Logic families (TTL, CMOS)
advertisement

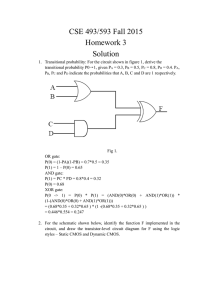
Logic families (TTL, CMOS) When you work with digital IC's, you should be familiar, not only with their logical operation, but also with such operational properties as voltage levels, noise immunity, power dissipation, fan-out, and propagation delays. DC Supply Voltage The nominal value of the dc supply voltage for TTL (transisitor-transistor logic) and CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) devices is +5V. Although ommitted from logic diagrams for simplicity, this voltage is connected to Vcc or VDD pin of an IC package and ground is connected to the GND pin. TTL Logic Levels B122L – Principles of Digital System : Hassan Parchizadeh Page 1 CMOS Logic Levels Noise Immunity Noise is the unwanted voltage that is induced in electrical circuits and can present a threat to the poor operation of the circuit. Wires and other conductors within a system can pickup stray high-frequency electromagnetic radiation from adjacent conductors in which currents are changing rapidly or from many other sources external to the system. In order not to be adversely effected by noise, a logic circuit must have a certain amount of 'noise immunity'. This is the ability to tolerate a certain amount of unwanted voltage fluctuation on its inputs without changing its output state. Consider Now Consider B122L – Principles of Digital System : Hassan Parchizadeh Page 2 Noise Margin A measure of a circuit's noise immunity is called 'noise margin' which is expressed in volts. There are two values of noise margin specified for a given logic circuit: the HIGH (VNH) and LOW (VNL) noise margins. These are defined by following equations : VNH = VOH (Min) - VIH (Min) VNL = VIL (Max) - VOL (Max) Example : Determine the noise margins for TTL and CMOS using the information given above. TTL : VIH(Min) = 2.0 V, VIL(Max) = 0.8 V, VOH(Min) = 2.4 V, VOL(Max) = 0.4 V VNH = VOH (Min) - VIH (Min) = 2.4 V – 2.0 V = 0.4 V VNL = VIL (Max) - VOL (Max) = 0.8 V – 0.4 V = 0.4 V CMOS : VIH(Min) = 3.5 V, VIL(Max) = 1.5 V, VOH(Min) = 4.9 V, VOL(Max) = 0.1 V VNH = VOH (Min) - VIH (Min) = 4.9 V – 3.5 V = 1.4 V VNL = VIL (Max) - VOL (Max) = 1.5 V – 0.1 V = 1.4 V Power Dissipation A logic gate draws ICCH current from the supply when the gate is in the HIGH output state, draws ICCL current from the supply in the LOW output state. 5V 5V ICCH ICCL L X H H H 0V Average power is PD = VCC ICC L 0V where ICC = (ICCH + ICCL) / 2 B122L – Principles of Digital System : Hassan Parchizadeh Page 3 Example : A certain gate draws 2 mA when its output is HIGH and 3.6 mA when its output is LOW. What is its average power disspiation if VCC is 5 V and the gate is operated on a 50% duty cycle. ICC = ( ICCH + ICCL)/2 = ( 2 mA + 3.6 mA ) / 2 = 2.8 mA PD = VCC ICC = 5 V * 2.8 mA = 14 mW Propagation Delay time When a signal passes ( propagates ) through a logic circuit, it always experiences a time delay as shown below. A change in the output level always occurs a short time, called 'propagation delay time' , later than the change in the input level that caused it. input output H tPLH tPHL Loading and Fan Out of Gates When the output of a logic gate is connected to one or more inputs of other gates, a load on the driving gate is created. There is a limit to the number of load gates that a given gate can drive. This limit is called the 'Fan-Out' of the gate. TTL Loading : A TTL driving gate, when HIGH, sources current (ISource) into a load gate input (IIH) and sinks current (IOL) from the load gate in the LOW state ((ISink). B122L – Principles of Digital System : Hassan Parchizadeh 0V Page 4 CMOS Loading : Loading CMOS differs from TTL because the fieldeffect-transistors (FET used in CMOS logic present a predominantly capacitive load to the driving gate. In this case the limitations are charging and discharging times associated time with the output resistance of the driving gate and input capacitance of the load gate. TTL Circuits TTL Inverter : Open Collector : B122L – Principles of Digital System : Hassan Parchizadeh Page 5 Gates with TriState output : CMOS Circuits CMOS Inverter : Open Drain : B122L – Principles of Digital System : Hassan Parchizadeh Page 6 CMOS Gates with TriState output : Schmitt triggers Many logic elements (flip-flops, monostables, etc.) require fast rising and falling edges for reliable operation. Edges can be degraded for a variety of reasons ; stray capacitance or even a signal from some slow external device. The schmitt trigger always gives fast edges on its output signal regardless of the input edge speed. The transfer functions of a schmitt trigger gate, is shown below. B122L – Principles of Digital System : Hassan Parchizadeh Page 7