5. BASIC PARAMETERS OF RADIO RECEIVER Goals of
advertisement
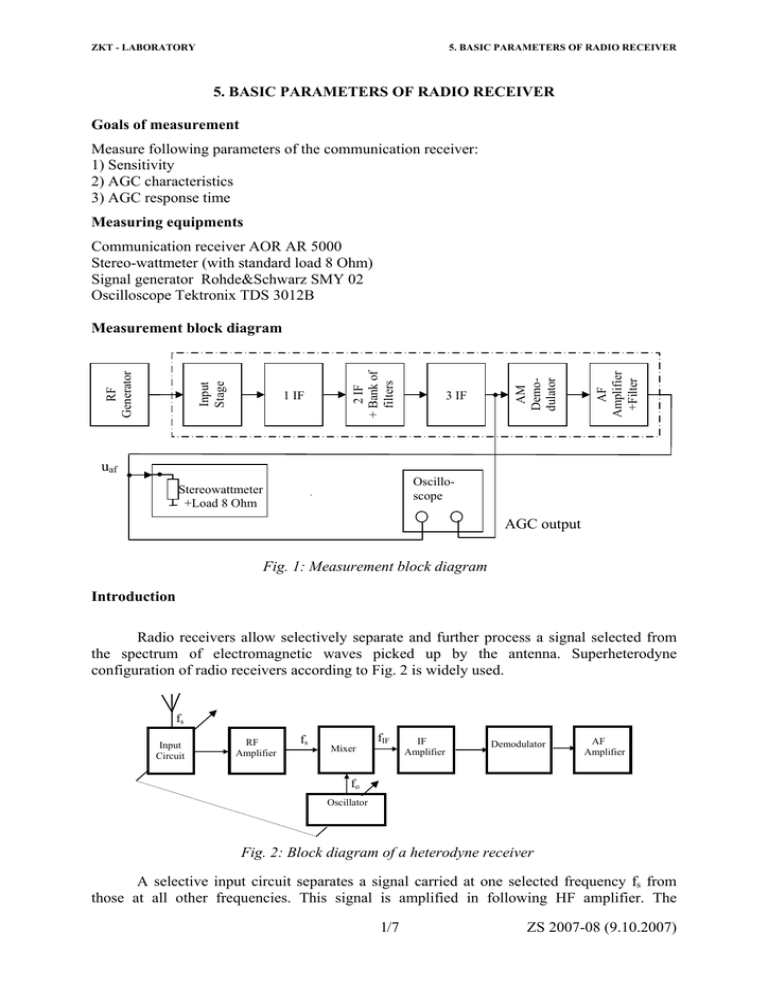
ZKT - LABORATORY 5. BASIC PARAMETERS OF RADIO RECEIVER 5. BASIC PARAMETERS OF RADIO RECEIVER Goals of measurement Measure following parameters of the communication receiver: 1) Sensitivity 2) AGC characteristics 3) AGC response time Measuring equipments Communication receiver AOR AR 5000 Stereo-wattmeter (with standard load 8 Ohm) Signal generator Rohde&Schwarz SMY 02 Oscilloscope Tektronix TDS 3012B AF Amplifier +Filter 3 IF AM Demodulator 1 IF 2 IF + Bank of filters Input Stage RF Generator Measurement block diagram uaf Oscilloscope Stereowattmeter +Load 8 Ohm AGC output Fig. 1: Measurement block diagram Introduction Radio receivers allow selectively separate and further process a signal selected from the spectrum of electromagnetic waves picked up by the antenna. Superheterodyne configuration of radio receivers according to Fig. 2 is widely used. fs Input Circuit RF Amplifier fs Mixer fIF IF Amplifier Demodulator AF Amplifier fo Oscillator Fig. 2: Block diagram of a heterodyne receiver A selective input circuit separates a signal carried at one selected frequency fs from those at all other frequencies. This signal is amplified in following HF amplifier. The 1/7 ZS 2007-08 (9.10.2007) ZKT - LABORATORY 5. BASIC PARAMETERS OF RADIO RECEIVER undesired signals, which frequencies are far from desired signal, are there suppressed. Frequency conversion is achieved in frequency converter mixer by mixing the received signal of frequency fs with a local oscillator (LO) signal of frequency fo to obtain an intermediate signal IF (intermediate frequency) fIF = fo - fs (fo > fs). By arranging for the local oscillator to be tuned simultaneously with the input circuit across the band intermediate frequency fIF will always be constant. Following IF amplifier than can operate at only one frequency fIF. A high gain and also a high selectivity and sensitivity are produced. Depending on the application there may be one, two or three frequency conversions. The last IF amplifier output is applied to the demodulator. This circuit derives from the IF signal the modulating (AF) signal, which may be amplified by the base band (BB) amplifier to the level required for output. The measurement will be performed on the Japanese communication receiver AOR. It is superheterodynne receiver with three frequency converters. Its basic architecture is on a Fig. 3 and technical parameters in tables 5, 6 and 7. This receiver serves both professional and radio amateur monitoring analog radio services in bands 10 kHz - 2600 MHz with different types of modulation (FM – frequency modulation, AM – amplitude modulation, SSB – single side band modulation, CW – continual wave and so on). Different antennas are fit for different radio bands and therefore the receiver is equipped with several antenna inputs. The receiver is also equipped with the bank of adjustable IF filters (see table 7) for different types of radio services. Automatic gain control function (AGC) secures a constant volume at