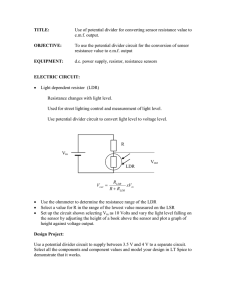
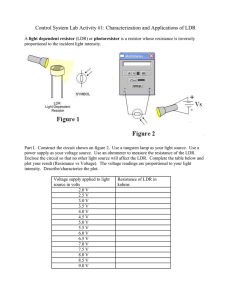
Potential Divider Circuits
advertisement

Potential Divider Circuits National 5 Extension In a series circuit the supply voltage is divided up between the components in the circuit i.e. V V = V +V s s 1 where R1 Vs = supply voltage V1 = voltage across R1 V2 = voltage across R2 R2 V1 2 V2 From Ohm’s law we know that since current is constant in a series circuit, the higher the resistance of a component the greater the potential difference across it. This idea is used in the following example to calculate the potential difference across components in a ‘potential divider’ i.e. series circuit. 24V Example 8 4 Use the fact that the voltage ‘split’ across each component is in the same ratio as the resistance of each component. V1 = = = R1 x Vs Rt 4 x 24 12 8V V2 = = = R2 x Vs Rt 8 x 24 12 16 V where Rt = total resistance ( Remember to check your answer e.g. does V1 + V2 = Vs ) Lastly! Circuit problems in electronics are usually drawn slightly differently than you are used to seeing. e.g. + 24 V 24 V 8 would be drawn as 4 8 4 0V Find the potential difference across each resistor in the following circuits: (1) + 12 V (2) + 24 V 10 6 3 10 6 3 0V (4) + 12 V 0V 0V (5) + 10 V (6) +36 V 2 4 20 10 6 16 0V (7) + 24 V 0V 0V (8) + 24 V (9) + 24 V 10 8 36 5 4 18 0V (10) 0V (11) + 36 V 0V (3) + 36 V 0V (12) + 36 V +36 V 9 12 21 3 4 7 0V 0V (13) (14) + 10 V + 12 V (15) + 240 V 6 40 36 3 120 144 0V 0V (16) 0V (17) +5V (18) + 36 V + 24 V 2 k 15 36 3 k 25 180 0V 0V (19) 0V (20) + 240 V 0V + 20 V 62 22 434 100 0V Helpful Hint LDR’s and thermistors often make up part of a potential divider circuit in electronic systems. It is important to remember that the resistance of these components varies with external conditions. Use the following data to answer questions 21 – 25. The tables below show how the resistances of a certain LDR and thermistor vary with external conditions. LDR Thermistor light condition dark light bright resistance () 10 000 2 500 20 temperature (oC) 10 40 100 resistance () 4 000 1 980 200 21. The following circuit is part of the input to an electronic frost alarm. + 230 V Calculate the potential difference across the thermistor when it is 100 (a) (b) 10 o C 40 o C 0V 22. The following circuit could be part of a light meter for a camera. + 12 V Use the information above to find the potential difference across the LDR when it is: (a) (b) 1 k 0V dark light 23. Calculate the potential difference across the resistor in the following circuit when the temperature is: + 24 V (a) 100 o C (b) 40 o C 500 0V 24. A young engineer designs part of an electronic system to trigger an alarm when it gets too bright. Determine the ‘trigger voltage’ across the resistor in the following system when the light level becomes ‘bright’. + 36 V 1·5k 0V 25. Determine the temperature at which the following voltmeters will show identical readings. + 230 V V1 200 0V V2