Determination of the Relative Permittivity and Dielectric Dissipation

Material Testing: Electrical & Physical
CH- 4057 BASEL
Determination of the Relative Permittivity and
Dielectric Dissipation Factor of Electrical Insulating
Materials
Definition:
The relative Permitivity of a material is the relation between the capacity C x
of a capacitor which is filled with the material in question and the capacity C
0
of the same capacitor when vacuum is the dielectric.
ε r
=
C x ε ε ε
0
ε
0
= −
12
Fm
−
1
C
0
The dielectric loss angle
δ
is the angle by which the phase difference between applied voltage and resulting current deviates from 90° when the dielectric of the capacitor consists exclusively of the insulating material. The dielectric dissipation factor is the tangent of the loss angle
δ
.
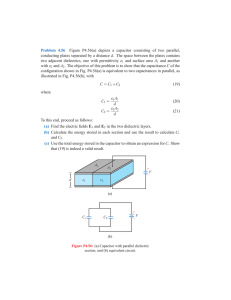
Figure 1: Equivalent parallel circuit and vector-diagram
Permitivity and tan
δ
are both influenced by temperature and frequency.
Typical graphs of SiO
2
-filled polymers: 50 Hz
50 Hz
16
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0 100 200 300
1 MHz
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
0 50
T [°C]
Figure 2 :
ε r
and tan
δ shown as function of temperature and frequency
100
T [°C]
150 200 250
1 MHz