the speaker even though the signal strength at the antenna may vary widely (of 100 dB or more). Measurement notes The measurement will be performed in accordance with standard RTCA (Requirements and Technical Concepts for Aviation) for airborne radio communications equipment operating within the radio frequency range 117,975 – 137 MHz. Basic HF generator setting: Carrier frequency (RF) 130 MHz, amplitude modulation (AM); modulation index 30% and modulation frequency (AF) 1 kHz (standard values); level (LEVEL) 100 µV. Communication receiver setting: A small knob placed in the lower right corner can set communication receiver. Setting is confirmed by pushing the key (ENT), a wrong choice can be cancelled by the key CLR. Check out or set following parameters: • VFO: key (VFO) – press the key repeatedly until the required VFO is chosen - VA is displayed in the lower right corner of the LCD (this choice allows a manual receiver setting). • Modulation: key (MODE) - AM • Antenna: FUNC – ANT (key (ATT)) - antenna 1 • Attenuator: key (ATT) – 0 dB for task 1); 10 dB for task 2) and 3)-see measurement tasks • AGC: FUNC – AGC (key (STEP)) - FAST • Gain: FUNC – RF GAIN (key (6)) - manual setting (N-SQL is not displayed) - chose maximal gain by rotating squelch control SQUELCH anticlockwise (note: The squelch control is used to eliminate unwanted background noise by the different configuration of the receiver) • IF bandwidth: FUNC – IF BW (key (3)) - 6 kHz • AF output: FUNC – AF.SET key (MODE)) – next by choice UP/DOWN - Low pass filter: A–LPF - 3 kHz 2/7 ZS 2007-08 (9.10.2007) ZKT - LABORATORY 5. BASIC PARAMETERS OF RADIO RECEIVER - High pass filter: A–HPF - 300 Hz - De-emphasis switched off – DE.EMP - THRU • Frequency 130 MHz • Volume: volume control AF GAIN – set on output power 50 mW (read on the stereowattmeter by the basic HF generator setting) Select standard load 8 Ω on the stereo-wattmeter. Task 1) A receiver’s sensitivity refers to the ability to produce an acceptable sound from weak signals. The sensitivity is determined namely by a receiver’s gain and its noise characteristics. Maximum sensitivity describes the ability to amplify weak signals without respect to receiver noise characteristics. When the gain is sufficiently high, the weakest signal power that may be processed satisfactorily is noise-limited, which is represented by the sensitivity (noise limited sensitivity, effective sensitivity). The sensitivity is the minimum level of the standard modulated input signal when the receiver is adjusted to produce the standard output by selected S/N (x dB). Manufacturer usually specifies standard output; other standard parameters are defined by standards. All standards for AM receivers employ sinusoidally modulated input signal with modulation index 30% and modulation frequency 1 kHz, S/N depends on type of a receiver [radio receivers 26 dB (by standard ČSN IEC 315-3), communication receivers 10 dB, aviation receivers 6 dB]. Receiver sensitivity measurement block diagram is on the Fig.1. RF signal generator is connected to the antenna input of the