Chapter 10
Existing Wireless Systems
Part II
Adapted from class notes by
Prof. Leszek T. Lilien, CS, Western Michigan University
and
Prof. Dharma P. Agrawal & Qing-An Zeng, University of Cincinnati
Most slides based on publisher’s slides for 1st and 2nd edition of:
Introduction to Wireless and Mobile Systems by Agrawal & Zeng
© 2003, 2006, Dharma P. Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng. All rights reserved.
0
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
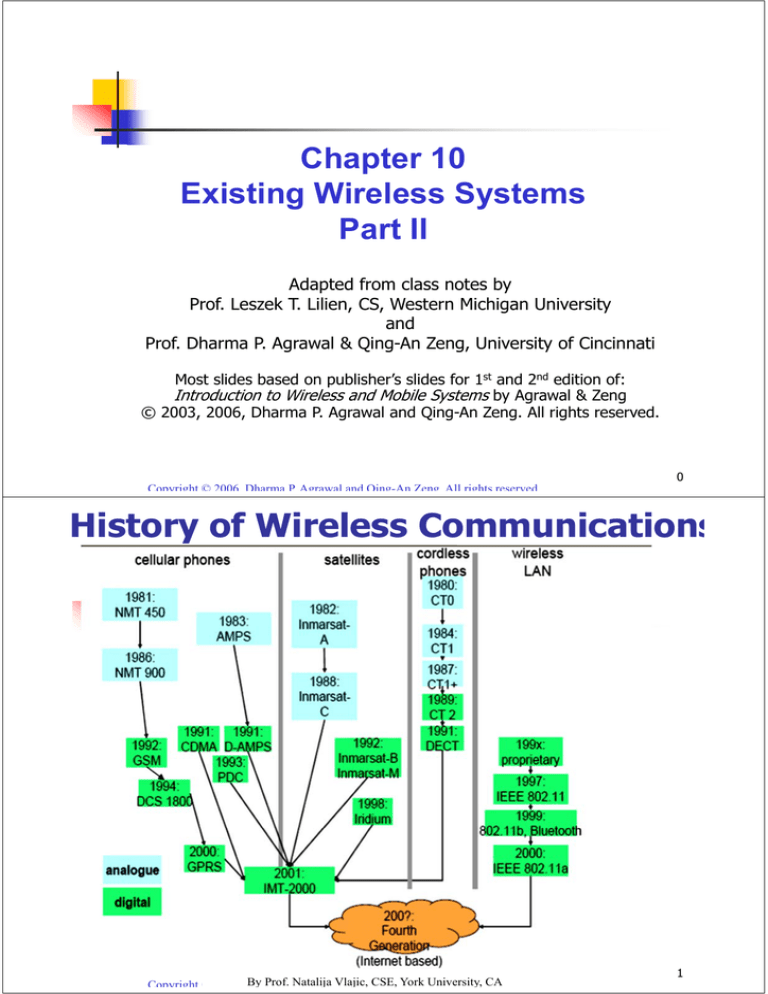
History of Wireless Communications
By Prof.PNatalija
Vlajic,
CSE, York
University,
CA
Copyright © 2006 Dharma
Agrawal
and Qing-An
Zeng
All rights
reserved
1
Mobile Communication (2/2)
2
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
Mobile Communication (1/2)
WiMAX
4G
LTE
HSDPA
3.5G
HSUPA
HSPA+3.9G
2G
2.5G
2G
CDMA
2.9G
3G
3G
3
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
LTE
300M/75M
LTE-Adv 3G/1.5G
4
Source: P
p. Agrawal
32, Jan. 2014
IEEE Spectrum
Copyright © 2006 Dharma
and Qing-An
Zeng All rights reserved
IMT-2000
5
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
IMT–2000
Key Features
International Spectrum allocation
Radio Interfaces
Harmonized 3G Systems
UMTS
UTRAN
Channels in UTRAN
6
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
Key Features
High degree of commonality of design
worldwide.
Compatibility of services within IMT-2000
and with fixed networks.
High quality.
Small terminal for worldwide use,
including pico, micro, macro and global
satellite cells.
Worldwide roaming capability.
Capability for multimedia applications and
a wide range of services and terminals. 7
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
8
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
3G - WCDMA (cont.)
Nokia 3G
concept phones
9
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
3G - WCDMA (cont.)
10
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
3G - WCDMA (cont.)
iMode handset
NEC FOMA 2002 for
NTT DoCoMo 3G WCDMA
FOMA(Freedom Of Mobile multimedia Access) 11
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
3G - cdma2000 (cont.)
Korea – 5/7/2001 Samsung cdma2000 1x
(up to 144Kbps) SCH-X350, SCH-X130
12
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
3G - cdma2000 (cont.)
