MEASUREMENT OF POWER IN THREE PHASE CIRCUIT
advertisement

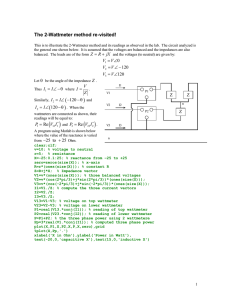
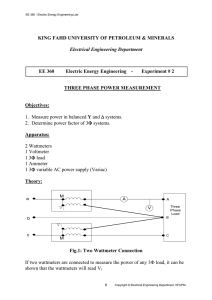
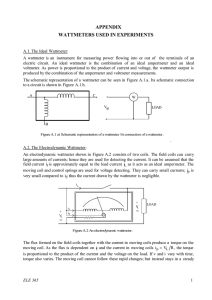
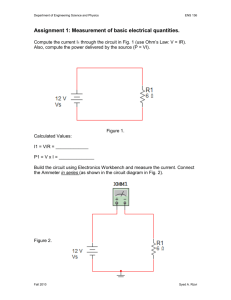
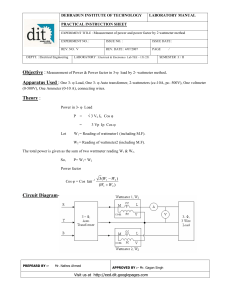
PREMIER TRADING CORPORATION MEASUREMENT OF POWER IN THREE PHASE CIRCUIT AIM : (a) (b) To measure power drawn by a 3 phase Resistive load using two wattmeters. To calculate the power factor of the load from the readings of two wattmeters. INSTRUMENTS REQUIRED : S No. 1. 2. 3. 4. Name Wattmeter Voltmeter Ammeter 3 Phase Resistive Load Type Dynamometer MI MI Resistive Range 5/10A,125/250/500V 0-500V 0-10A Quantity 2 1 1 1 THEORY Power consumed by a 3 phase balanced or unbalanced load (star connected) can be measured by using two Wattmeters properly connected in the load circuit. The current coils of the wattmeters are connected in series with the load in any two lines, whereas the two pressure coils are connected between these lines and the third line as shown in figure. Schematic Diagram for Power measurement by two wattmeter method The phasor diagram of this circuit, assuming balanced lagging load has been shown in figure. As such, rms values of currents, IR, IY and IB are taken equal in magnitude and lagging by an angle f with respect to its own phase voltage. Similarly, rms values of phase voltage are also equal in magnitude but displaced by 120 O. The phase sequence has been assumed as RYB. Based of the phasor diagram, power consumed and the power factor of load can be calculated from the readings of two wattmeters W1 and W2 as explained below :(i) Power consumed by the load :Current through the current coil of Wattmeter, W1 = IR Voltage across the pressure coils of wattmeter, W1 = VRB 1 PREMIER TRADING CORPORATION Phase difference between IR and VRB (ref. phase diagram) = 30 - f Hence, reading of wattmeter, W1 = IR VRB COS (30 - f) W2 = IY VUB COS (30 - f) Similarly, reading of wattmeter, ---------(i) ---------(ii) Phasor diagram Moreover, IR = IY = IB = IL (line current) ---------(iii) Also, VRY = VRB = VBR = VL (line current) ---------(iv) Substituting eqns (iii) and (iv) into eqns. (i) and (ii) and then adding these, 3 VL IL COS f = Power drawn by 3 ph. Load W1 + W2 = ----------(v) Hence, the sum of two wattmeter reading is equal to the total power by a 3 phase balanced load. (ii) Power factor of the load :Subtracting eqn. (ii) from eqn (i) = VL IL COS (30 - f) – VL IL COS (30 + f) = VL IL SIN f W1 – W2 --------(vi) Dividing eqn. (vi) be eqn. (v) W1 – W2 Tan f = 3 W1 + W2 1 Thus, power factor of the load, = 1 + 3 (W1 – W2/W1 + W2)2 Hence, the power factor of the load can also be calculated from the observed readings of the two wattmeters. 2 PREMIER TRADING CORPORATION CONCLUSIONS Following important conclusions can be drawn from the above derivation, regarding the balanced resistive load. 1. When the power factor of the load is low (less that 0.5), the reading of wattmeter W2 will be negative. 2. When the power factor of the load is 0.5 lagging, reading of Wattmeter W2 will be zero. 3. When the power factor of the load is greater than 0.5, both the Wattmeter will record positive readings. 4. When the power factor of the load is unity, the readings of both the wattmeter will be the same. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM The circuit diagram to perform the experiment has been shown as attached sheet. The various details of the same have already been explained above. WORKING OF CONTROL PANEL 1. Connect the circuit as per panel layout diagram. 2. Ensure that the output voltage of 3 phase Variac is at zero or low. 3. Connect the Resistive load as per attached panel layout diagram. On the panel the two wattmeter W1 & W2 and are to be externally connected as per connection diagram. The three-phase power measurement is conducted by connecting two wattmeters, as shown in fig. The power value is indicated by the algebraical addition of the indication value on the two wattmeters. When the power factor of the circuit being measured is greater than 50%, both meters will indicated “positive” values. The total load power is then calculated by the addition of these two values. However, if the power factor of the circuit is less than 50%, one of the two wattmeter will give a negative indication (the pointer will deflect to the left). If this occurs, reverse the voltage connections of the meter with the negative deflection. This and the meter should then indicate on the other meter, to obtain the total load power. In duel current range wattmeter for lower current range short the terminal B1 & B2 (series connection) & for higher current range short the terminal B1 -E1 & B2 -E2 (Parallel connection). 4. Ensure that the resistive load is in OFF position (operated through rotary switch). 3 PREMIER TRADING CORPORATION 5. Switch-on 3 phase AC mains and increase the applied voltage till its rated value as indicated by the voltmeter (415 V). 6. Now switch ON the load using rotary switch. Now turn the rotary switch of the resistive load for various load settings as indicated by the ammeter till its rated load current. 7. Take-down the readings of all the meters i.e. voltmeter, Ammeter & Wattmeter for various load setting of resistive load. 8. Decrease the load gradually by turning the rotary switch. 9. Switch-off the supply and turn the rotary switch of the load. OBSERVATIONS : S No. V May be tabulated as follows. I W1 W2 W1 +W2 W1 -W2 COS f 4 PREMIER TRADING CORPORATION CONNECTION DIAGRAM FOR MEASUREMENT OF POWER BY TWO WATTMETER METHOD WATTMETERS The three-phase power measurement is conducted by connecting two wattmeter, as shown in above Fig. The power value is indicated by the algebraically addition of the indication value on the two wattmeter. When the power factor of the circuit being measured is greater than 50%, both meters will indicated “positive” values. The total load power is then calculated by the addition of these two values. However, if the power factor of the circuit is less than 50%, one of the two wattmeter will give a negative indication (the pointer will deflect to the left). If this occurs, reverse the voltage connections of the meter with the negative deflection. This and the meter should then indicate on the other meter, to obtain the total load power. In duel current range wattmeter for lower current range short the terminal B1 & B2 & for higher current range short the terminal B1 & E2. 5