receiver; standard load 8 Ω is connected to the output instead of speaker. Method of measurement a) Set RF generator carrier frequency 130 MHz, modulating signal frequency 1 kHz, internal amplitude modulation, modulation index 30% and output level 100 µV. b) Set volume control key (AF GAIN) of the receiver on output power 50 mW, measure RMS output voltage include noise uAF (audio frequency) on the oscilloscope (signal + noise = S+N) and mark the value into all three lines in the table 1. Calculate the values of noise uN (N) so that (S+N)/N are 6, 10, or 26 dB (use ratio from homework) and fill the results in the tab.1. c) Switch off the modulation. In this case the oscilloscope measures RMS level of noise uN (N) that depends on the input RF signal level, but only if the time base of the oscilloscope is adequately long (minimum 200 ms). Set lower input RF signal level (but not lower than 0,4 µV) so that measured output noise level uN corresponds to level calculated in b). d) This RF signal level [µV] is the sensitivity for required (S+N)/N (in case the output power level of the receiver is minimally 10% of standard power set in a) so 5 mW). e) Measure the sensitivity for (S+N)/N = 10 dB and 26 dB by the same way. f) Repeat the measurement for both side frequency of the band but only for (S+N)/N = 10 dB. Enter the results to tables 1 and 2. Table 1: f = 130 MHz (S+N)/N [dB] 6 10 26 uAF [mV] uN [mV] 3/7 Sensitivity [µV] ZS 2007-08 (9.10.2007) ZKT - LABORATORY 5. BASIC PARAMETERS OF RADIO RECEIVER Table 2: (S+N)/N = 10 dB f [MHz] uAF [mV] 130 137 117,975 uN [mV] sensitivity [µV] Task 2) The receiver must often be capable of handling a wide range of signal power. In case the input signal is weak the sensitivity and gain of the receiver have to be high. In case the input signal is strong the gain has to be reduced to produce a nearly constant signal level at the demodulator. This is accomplished automatically by the AGC circuit (AGC – Automatic Gain Control). AGC characteristics: According to RTCA standard audio output power shall not vary more than 6 dB when the level of an RF input signal, modulated 30% at 1 kHz, is varied over the range from 10 µV to 100 mV. Method of measurement a) Set attenuator 10 dB – (key ATT) to the input of the receiver. b) Set RF generator to carrier frequency 130 MHz, standard amplitude modulation, and output level 10 µV. c) Set volume control in order not to exceed the output power 50 mW by changing the input signal level in the range from 10 µV to 10 mV according table 3. d) Measure RMS output voltage uAF and DC voltage UAGC on the output of AGC for input levels uRF according to table 3 and enter the results to the table. e) Explain in the conclusion of measurement whether the receiver meets the standard. Table 3 uRF uAF [mV] UAGC [V] 10 µV 100 µV 1 mV 10 mV 100 mV 200 mV Task 3) AGC response time: When the level of an RF input signal, modulated 30% at 1 kHz, is suddenly reduced from 200 mV to 10 µV, the receiver audio output shall, within 0,25 s, return to and remain within 3 dB of the normal steady-state output obtained