units A V A A V A Default Value 1.00E-016 100 1 inf inf 0 1.5 1 1 inf inf 12 ISC current B-C leakage saturation current A 0 current B-C leakage emission coefficient 2 13 NC resistance zero-bias base resistance ohms 0 14 RB 15 IRB resistance current where base resistance falls half-way to its minimum A inf ohms RB 16 RBM resistance minimum base resistance at high currents 17 RE resistance emitter resistance ohms 0 resistance collector resistance ohms 0 18 RC capacitance B-E zero-bias depletion capacitance F 0 19 CJE 20 VJE capacitance B-E built-in potential V 0.75 0.33 21 MJE capacitance B-E junction exponential factor 22 TF capacitance ideal forward transit time s 0 0 23 XTF capacitance coefficient for bias dependence of TF V inf 24 VTF capacitance voltage describing VBC dependence of TF 25 ITF capacitance high-current parameter for effect on TF A 0 excess phase at freq=1.0/(TF*2PI) Hz deg 0 26 PTF 27 CJC capacitance B-C zero-bias depletion capacitance F 0 28 VJC capacitance B-C built-in potential V 0.75 0.33 29 MJC capacitance B-C junction exponential factor 30 XCJC capacitance fraction of B-C depletion capacitance connected to internal base node 1 31 TR capacitance ideal reverse transit time s 0 32 CJS capacitance zero-bias collector-substrate capacitance F 0 33 VJS capacitance substrate junction built-in potential V 0.75 34 MJS capacitance substrate junction exponential factor 0 35 XTB forward and reverse beta temperature exponent 0 36 EG energy gap for temperature effect of IS eV 1.1 37 XTI temperature exponent for effect of IS 3 flicker-noise coefficient 0 38 KF 39 AF flicker-noise exponent 1 40 FC coefficient for forward-bias depletion capacitance formula 0.5 41 TNOM parameter measurement temperature deg.C 27 [2] References ^ a b H. K. Gummel and H. C. Poon, "An integral charge control model of bipolar transistors", Bell Syst. Tech. J., vol. 49, pp. 827–852, May–June 1970 2. ^ http://virtual.cvut.cz/dynlabmodules/ihtml/dynlabmodules/semicond/node48.html Summary of model with schematics and equations 1. External links An Integral Charge Control Model of Bipolar Transistors manuscript Bell System Technical Journal, v49: i5 May-June 1970 Summary of model with schematics and equations Agilent manual: The Gummel–Poon Bipolar Model as implemented in the simulator SPICE Designers-Guide.org comparison paper Xiaochong Cao, J. McMacken, K. Stiles, P. Layman, Juin J. Liou, Adelmo Ortiz-Conde, and S. Moinian, "Comparison of the New VBIC and Conventional Gummel– Poon Bipolar Transistor Models," IEEE Trans-ED 47 #2, Feb. 2000. The spice Gummel-Poon model online Course on modeling and simulation. Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gummel%E2%80%93Poon_model" Categories: Transistor modeling