Lecture 1
advertisement
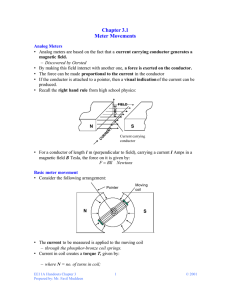
1. ANALOG MEASURING INSTRUMENTS permanent magnet moving coil meter movement: principle, deflecting torque, connection of PMMC voltmeter and ammeter – PMMC meters with rectifier (basic connection, what it measures, frequency dependence) iron-vane meter movement: principle, measured value, V-meter, A-meter measured value electrodynamic meter movement: principle, measured value, W-meter, measured value electrostatic meter movement AE1BEM38EMA – L1 1 ANALOG MEASURING INSTRUMENTS X F (T d ) X – measured quantity; F (M P ) – deflecting force (deflecting torque); - angular deflection kd kd f ( X ) X T d = k d ·f(X); T r = - k r ·; T d + T r = 0; ; kr kr - angle; - deflection in scale divisions PMMC METER F = B·l·I Td = 2B·l·r·N·I permanent magnet l moving coil Fixed cylinder from ferromg. material AE1BEM38EMA – L1 r pole pieces B Basic range: 10 A - 100 mA Coil resistance: 10 - 1 k Usage: - DC PMMC ammeters and voltmeters; - AC PMMC ammeters and voltmeters (with rectifiers) 2 PMMC AMMETER a) single-range meter I I = I m + I b = U m /R m + U m/R b Im Ib U Rb Rm Um Rb Um I I m b) several-ranges meter Ayrton shunt: NO! I m I I R1 R2 R3 I1 I2 I3 Im R1 R ADC R2 Rm U Um ADC U ADC R3 (Voltage drops on resistors of switch are added to voltage drop on shunt) AE1BEM38EMA – L1 U m = (R 1 + R 2 + R 3 )(I 1 - I m) U m + R 1 I m = (R 2 + R 3 )(I 2 - I m) U m + (R 1 + R 2 )I m = R 3 (I 3 - I m) Note: DMMs use the same range-changing principle 3 PMMC VOLTMETER U = I m (R p + R m ) Rp U Rm Um RV U Rp Rm Im Resistance usually given as R i v (/V) – related to the range! AE1BEM38EMA – L1 R1 R2 R AČP AČP U AČP Note: A voltage divider is usually used by DMMs for voltage range changing 4 (PMMC) METER WITH RECTIFIER i(t) u(t) i r2 (t) IDEAL FULLWAVE RECTIFIER u r2 (t) i(t) R2 FILTER ADC i r2 (t) I sa t t I RM 1T 1T ir 2 (t )dt i (t ) dt T0 T0 Meter measures rectified mean (RM), it is however calibrated in RMS values for sinusoidal waveform. RMS value cannot be found from meter reading for non-sinusoidal waveform! Rectified mean value can be found by dividing meter reading by the form-factor for the sinusoidal waveform (i.e. by 1,11) AE1BEM38EMA – L1 5 PMMC METER WITH RECTIFIER V-meter: I A-meter:I R1 RS U U RM Actual passive rectifier: partial linearization by series resistor R m 2R d 2R d +R m I Rp 2R d +R m +R p RS R2 RM Electronic (digital) meters: linearization of rectifier using operational amplifier (see lecture 3) Frequency dependence: - of amplifier - of input divider (parasitic capacitances of resistors) U - of Ayrton shunt (parasitic inductances of resistors) Frequency dependence: - parasitic capacitances of series resistors (V-meter) - (parasitic inductances of resistors (A-meter)) AE1BEM38EMA – L1 6 PMMC METER WITH THERMOCOUPLE U t , measured by PMMC (milli)voltmeter, mV It is proportional to difference of θ a θ 0 Temperature θ, of the heating wire, Is proportional to the square of the heating current Ut θ0 I Rt θ PMMC meter with thermocouple measures the RMS value Advantages: low frequency dependence, Measures correctly also by large crest-factor values. Disadvantage: Low accuracy, low overloading capacity. IRON-VANE (FERROMAGNETIC, MOVING IRON) INSTRUMENT Principle: I B Ferromg. core AE1BEM38EMA – L1 F F~B2 B~I 2 Td = kd I ; 1T 1T 2 2 Td td (t )dt kd i (t )dt kd I RMS T0 T0 Basic range: 10 mA to 100 A Range changing of A-meter: - coil taps - series-parallel connection of equivalent coil sections 7 Practical construction: ferromagnetic axis pointer needle Movable segment Fixed segment coil coil pointer coil air damping axis Iron-vane voltmeter: RS RV = RS + Rm I Range changing: R S R m, L m U I U RV2 2 L2m Strong frequency dependence (used almost exclusively for 50 or 60 Hz) AE1BEM38EMA – L1 8 ELECTRODYNAMIC INSTRUMENT Used as wattmeter MOVABLE COIL - current I 2 POINTER B F ~ B I2 B ~ I1 FIXED COIL - 2 SECTIONS - current I 1 T d = k d I 1 I 2 ; I1 = I CC , I 2 = U VC / R VC For AC waveforms: AXIS 1T 1T 1 1T P Td t d dt k d i1i2 dt k d iCC u VC dt k d T0 T0 RVC T 0 RVC (For harmonic waveforms: M P ~ U I cos) Frequency dependence: Range changing: Finding constant: Td k d U VC I 1 cos( ) 2 2 2 R VC L VC Voltage ranges – series resistor Current ranges – series-parallel connection of equivalent coil sections U I P = k W Only in spec. cases k W N N ( cos N ) max AE1BEM38EMA – L1 for cos = 0,1 or 0,2. 9 ELECTROSTATIC METER MOVEMENT Usage: High voltage (HV) measurement TD = kD U 2 For DC voltage: R in ∞ For AC voltage: T T 1 1 2 TD t D dt k D u 2 dt k D U RMS T0 T0 t D is instantaneous deflecting torgue AE1BEM38EMA – L1 10