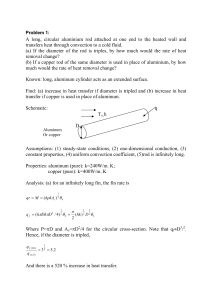
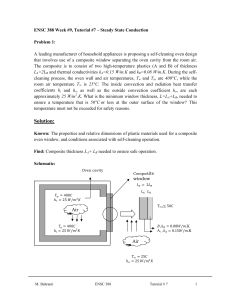
Example 5: A rectangular plate 12.0 mm by 12.0 mm cannot exceed
advertisement

Example 5: A rectangular plate 12.0 mm by 12.0 mm cannot exceed 75.0 °C, so aluminum pin fins with a thermal conductivity of 186 W/m•K, 1.50 mm in diameter, 15.0 mm long are to be attached to the surface. The plate and fins are exposed to ambient air at 30.0 °C with a convection coefficient of 40.0 W/m2•K. The total heat transfer rate from the surface is 1.00 watt. Calculate the following: (a) efficiency and effectiveness of each fin, (b) number of fins that must be attached to the plate, (c) overall efficiency for fin array, and (d) temperature at the base and tip of each fin. Known: A plate with maximum temperature and specified heat transfer rate, A = (0.0120 m)2, Tb,max = 75.0 °C, D = 1.50 mm, L = 15.0 mm, qt = 1.00 W, k = 186 W/m•K, T∞ = 30.0 °C, h = 40.0 W/m2•K Assumptions: 1. Steady state 2. One-dimensional conduction 3. Constant properties 4. Negligible radiation 5. No internal heat generation 6. No contact resistance Find: (a) ηf and εf, (b) N, (c) ηo, and (d) T(x = 0) and T(x = L) Solution: Answer: (a) 95.7%, 39.2, (b) 6.1 fins, (c) 96.6% for N = 7, (d) 70.5 ˚C, 67.9 ˚C for N = 7 D = 1.50 mm pin fins L = 15.0 mm 12 mm base 12 mm Figure 1. Number of fins required to remove 1.00 watt of heat from a surface versus the convection heat transfer coefficient. Figure 2. Number of fins required to remove 1.00 watt of heat from a surface versus the fin length.