Specially Designed Instruction: Putting the “S” in DI
advertisement

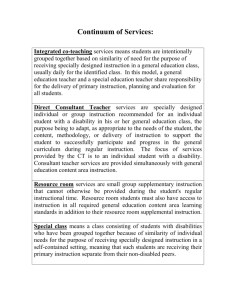
GreatIdeasConvention2016 LearningLab SpeciallyDesignedInstruction:Puttingthe“S”inDI KellyBevisWoodiel,SomersetISD To locate documents electronically, please go to LiveBinders.com, and follow the directions in the diagram. 1 TCASE 2016 | educationINC Specially Designed Instruction Questions & Answers How does IDEA 2004 define Specially Designed Instruction? A no cost [service] to the parents, to meet the unique needs of a child with a disability” (34 CFR §300.39(a)(1)). Adapting, as appropriate, to the needs of an eligible child under this part, the content, methodology or delivery of instruction to address the unique needs of the child that result from the child’s disability; and to ensure access of the child to the general curriculum, so that the child can meet the educational standards within the jurisdiction of the public agency that apply to all children” (34 CFR §300.39 (b)(3)). How is specially designed instruction different than differentiated instruction? Differentiated instruction is a framework or a philosophy for effective teaching that involves providing students with a variety of paths to learning based upon students’ learning preference and needs. Specially designed instruction addresses the unique learning needs of students who have a disability, so they may accomplish their IEP goals and objectives. Services may include: accommodations, modifications, and adaptations in instructional methods, materials, techniques, media, physical setting, or environment. How do I differentiate instruction for students? Teachers can differentiate according to the CONTENT, PRODUCT, and PROCESS. For a list of examples, please see the document titled, Differentiated Instruction v. Specially Designed Instruction. What does specially designed instruction look like? Specially designed instruction looks different for each child with a disability. The law asks the ARD committee to consider the unique needs of each child with a disability, AND adapt the content, methodology, or delivery of instruction, so s/he may make progress in the general curriculum and close achievement gaps. For a list of examples, please see the document titled, Differentiated Instruction v. Specially Designed Instruction. 2 TCASE 2016 | educationINC How does specially designed instruction relate to measurable annual goals? Instruction for students with disabilities outlined in the IEP defines the specially designed instruction. The ARD committee uses the information from the student’s Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance (PLAAFP) statements to develop measurable annual goals. Once the goals are written, the ARD committee determines what adaptations, accommodations, and/or modifications are needed to support the student’s progress towards achieving the annual goals and make progress in the general curriculum. The specially designed instruction is embedded in the student’s IEP in various sections. Where do I find specially designed instruction in the IEP? A student’s specially designed instruction may be found in different locations within the IEP based on how the student qualifies for special education services and needs. Look at the Transition Plan for students 14 or older, Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance (PLAAFP) Statements, Annual Goal and Objectives, Instructional & State Assessment Accommodations, Behavior Intervention Plan, Supplements; such as, Autism, Personal Care, etc., and/or Deliberations. Who is responsible for delivering specially designed instruction to students with disabilities? Any staff member who works with a student with a disability is responsible for reporting datarich information to the ARD committee on the effectiveness of the current strategies outlined in the IEP and for updating the strategies based upon current needs. According to Doe v. Withers, the multidisciplinary team, consisting of all staff that work with the student with a disability, is responsible for ensuring the student is receiving his/her specially designed instruction outlined in the IEP. Working collaboratively together as a team to implement the IEP is the responsibility of ALL involved. Should ARD committees still consider modified content if there is no modified state assessment available? Yes. The decision is based on the PLAAFP and there must be a corresponding goal in the subject area where the student is receiving the modified content. The elimination of the modified assessment does not equate to the removal of modified instruction in the classroom. If modified instruction is part of the student’s specially designed instruction in the student’s IEP, its implementation is required by IDEA 2004. From the: 2014 Individualized Education Program (IEP) Annual Goal Development: Question and Answer Document. Question 2.18. Retrieved from: http://www.esc20.net/default.aspx?name=ci_se.agc.Resources 3 TCASE 2016 | educationINC Differentiated Instruction v. Specially Designed Instruction Content, or what is taught and learned, is the curricular topics, concepts, or themes presented to the student by the teacher. The student engages with the content based upon his/her level of readiness, i.e., current skill level. DI SDI Simplify numbers, graphics, vocabulary Spiral the TEKS Chunk complex information Curriculum Scope and Sequence of Content Reduce the breadth & level of difficulty Remove extraneous information Frequent reminders of key concepts Prerequisite skills Process refers to how the student makes sense of what is learned based upon his/her interests, background, and preferences. DI SDI Activate prior learning using anticipatory steps Pre-teach targeted key concepts; preview text before reading to activate prior knowledge; draw conclusions; set a purpose for reading Flexible Grouping/Cooperative Learning Small groups or individualized instruction to emphasize key concepts and provide direct, intensive instruction Games Repetitive tasks in game form to encourage and motivate learning Questioning Questioning with visuals and choices Technology Text-to-speech; speech-to-text; calculator; word processing rather than paper & pencil Metaphors, Analogies, and Similes Clarification or rewording of vocabulary, complex sentences, and concepts using definitions, similes, literal language, graphics, animation, etc Product is how the student demonstrates or shows evidence of what has been learned to the teacher, class, or other audience(s). DI SDI Graphic Organizers Partially completed graphic organizers Project-Based Learning Choice to complete a project or other assignment Role-Play Pre-teach concepts and practice role-play prior to instruction Paper and Pencil Tasks Provide alternative grade-level assignments based upon skill set and need Artwork Choose/Indicate from a set of preselected pictures to create a product based upon topic or assignment Writing & Journals 4 Use writing process checklist, transcribe what student says, and ask student to read and write selected words from the transcripted text TCASE 2016 | educationINC ALL SOME FEW 5 • CORE Curriculum, Interventionists, Counselors, Tutoring (During/After), Istation, Teacher Specialists, TCMPC/TEKS Resource, Think Through Math, PALS, Reading A Through Z, Sidewalks, Instructional Technologists, UTSA Roadrunner Reading Program, College Guidance Center, Career Exploration Center, Formative Assessments • Interventions, Accommodations (Linguistic, Academic, Behavior, Executive Functioning), Read 180, Esperanza, BIL Aides, Inclusion & Co-Teach Support, Gear Up, Internships, Credit Recovery • Clinical, Dyslexia Teachers, Sec. 504 Services, G/T Teachers, Modified Curriculum, Prerequisite Skills, Direct & Intensive Instruction from Specialists, Instructional Paraeducators, SelfContained, Resource TCASE 2016 | educationINC 6 TCASE 2016 | educationINC