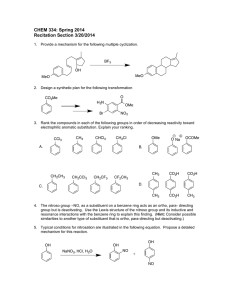
1. Draw structures for the products you would expect to obtain from
advertisement

-1- 1. Draw structures for the products you would expect to obtain from reaction of β-Dgalactopyranose (A) with each of the reagents below. Be sure to include all relevant stereochemistry. (40 pts). OH HO O HO OH O H β-D-galactopyranose (A) CH3I a) A Ag2O OMe MeO O MeO OMe O Me HNO3 b) A ∆ (CH3CO)2O c) H HO HO H A pyridine CO2H OH H H OH CO2H OAc AcO O AcO OAc O Ac NaBH4 d) H HO HO H A H 2O OH MeOH e) HO A dry HCl CH2OH OH H H OH CH2OH O HO O H OMe -2- H H HO HO H 1) HCN f) A 2) DIBAH 3) H3O+ CHO OH OH H H OH CH2OH Br2 g) A H 2O A 2) (CH3CO)2O 3) NaOMe i) A H HO HO H CO2H OH H H OH CH2OH CHO H OH H H OH CH2OH CHO HO H HO H H OH CH2OH H2NOH h) + HO H HO HO H red P / ∆ HI (n-hexane) 2. The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of agniotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin shows the presence of the following amino acids : Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, 2 Val. Briefly describe a plausible technique for analyzing the amino acid content of saralasin. Two-three sentences plus a diagram will suffice. (10 pts). a) 3 2 absorbance Rigorous hydrolysis of a protein with aqueous HCl will cleave all peptide bonds to liberate the component amino acids. Analyze the amino acids by chromatography, where the retention time is characteristic of each AA, and the absorbance of a suitable derivative is proportional to molar quantity. 2 2 2 1 retention time 1 -3- N-terminal analysis by the Edman method shows that saralasin contains sarcosine (N-methyl aminoethanoic acid) at the N-terminus (see below). Provide structures for C and D, and a detailed mechanism for this cleavage. (15 pts). b) B H Me 1) Ph-N=C=S / H+ / ∆ O N N peptide CO2H H Ph N C C 2) H3O+ + D S H nucleophilic addition B H N Ph S Me H H+ catalyzed O N N peptide CO2H Ph cyclization H N Me S O N peptide N H CO2H H H N Me S N + (peptide) Ph B NH2 O H catalyzed cleavage CO2H Ph H N Me S O N peptide N H CO2H H C H+ catalyzed Ph S rearrangement Me N N O D c) Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute HCl yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His, Sar-Arg-Val, His-Pro-Ala, Val-Tyr-Val, Arg-Val-Tyr. What is the structure of saralasin? (10 pts). Sar-Arg-Val The Complete Sequence is: Arg-Val-Tyr Sar-Arg-Val-Tyr-Val-His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Tyr-Val-His His-Pro-Ala -4Propose a solid state synthesis of the fragment Tyr-Val-His beginning with polymer P (see below), and utilizing any protected derivatives of Try, Val and His of your chosing. Show all reagents and steps clearly. (15 pts). d) CO2H P CH2Cl NH2 HO NH2 N H NH2 Val Tyr CO2H N CO2H His O C N O- NHBOC N H O O C C N O TFA P H2C N NHBOC N H CO2H O H2 C NHBOC P NH2 N H DCC CO2H BOC N H H O N C O TFA P H2C H2N O H O N C NHBOC HO O H2C P DCC O N N N H N H O N HN H BOC HO H O N C 1) TFA O H2C Tyr-Val-His P 2) H2 / Pd O N N H 3. For each reaction given below, provide either the missing reagents or products (in the boxes). Show any intermediates in the space provided. For multistep syntheses, be sure to list the reagents in the order they are utilized (none require more than 3 steps). (40 pts). Et-CH CH-CO2Me NaOMe a) + O MeO2C-CH2 C CH3 MeOH Et-CH CH2-CO2Me MeO2C-CH C CH3 O H3O+ Et-CH CH2-CO2H ∆ CH2 C CH3 O -5Cl 1) NH3 b) NO2 c) CH3 C NH2 2) Br2 / HO- O NH2 3) H2 / Pd CH CH2 CH CH-CO2Me 1.0 eq HBr Br CH3 C CH2 CH2 CH3 HC CH-CO2Me CH3 1) RCO3H O 2) MeO - d) O 3) Ac2O Me Et e) 1) 1 equiv LDA OMe Me Me Et O 2) MeI O 1) HO- f) OHC-(CH2)5-CHO 2) H2 NEt / H2 / Pd Cl NMe2 3) excess MeCl Et -6excess CH3NH2 g) Me ∆ CH2 Br OH 1) KMnO4 / ∆ 2) ∆ (-H2O) h) O OMe 3) MeOH O 4. Provide a detailed mechanistic rationale for the transformation shown below. (15 pts). OMe O18 H2O18 MeO MeO MeO + H H + + H -H H H OMe OMe MeO MeO MeO H MeO O H H -MeOH 18 H2O P.T. -MeOH H OMe OMe MeO 18 H2O MeO H O O18 -75. If the DNA sequence -TAA-CCG-GAT- were incorrectly copied during replication and became -TGA-CCG-GAT-, what effect would there be on the sequence of the protein produced during translation (use the data from the table below). (15 pts). Codon Assignments 1st base (5’ end) 2nd base U ___________Third base (3’ end)___________ C A G U U C A G Phe Ser Tyr Cys Phe Ser Tyr Cys Leu Ser Stop Stop Leu Ser Stop Trp C U C A G Leu Pro His Arg Leu Pro His Arg Leu Pro Gln Arg Leu Pro Gln Arg A U C A G Ile Thr Asn Ser Ile Thr Asn Ser Ile Thr Lys Arg Met Thr Lys Arg G U C A G Val Ala Asp Gly Val Ala Asp Gly Val Ala Glu Gly Val Ala Glu Gly replication DNA : -TAA-CCG-GAT- -TGA-CCG-GAT(error) transcription transcription -AUU-GGC-CUA- mRNA : -ACU-GGC-CUA- translation Protein fragment : translation -Ile-Gly-Leu- -Thr-Gly-Leu- 6. Shown below are the structures of adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (C). Please show the hydrogen bonds between the appropriate base pairs (this will require accurate drawings. (10 pts). NH2 O N N N HN N H N O H2N N H N A Me HN O H O N H N O T H N N Me N NH O H H N N H N H O N NH N O A H T N H C HN HN N N H G N NH2 G C