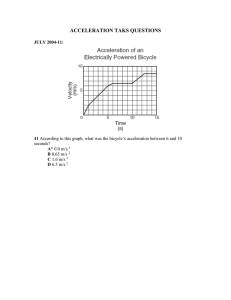
Time (seconds) 1 2 3 4 Time (seconds) 1 2 3 4
advertisement

Contemporary Physics Laboratory Report Sheet Lab 1 - Constant Acceleration of Cart September 10, 1999 My Name _________________ Section: _____ MWF My Lab Partner’s Name(s) _______________________________ Apparatus: _____TThF Include Block Diagram Sketch of Apparatus here: Describe in a few sentences how the position, velocity and acceleration are determined by the motion sensor. Prediction: Draw a quick sketch of position versus time, velocity versus time and acceleration versus time that would result if the motion sensor begins measuring time and 1 second later the cart is pushed away from the sensor moving at a speed of .5 m/s. Do this over a time of 4 seconds. Turn Page 1 2 Time (seconds) 3 4 1 2 Time (seconds) 3 4 1 2 Time (seconds) 3 4 Data Collection: Launch the cart toward the motion sensor up the inclined track, collect data and complete the following: Attach graphs for the displacement, velocity and acceleration as functions of time printed from Science Workshop. Fit the distance versus time graph to a quadratic curve and fit the velocity versus time graph to a linear relationship. For the acceleration graph record the mean and standard deviations of the acceleration. For the distance versus time graph record the value of the acceleration, 2 times the coefficient of x^2 (time squared) as the acceleration. a = 2 × a2 = _______________________ For the velocity versus time graph record the value of the acceleration, the slope. v = slope = ______________________ For the acceleration versus time graph record the value of the mean of the acceleration and its standard deviation. a = mean = _____________________ sd of a = _______________________ Compare the values of acceleration obtained form these three approaches. Relate your graph predictions with your observation and describe briefly what you have learned.