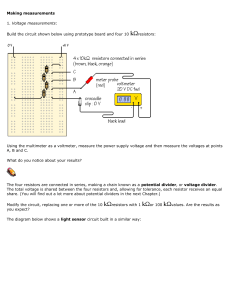
3 MB Mon, 4 Apr 2016 Physics Intervention Resources
advertisement

Questions
Q1.
(a) A technician investigates a light-dependent resistor (LDR) connected in series with a 120 Ω
resistor and a voltage source.
The technician measures the voltage across the LDR and also the current in the LDR.
(i) Which one of these circuits should the technician use?
Put a cross (
) in the box next to your answer.
(1)
(ii) When the LDR is in bright sunlight, its resistance is 185 Ω.
The voltage across the LDR is then 7.2V.
Show that the current in the LDR is about 0.039 A.
(2)
(iii) Complete the sentence by putting a cross (
) in the box next to your answer.
The current in the 120 Ω resistor is
(1)
A
much more than the current in the LDR
B
much less than the current in the LDR
C
the same as the current in the LDR
D
the opposite of the current in the LDR
(iv) The technician repeats the readings with the LDR in different light conditions.
The table gives two of the readings.
Explain why the two current readings are different.
(2)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
*(b) The photograph shows a temporary traffic sign.
The traffic sign uses many small lights all powered by a rechargeable battery.
These lights need to be very bright during the day so that they can be seen clearly.
They do not need to be as bright at night.
Explain how using a light-dependent resistor can make the energy stored in the battery last
longer.
(6)
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................
Q2.
An inventor is designing a battery-powered torch.
She wants the torch to have a brightness control.
(a) Which of these could she use in this control?
Put a cross (
) in the box next to your answer.
(1)
A a diode
B a light-dependent resistor
C a thermistor
D a variable resistor
(b) She builds this circuit to test the lamp in the torch.
(i) Add a voltmeter to the circuit which will measure the potential difference (voltage)
across the lamp.
(1)
She sets the control at the "bright" position.
The current is 0.26 A and the potential difference (voltage) across the lamp is 6.0 V.
Calculate the resistance of the lamp.
(2)
resistance of the lamp = . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ω
(c) The inventor takes readings of the potential difference (voltage) across the lamp and the
current at different positions of the
control from "dim" to "bright".
She plots a graph of the readings.
(i) Complete this graph by plotting the missing point and drawing the curve of best fit.
(2)
(ii) Describe what this graph shows about how the current changes as the voltage
changes.
(2)
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
(iii) The lamp gives no light when the brightness control is at its lowest setting.
Suggest why the torch would still need an on/off switch as well as the brightness control.
(2)
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
(Total for Question = 10 marks)
Q3.
A student is investigating a filament lamp.
(a) (i) Complete the sentence by putting a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer.
The current in the filament lamp is a flow of
(1)
A protons
B neutrons
C electrons
D atoms
(ii) The student uses this circuit in his investigation.
State what is measured by the meters.
(2)
Meter 1 measures
.............................................................................................................................................
Meter 2 measures
.............................................................................................................................................
(b) The normal operating potential difference (voltage) and current of the filament lamp is 6 V,
0.4 A.
Calculate the energy supplied to the lamp under these conditions in 20 s.
(2)
energy = ........................................................... J
(c) The graph shows how current varies with potential difference (voltage) for another filament
lamp.
Calculate the resistance of the lamp when the current in the lamp is 0.3 A.
resistance = potential difference ÷ current (R = V / I)
(3)
resistance = ........................................................... Ω
(Total for Question = 8 marks)
Q4.
An inventor is designing a battery-powered torch.
She wants the torch to have a brightness control.
The inventor takes readings of the potential difference (voltage) across the lamp and the
current at different positions of the
control from "dim" to "bright".
She plots a graph of the readings.
(i) Complete this graph by plotting the missing point and drawing the curve of best fit.
(2)
(ii) Describe what this graph shows about how the current changes as the voltage
changes.
(2)
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
(iii) The lamp gives no light when the brightness control is at its lowest setting.
Suggest why the torch would still need an on/off switch as well as the brightness control.
(2)
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
Q5.
The photograph shows a device used to measure the amount of light.
The circuit diagram shows how the components inside this device are connected.
(i) Complete the sentence by putting a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer.
The meter used in this circuit is
(1)
A a voltmeter connected in series with the LDR
B a voltmeter connected in parallel with the LDR
C an ammeter connected in series with the LDR
D an ammeter connected in parallel with the LDR
(ii) The amount of light entering the light-dependent resistor (LDR) increases.
Which row of the table correctly describes the change in the resistance of the LDR and the
change in the current in the circuit?
Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer.
(1)
A
B
C
D
resistance of the LDR
increases
increases
decreases
decreases
current in circuit
decreases
increases
decreases
increases
(iii) The device is used as a light meter.
