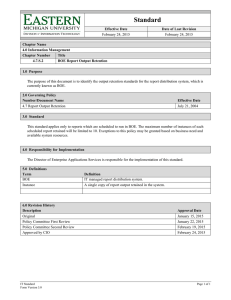
Typical Arrhythmia Waveforms
advertisement

Typical Arrhythmia Waveforms Premature Supraventricular Contractions (Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC)) P’ Diagnostic ECG Electrode Placement Atrial Fibrillation (AF) IEC R and L electrodes should be placed just below the right and left clavicle. N and F electrodes should be placed on the lower edge of the rib cage, or at the level of the umbilicus at the mid-clavicular line. P’ t/BSSPX234FYDMVEJOHBCFSSBOUWFOUSJDVMBSDPOEVDUJPO t&DUPQJDGPDVTIJHIFSUIBO)JTCVOEMFt/PODPNQFOTBUPSZQBVTF Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVC) t4MJHIUSJQQMFTPOUIFCBTFMJOFt*SSFHVMBS33JOUFSWBMT t*OWFSUFE234DPNQMFYFTt/PODPNQFOTBUPSZQBVTF Lead Electrode Placement R Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) L C1 C2 C3 C4 t1SFNBUVSFDPOUSBDUJPOTt#J[BSSFBOEXJEF234DPNQMFYFT t'VMMDPNQFOTBUPSZQBVTFt'SFRVFOU17$TBSFTFSJPVT Multi-focal PVC t'BTUQVMTFSBUFHSFBUFSUIBOCQNtPSNPSFJSSFHVMBSCFBUT t/FFETFNFSHFODZUSFBUNFOUBOEDPVOUFSTIPDLt.BZQSPHSFTTUPWFOUSJDVMBSGJCSJMMBUJPO N C5 C6 F C1 Fourth intercostal space at the right border of the sternum C2 Fourth intercostal space at the left border of the sternum C3 Midway between locations C2 and C4 C4 At the mid-clavicular line in the fifth intercostal space C5 At the anterior axillary line on the same horizontal level as C4 C6 At the mid-axillary line on the same horizontal level as C4 and C5 Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) Heart Anatomy 15 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 16 17 2 2 1 t.VMUJGPSN17$Tt#J[BSSFBOEXJEF234DPNQMFYFT t.BZQSPHSFTTUPWFOUSJDVMBSGJCSJMMBUJPO7' 7 7 8 t/PEJTDFSOBCMF1XBWFT3XBWFT13SIZUINPS234DPNQMFYFT t/FFETFNFSHFODZUSFBUNFOUBOEDPVOUFSTIPDL 14 9 Short run PVC Second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, Mobitz type II 8 13 10 7 3 12 6 P P P 11 4 1 5 t$POTFDVUJWF17$Tt.BZQSPHSFTTUPWFOUSJDVMBSUBDIZDBSEJBPSWFOUSJDVMBSGJCSJMMBUJPO R-on-T PVC t4VEEFOBCTFODFPG234DPNQMFYFT1XBWFTPCTFSWFE t.BZQSPHSFTTUPDBSEJBDBSSFTU t1PTTJCJMJUZPG"EBNT4UPLFTTZOESPNFt0DDBTJPOBMMZOFFETQBDJOH Third-degree (complete) atrioventricular (AV) block 18 Cardiac Conduction System SA node His bundle Atria P P P P P P P P P P Left bundle branch P AV node t17$POTVNNJUPG5XBWFt#J[BSSFBOEXJEF234DPNQMFYFT t.BZQSPHSFTTUPWFOUSJDVMBSGJCSJMMBUJPO Electrocardiographs t*OEFQFOEFOUEFWFMPQNFOUPG1XBWFTBOE234DPNQMFYFTt1PTTJCJMJUZPGCSBEZDBSEJB t1PTTJCJMJUZPG"EBNT4UPLFTTZOESPNFt/FFETQBDJOH Defibrillators Right bundle branch Purkinje fibers Purkinje fibers Ventricles R The sinoatrial (SA) node generates a wave of electrical excitation. The excitation travels through the internodal pathways to the atria and the atrial muscles contract. This is recorded as the P-wave. The excitation travels to the atrioventricular (AV) node. The excitation then travels through the bundle of His and down through the right and left bundle branches. Bedside monitors T P Nihon Kohden products which detect arrhythmia Inferior vena cava Superior vena cava Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Pulmonary valve Pulmonary artery Pulmonary vein Left atrium Mitral valve Left ventricle Aortic valve Coronary artery Aorta Brachiocephalic artery Left common carotid artery Left subclavian artery Descending aorta Q S The excitation terminates at the Purkinje fibers in the ventricles and the ventricular muscles contract. This is the depolarization and is recorded as the QRS complex. The ventricular muscles relax. This is the repolarization and is recorded as the T-wave. 6727 SP60-075 '11.11.SZ. A