Korea – 5/7/2001 Samsung cdma2000 1x
(up to 144Kbps) SCH-X350, SCH-X130
13
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
Radio Interfaces
p. 251 (页275) Fig. 10.35
14
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
3G Standard by Access Technology
15
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
Harmonized 3G Systems
High speed data services including Internet and intranet
applications
Voice and non-voice applications
Global roaming
Evolution from the embedded base of 2G systems
ANSI-41 and GSM-MAP core networks
Regional spectrum needs
Minimization of mobile equipment and infrastructure cost
Minimization of the impact of IPRs
The free flow of IPRs
Customer requirements on time.
16
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
Source: WCDMA for UMTS
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
17
3G Transmission
UE
(User Equipment)
Node-B
(Base Station)
Uplink (Reverse Link)
3G
2G
Variable (9.6kbps)
Rate: 9.6kbps~2Mbps
Multimedia
Transmission
Voice/SMS
Downlink (Forward Link)
GSM手机
3G手机
基地台
18
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
CDMA 2000 Architecture
SS7
Network
VLR
Visited Access
Provider Network
AAA
Server
AAA Broker
Network
Visited
AAA
HLR
Home Access
Provider Network
Home
AAA
Home IP
Network
IP
Network
R-P
Interface
FA
HA
Mobile Station
Mobile
Client
Access Network
BSC/PCF
PDSN
FA
Home ISP
Private Network
Visited Provider
Home Provider
R-P interface
A10/A11 MIP/GRE
: Cisco’s current Product Offerings
Copyright © 2006 Dharma PSource:
Agrawal and
Qing-An
Zeng
All rights reserved
www
cisco
com
19
WCDMA Architecture
Source:
IEEE
Copyright © 2006 Dharma
P Agrawal
andcommunications
Qing-An Zeng All magazine
rights reserved
20
TD-SCDMA System for
Mobile communications
Partial Source: Siemens
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
21
TD-SCDMA Frame
TDMA frame length: 5ms
7 normal time slots (duration = 675
us)
3 special time slots: Downlink Pilot
Time Slot (DwPTS), Uplink Pilot Time
Slot (UpPTS), Guard Period (GP1)
22
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
Advantage:
Increased coverage
Reduce Xmission Power
Avoiding shadowing
Overcome dead spots
Benefits of Ad hoc wirless
ODMA scenario showing routing with path
broken into shorter links, and avoiding shadowing
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
23
Effective BS (relaying MS) in ODMA cell
SEED
Full probing
UER High
battery
Duty Maintained probing
TD-SCDMA
Gateway UER
ot UER
Vehicle-mounted
Full probing
UER Poor
battery
Duty
Maintained
Illustration of probing process assignment (ODMA)
24
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
Smart Antenna
The geometric illustration
of circular array
A typical smart antenna architecture
25
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
WCDMA Architecture
of Motorola
Copyright © 2006 Dharma PSource:
AgrawalBroche
and Qing-An
Zeng All rights reserved
27
WCDMA Architecture (cont.)
Source:
WCDMA
for UMTS
Copyright © 2006 Dharma
P Agrawal
and Qing-An
Zeng All rights reserved
28
UMTS-Network Reference
Architecture
p. 253 (页278) Fig. 10.37
29
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
30
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
31
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access
Network (UTRAN)
The UTRAN consists of a set of radio network subsystems (RNSs).
Two main elements:
Node B
Radio Network Controller (RNC)
RNC Responsible for:
Intra UTRAN Hand off
Macro-diversity combining and splitting of the Iub datastreams
Frame Synchronization
Radio Resource Management
Outer loop power control
Serving RNS relocation
UMTS radio link control (RLC) sublayers function execution
32
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
UTRAN – Architecture
p. 254 (页279) Fig. 10.38
33
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
GC
Nt
DC
UuS boundary
U-plane information
C-plane signalling
L3
control
Radio
Bearers
control
control
control
control
RRC
PDCP
PDCP
L2/PDCP
RLC
RLC
BMC
L2/BMC
RLC
L2/RLC
RLC
RLC
RLC
RLC
RLC
Logical
Channels
MAC
L2/MAC
Transport
Channels
PHY
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved
L1
35
I-mode Success Factors
Always on
First mover advantage
Timing
Consumer focus
Low basic sub rate $3/month, with an Imode e-mail address
Low home PC penetration in Japan 13%
Localization of Internet content
Specially designed web pages
Application Alliance Partners
Japanese culture
Handset volume
41
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal
and NTT
Qing-An
Zeng All
rights reserved
Sources:
DoCoMo
Business
Week
C-Mode,感应一下就得到
1.C-Mode的贩卖机系统是
由NTT DoCoMo与可口可乐公
司共同研发。
2.透过移动电话申请专用
的会员证。
3.C-Mode的自动贩卖机有
设置FOMA手机专用的传感器。
4.也可以利用贩卖机投入
现金进行储值。
5.屏幕上显示储值余额。
6.以手机贴近传感器,即
可直接取得贩卖机中的饮料。
DoCoMo
Copyright © 2006 DharmaSource:
P AgrawalNTT
and Qing-An
Zeng All rights reserved
42
The End of Chapter 10
43
Copyright © 2006 Dharma P Agrawal and Qing-An Zeng All rights reserved