It has a 9 V battery.
Calculate the current when the resistance of the LDR is 600 Ω.
(3)
current = ........................................ A
(iv) When the light meter has been used for a long time, the meter reading becomes incorrect.
Suggest what has happened.
(2)
....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
......................
....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
......................
....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
......................
....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
......................
Q6.
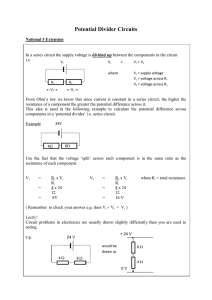
(a) The diagram shows an electric circuit with two resistors, R and S.
(i) R has a resistance of 11 ohms.
Calculate the potential difference across R.
(2)
potential difference = . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
(ii) Use information from the diagram to calculate the current in S.
(1)
current = . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A
(iii) Complete the sentence by putting a cross (
) in the box next to your answer.
A student wants to measure the battery voltage with a voltmeter.
The voltmeter should be placed
(1)
A in series with the battery
B in parallel with the battery
C in parallel with the ammeter
D in series with either resistor R or S
(b) Explain why the temperature of a resistor increases when a current passes through it.
(2)
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
*(c) A resistor is a circuit component.
Two other circuit components are a light dependent resistor (LDR) and a thermistor.
Explain how LDRs and thermistors can be used to control the current in a circuit.
(6)
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
(Total for Question is 12 marks)
Q7.
(a) A designer is going to use a thermistor in a temperature gauge. He connects the thermistor
into this circuit.
He heats the thermistor and measures the current at different temperatures. Here are
some of the results plotted on a graph.
At 47 °C the current was 0.138 A.
(i) Plot this value on the graph.
(1)
(ii) Draw the curve of best fit through the points.
(1)
(iii) The supply voltage is 12 V.
At 20 °C the current is 0.047 A.
Calculate the resistance of the thermistor at this temperature.
(3)
resistance = . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ω
(iv) Use this graph of current against temperature to explain the relationship between
resistance and temperature for
this thermistor.
(2)
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
(b) (i) When there is an electric current in a resistor, the resistor gets hot.
Explain why the resistor gets hot.
(2)
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
.....................
.............................................................................
.....................
(ii) Suggest why the thermistor in a temperature gauge might indicate a temperature
slightly higher than the actual
temperature of its surroundings.
(1)
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
......................
.............................................................................
.....................
(Total for Question = 10 marks)
Mark Scheme
Q1.
Q2.
(a)
(b)(i)
Answer
D a variable resistor
connected in parallel with lamp (1)
(b(ii)
Substitution
R = 6.0 / 0.26
(1)
Acceptable answers
recognisable symbol such as a box
with letter V inside or box with the
word voltmeter inside it accept
voltmeter across both lamp and
ammeter
Mark
(1)
(1)
An answer which rounds to 23
(2)
Evaluation
= 23
(1)
point correctly plotted at 2.0, 0.14 to
within half a small square (1)
Give full marks for correct answer no
working
(c)(i)
Judge curve by eye.
(2)
If more than one line present then
ignore any that appear to be erased or
smooth curve of best fit connecting all deleted.
given points within half a small square Ignore any part of line which goes
(1)
beyond given points.
If plotted point is incorrect then allow
ecf for line
(c)(ii) a description includingtwo of the
(2)
following:
Allow reverse argument
current increases as voltage
increases (1)
positive correlation (between them )
current is not proportional to
the pd (1)
graph is not a straight line not in equal
steps
gradient gets less (1)
current does not increase as much (as
it gets higher)
accept resistance has increased with
increase in current for two marks
(c)(iii) a suggestion to include:
(2)
there is still a current (when control is to break the circuit
at min position) (1)
to switch the currentoff accept flow
of
make the battery last longer (1)
electricity/charge/electrons for current
{battery / energy} would be {drained
/used up/ wasted} otherwise accept
reverse arguments
ignore reference to power / volts
Q3.
Q4.
(i)
(ii)
Answer
point correctly plotted at 2.0, 0.14 to
within half a small square (1)
Acceptable answers
Mark
Judge curve by eye.
(2)
If more than one line present then
ignore any that appear to be erased or
smooth curve of best fit connecting all deleted.
given points within half a small square Ignore any part of line which goes
(1)
beyond given points.
If plotted point is incorrect then allow
ecf for line
a description includingtwo of the
(2)
following:
Allow reverse argument
current increases as voltage
increases (1)
positive correlation (between them )
current is not proportional to
the pd (1)
graph is not a straight line not in equal
steps
gradient gets less (1)
current does not increase as much (as
it gets higher)
accept resistance has increased with
increase in current for two marks
(iii)
a suggestion to include:
(2)
there is still a current (when control is to break the circuit
at min position) (1)
to switch the currentoff accept flow
of
make the battery last longer (1)
electricity/charge/electrons for current
{battery / energy} would be {drained
/used up/ wasted} otherwise accept
reverse arguments
ignore reference to power / volts
Q5.