with an input of 10 µV. Method of measurement a) Set attenuator 10 dB – (key ATT) to the input of the receiver. b) Set RF generator to carrier frequency 130 MHz, standard amplitude modulation and output level 200 mV. c) Set an oscilloscope to an appropriate amplitude and to a time base 400 ms. d) Get ready for modification of the RF generator output level to 10 µV (instead of 200 write 10), push key SINGLE on the oscilloscope and speedily push the key µV on the generator. e) Read AGG response time by means of vertical cursors. 4/7 ZS 2007-08 (9.10.2007) ZKT - LABORATORY 5. BASIC PARAMETERS OF RADIO RECEIVER Homework – shall be done before the measurement starts • Calculate a voltage level ratio and a power level ratio matching with 3 dB, 6 dB, 10 dB and 26 dB fall. Enter the results to the table and apply them for the measurement. dB Ux / U0 Px / P0 -3 -6 - 10 - 26 Final questions – answers will be done after the measurement 1) Find out whether the sensitivity of the receiver meets the standard. Manufacturer specification: Measured value: 2) Find out whether the AGC characteristics and AGC response time meet the parameters of airborne radio receivers. Tab. 5: Technical parameters AR5000 Frequency range 10 kHz ~ 2600 MHz (minimum accepted frequency input 5 kHz) Tuning NCO 1Hz ~ 999.999999 kHz Modes AM, FM, USB, LSB & CW I.F frequencies 1st I.F. 622.0 MHz, 2nd I.F. 10.7 MHz, 3rd I.F. 455 kHz Standard fitted filters 3 kHz, 6 kHz, 15 kHz, 30 kHz, 110 kHz & 220 kHz (provision for 500 Hz option) Memory channels 1000 (100 ch. x 10 banks) Search banks 20 banks Memory scan speed 25 channels per second in standard mode, 45 channels per second (max) in Cyber Scan Search speed 25 increments per second in standard mode, 45 increments per second (with step size of 100 kHz or less) in Cyber Search PASS frequencies 2100 total (21 banks x 100 ch. inc VFO) Priority 1 channel I.F. output 10.7 MHz with maximum ± 5 MHz bandwidth External reference 10.0 MHz Mute Phono/RCA socket CMOS input pull-up to 5 V @ 100 kOHMS Operating temp. 0 to + 50 C Aerial input 50 OHM unbalanced N-TYPE & SO239 Audio output (13.5V) 1.7 WATT into 8 OHMS @ 10 % THD Size 217(W) x 100(H) x 260(D) mm approx. excluding projection Weight 3.5 kg CPU 8bit ROM 32 768 Byte, RAM 1 024 Byte EEPROM 131 072 byte (1M Bit) 5/7 ZS 2007-08 (9.10.2007) ZKT - LABORATORY 5. BASIC PARAMETERS OF RADIO RECEIVER Tab. 6: Selectivity [μV]) Receive frequency 10 dB S/N AM 6 kHz 12 dB SINAD SSB/CW 3 kHz 12 dB SINAD FM 15 kHz 12 dB SINAD FM 220 kHz 63.00 17.70 - - 4.46 1.25 - - 2.23 0.40 - - 1.25 0.40 0.56 1.58 0.63 0.30 0.40 1.25 0.63 0.30 0.36 0.89 10kHz - 40kHz 40kHz -100kHz 100kHz – 2MHz 2 MHz – 40MHz 40MHz – 1,000MHz 1,000MHz – 2.6GHz Tab. 7: IF filters bandwidth Filter kHz Total noise bandtwidth kHz/dB Total skirt bandtwidth kHz/dB 0.5 0.5 -3 2.0 -60 3 2.4 -6 4.5 -60 6 9 -6 20 -50 15 15 -6 30 -50 30 30 -6 70 -50 110 140 -3 350 -20 220 260 -3 520 -20 6/7 ZS 2007-08 (9.10.2007) ZKT - LABORATORY 5. BASIC PARAMETERS OF RADIO RECEIVER Obr. 3: Block diagram of communication receiver AOR AR 5000 7/7 ZS 2007-08 (9.10.2007)