Brightness and Color of Stars
advertisement

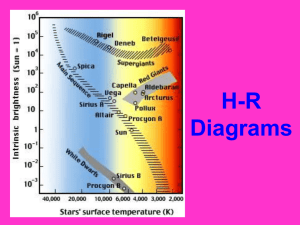
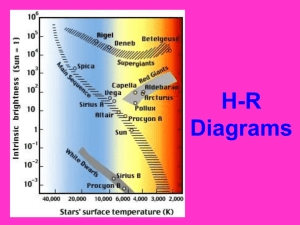
Brightness and Color of Stars Introduction to the Nature of Stars What factors contribute to a star’s brightness ? (What factors determine how bright a star looks when we go outside and look up?) What factors contribute to a star’s brightness ? • distance • temperature • size Proper Motion • Which stars will have the highest proper motion? • Can we use the doppler effect? What kind of relationship is this? Magnitude • An inverse logarithmic brightness scale that roughly parallels the untrained eye’s ability to perceive brightness changes • Originally qualitative; later based on 5 mag difference = 100x change in brightness • Scale is relative • Was “zeroed” by using Vega • There are several ways to define magnitude: two most common are apparent visual magnitude and absolute magnitude How do astronomers • Apparent measure stars magnitude – brightnesses? how bright an object appears from earth • Absolute magnitude – how bright at ten parsecs Measure a star’s absolute magnitude. This is a good approximation of overall luminosity Sub-2 is the fainter star; sub-1 is the brighter star This equation compares two stars – why would we do this? Distance Modulus How are distance and magnitudes related? m – M = 5log(d) – 5 m= apparent magnitude M= absolute magnitude d= distance in parsecs 1 parsec is the distance where the PARallax = 1 arcSEC (3.26 ly) How do we determine how size and temperature contribute to a star’s brightness? • Determined by experiment • Blackbody • Area of radiating object • T4 What factors contribute to a star’s brightness ? L= 2 4πr 4 σT The Stefan-Boltzmann Law – Where did this come from? What does it mean? The Sun’s Surface UBV (Johnson Morgan) System • A series of color indices • U,B,V,R,I • There are other systems in use Stars do have different temperatures! Who are these dudes? What is the H-R diagram? • Began as an experiment. • What was the question?? What is the H-R diagram? • Began as an experiment. • What was the question?? The H-R diagram Is now used as an important tool for discovery. How? The H-R Diagram bright • Aka color magnitude diagram • Plot of luminosity vs surface temperature faint hot cool What factors contribute to a star’s brightness ? L= 2 4πr 4 σT The Stefan-Boltzmann Law – Does the H-R diagram conform to this law? Comparison of Main Sequence Star Sizes Location on Main Sequence Depends on Mass • Many systems are multiple • Visual – observe over time • Spectroscopic – see doppler shifts from relative motion • Spectrum – overlapping spectrum of two stars • Eclipsing – light curves Using Kepler’s Laws we can determine the masses – this is still the only direct way we have of determining the masses of stars. (M1 + M2) P2 = a3 Eclipsing Binary Vs. Brightest Deneb: 19th 1500ly 60,000 Ls Vega: 5th 25ly 35 Ls Altair: 12th 17ly 10 Ls Arcturus: 4th 37ly 210Ls Antares: 16th 600ly 65,000Ls Rigel: 7th 770ly 66,000Ls Capella: 6th 42ly 78Ls Pollux: 17th 34ly 32Ls Procyon: 8th 11ly 8Ls