Living Things PowerPoint
advertisement

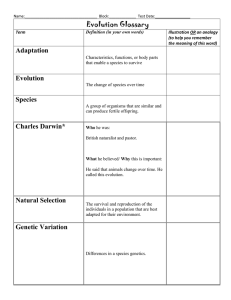
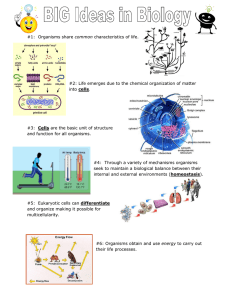
Characteristics of Living Things R. Bryant 2008 WSMS – Based on “Science Starters” by T. Trimpe at h<p://sciencespot.net Determine which objects are considered living or nonliving. A. B. C. E. D. F. The solution … Living NonLiving Why is R.O.G.E.R.S. a living thing? • Living things respond…… Respond/React to Changes • Organisms react to change in their surroundings. • Any reaction to change is called a response. – For example: A bright light may cause you to blink. Why is R.O.G.E.R.S. a living thing? • Living things are organized…………. Organized from smallest unit which are cells • Organisms are made up of one or more cells. • A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. – Cells = the of life. • Cells are organized into =ssues • Tissues are organized into organs • Organs are organized into organ systems • Organ systems are organized into organisms Why is R.O.G.E.R.S. a living thing? • Living things grow and develop……. Grow and Develop • Living things change, or develop, during their lifetimes. • One way organisms change is by growing. • Living things may also change in appearance. For example: tadpoles and frogs Why is R.O.G.E.R.S. a living thing? • Living things take in and use energy…… Use and Need Energy • Sunlight is the source of • All organisms energy for most living need and use things. energy to live. – Plants use the energy in • Energy is the sunlight to make food ability to do – Animals get energy by work. eating plants or other animals that have eaten plants. – Bacteria and fungi get energy from decaying plant or animal matter Why is R.O.G.E.R.S. a living thing? • Living things reproduce………. Reproduce Reproduc=on is not essen=al for the survival of individual organisms, but must occur for a species to survive. Why is R.O.G.E.R.S. a living thing? • Living things have Similar chemicals……. • Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements cons=tute about 95% of your body weight. Adapted to Their Surroundings • Organisms are adapted, or suited, to their surroundings. • All organisms have features that help them survive in their surroundings. – For example: fish have gills Other characteris=cs • Movement – Internal movement of organelles and fluids – External movement-­‐ up or down – Locomo=on • Maintain Homeostasis – Rela=vely constant internal environment, pH, temp, salinity (like humans body temperature stays right around 98.6) What do living things need? • SHELTER • AIR • FOOD • WATER