Human range of hearing, Loudness, Decibel scale, Beats, Doppler
advertisement

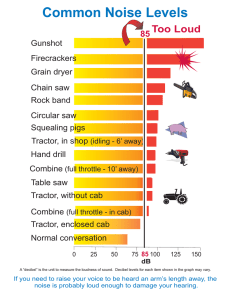
Human range of hearing, Loudness, Decibel scale, Beats, Doppler Effect. Human Range of Hearing • Remember: The human ear is built to sense pressure fluctuations above and below atmospheric pressure. It will sense fluctuations in the 20Hz – 20,000Hz range. Check out other organism’s hearing. Decibel (dB) Scale Measurement of a decibel is tricky, 0dB is the equivalent of an inaudible sound, 10dB is a 10 times larger pressure amplitude than an inaudible sound and 20dB is 100 times more than an inaudible sound. This is a logarithmic scale. Most people perceive a 10dB increase in sound level as about twice as loud as the original level. 0 dB to 10dB 10 times greater pressure than the reference amplitude. 0 dB to 20dB 10X10=100 times greater pressure than the reference amplitude. A decibel, or one unit of sound (abbreviated as dB,) is used to measure the intensity of a sound wave. Decibel (dB)Scale • The decibel scale is a logarithmic scale of sound pressure. • Since it is logarithmic, an increase of 10 dB results in a ten fold (10X) increase in pressure on the ear drum. • Zero dB is considered the Threshold of Human Hearing. • Sound intensity at this point is 1x10-12W/m2 Some common pressure & dB ratings Ha Ha!!! Above and Below • Frequencies above 20 kHz (20,000 Hz) are called Ultrasonic frequencies, • And those frequencies below 20 Hz are called Infrasonic frequencies. Beat Frequency • When sound waves from two different similar frequency sources overlap, interference occurs, both constructive and destructive. • A beat frequency is heard based on how often the sound waves interfere. • The more beats heard, the greater the difference between the two sound sources. • • Used to tune instruments. http://www.acs.psu.edu/drussell/De mos/superposition/superposition.ht ml Beat Frequency The beat frequency is the frequency of a sound which is created from two similar sound sources interfering. Example: If two tuning forks are set into vibration side to side, and the frequencies of each are 100Hz and 105Hz, the two waves will cause constructive and destructive interference and the beat frequency will be 5Hz. Check the math! Beat Frequency (Hz) = │F1 – F2 │ Where the beat frequency is equal to the absolute value of the difference between the frequencies of the two tuning forks. The frequencies of the red and blue sound waves are slightly different and their constructive & destructive interference determines the beat frequency, shown by the green wave. Doppler Effect • When either a sound source is moving or a person hearing a sound source is moving, there is a perceived shift in frequency for the listener. • Higher perceived frequency for approaching, lower perceived frequency for leaving. What do I hear? What do I hear? Simulations • • • • • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eo_owZ2UK7E http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h4OnBYrbCjY http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ude8pPjawKI http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=17tqXgvCN0E http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::800::600: :/sites/dl/free/0072482621/78778/Doppler_Nav.swf ::Doppler+Shift+Interactive • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uENITui5_jU