Question
Number
(i)
Answer
Acceptable answers
Question
Number
(ii)
Answer
Question
Number
(iii)
Answer
Acceptable answers
Mark
substitution (1)
allow substitution and
transposition in either
order
(3)
C
(1)
Acceptable answers
D
9 = I × 600
transposition (1)
I = 9/600
Mark
Mark
(1)
give full marks for
correct answer, no
working
evaluation (1)
= 0.015 (A)
OR
=15 mA
Question
Number
(iv)
Answer
An explanation linking
the following
Acceptable answers
Mark
(2)
• battery voltage has
decreased (1)
• (so) less current
(than expected) (1)
Q6.
Answer
11x 0.4 (substitution)
(1)
(a)(i)
(a)(ii)
(a)(iii)
(b)
Acceptable answers
Mark
(2)
Full marks for correct answer with
no calculation
4.4 (V)
(1)
0.6 - 0.4 (A)
0.2 or 1/5 (A)
(1)
B
An explanation linking: electrons
(1)
colliding with other electrons
{colliding with / bumping into}
ions in the lattice /atoms in the
If no other marks scored, allow
metal (1)
for 1 mark for "electrical energy
{transferred/changed} into
thermal/heat energy"
(1)
(1)
(2)
do not allow energy being
created or produced
QWC
*(c)
Indicative Content
M
A explanation including some of the following points
Light dependent resistors (LDR)
Resistance changes with light intensity
Bright light , low resistance
No light (dark), high resistance
Low resistance gives high current.(RA)
Thermistor
Resistance changes with temperature
Negative temperature coefficient
High temperature, low resistance
Low temperature, high resistance
Low resistance gives high current (RA)
Level
1
0
1-2
No rewardable content
a limited explanation linking light affecting LDR AND heat affecting
thermistor
OR a correct relationship for one device, e.g. thermistors change
(
2
3-4
3
5-6
resistance when the temperature changes and LDRs change
resistance when it gets dark OR the {resistance decreases/ current
increases} of a LDR when the light gets brighter
the answer communicates ideas using simple language and uses
limited scientific terminology
spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with limited accuracy
a simple explanation correctly linking the temperature and light with
resistance or current for both devices
OR a correct relationship for one device with a link to the way this
affects the current and resistance.
e.g. the resistance of a LDR increases when the light gets dimmer and
when the temperature lowers the resistance of a thermistor increases
OR the resistance of a LDR decreases when the light gets brighter
and this increases the current
the answer communicates ideas showing some evidence of clarity
and organisation and uses scientific terminology appropriately
spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with some accuracy
a detailed explanation including the qualitative relationships for both
devices and a link to the way resistance change affects the current in
BOTH of them, e.g. the resistance of a LDR is less when the light gets
brighter which increases the current. When the temperature lowers
the resistance of a thermistor increases. This means that the current
will decrease as the thermistor cools down.
the answer communicates ideas clearly and coherently uses a range
of scientific terminology accurately
spelling, punctuation and grammar are used with few errors
Total for question = 12 marks
Q7.
Answer
Acceptable answers Mark
(a)(i)
Correctly plotted point (1)
+/- ½ a small square
(1)
(a)(ii) Smooth line through most (at least 5)
(1)
crosses / points (1)
Do not accept clearly dot-to-dot or
excessive tramlining
Ignore any part of line after 45
(a) (iii) Substitution: (1)
transposition and substitution in either (3)
order
12 = 0.047 × R
substitution mark can be scored when
Transposition: (1)
incorrectly transposed word/symbol
equation is given
R = 12/0.047
255.3, 255
Evaluation: (1)
give full marks for correct answer no
working
R = 260
power of 10 errors with no
working score max 1 mark
(a) (iv) An explanation linking
current increases with
temperature (1)
with
(2)
(for this first MP)
ignore faster/slower
(charge/current)
ignore references to heat,
current flows more
(so) resistance decreases(1)
can score both marks by quoting two
suitable pairs of values from graph
or
the voltage is constant (1) with
For full marks, there must be a
(so) resistance decreases (with reference to change of either I or R
temperature increase)(1)
with temperature
(b)(i)
An explanation linking
(2)
{electrons / negative charges}
(1)
atoms / nuclei
collide with
{ions/lattice/electrons} (1)
allow for 1 mark,electrical energy
transferred to {thermal/heat} energy
if no other scored
(b) (ii) A suggestion including
energy transfer in {the thermistor/
any component part of the electrical
circuit} causes a rise in temperature thermistor/resistor {gets hot/is
of thermistor (above surroundings)(1) heated}
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
(1)