1. Title of subject Introduction to Machines and Power Systems 2
advertisement

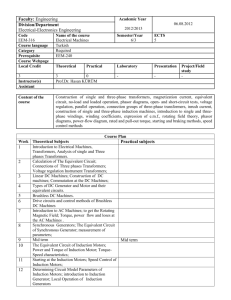
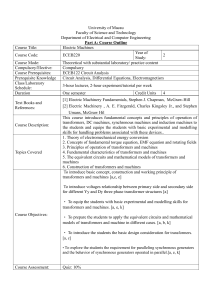
. 1. Title of subject Introduction to Machines and Power Systems 2. Subject code EPM1076 3. Credit Hour 3 4. Pre-Requisite ECT1016 Circuit Theory 5. Aim of Subject To introduce the basic concepts and working principles of electrical machines. To introduce the basic concepts of the electrical power system and its protection. 6. Learning Outcomes and Program Outcomes of Subject At the completion of the subject, students should be able to : Learning Outcomes: • LO1 – Distinguish the characteristics and mechanisms of transformers and other rotating electrical machines (Cognitive–Analyzing–Level 4) • LO2 – Analyze three-phase circuits in electrical machines and power systems (Cognitive–Analyzing–Level 4 ) • LO3 – Explain the principles of operation and constructional features of transformers, DC machines, induction machines and synchronous machines (Cognitive–Understanding–Level 2) • LO4 – Analyse the behaviour and performances of electrical machines and power systems (Cognitive–Analyzing–Level 4) • LO5 – Describe the components of electrical power systems (Cognitive–Understanding–Level 2) • LO6 – Interpret the feasibility of various fault detecting methods and protective devices in the basic protection schemes of electrical power systems (Cognitive–Applying– Level 3) Programme Outcomes: • PO1 – Acquire and apply knowledge of mathematics, science and engineering fundamentals 7. Assessment Scheme Lab Experiments Tutorial / Assignment • • • • • • Work in group Lab report writing Oral assessment at the end of lab Group assignment Focus group discussion To enhance understanding of basic concepts in lecture 10% 15% . 8. Details of Subject Test • Written exam 15% Final Exam • Written exam 60% Topics Hours Introduction to Machinery Principles Introduction to electrical machines and transformers. Rotational motion, Newton's law, and power relationships. Magnetic field, Faraday’s law, induced voltage on a conductor moving in a magnetic field, production of force on a wire in a magnetic field. 3 Three-phase Circuits Three-phase systems. Relation between line and phase quantities. Analysis of balanced three-phase circuits. Y-∆ transformation. Power, reactive power and complex power calculations. 5 Transformers Single-phase transformers: Construction, principle of operation and equivalent circuit, phasor diagram, efficiency and regulation. Short and open circuit tests. Parallel operation. Three-phase transformers: Construction and connections. Introduction to autotransformers and instrument transformers. 6 D.C. and A.C. Machines D.C. Machines Principles of operation and construction of DC machines, Emf equation and principle of commutation. Types of DC generators. DC motors: Torque equation, characteristics of shunt, series and compound motors. Starting and speed control. Losses and efficiencies of DC machines. Induction Machines Principles of operation and basic construction of three-phase induction motor. Slip equation, equivalent circuit, determination of equivalent circuit parameters by no-load and blocked-rotor tests. Torque-speed characteristics.. Starting methods. Introduction to single-phase induction motors. Synchronous Machines Principle of operation of Synchronous generators, Synchronous impedance and simple equivalent circuit.. Voltage regulation. Synchronizing procedures and parallel operation of synchronous machines. 12 . Introduction to Power System Generation of electrical power: Various types of conventional and non-conventional generation plants Single-line diagram and impedance diagram of power systems. Per-unit quantities. Components of a power system: Generation, Transmission and Distribution 6 Basic Protection Objective of power system protection. Basic principles and components of protection including fuses. Operating principles of overcurrent relays. Instantaneous and time grading relays. Safety grounding, Grounding practice in power systems and electrical installations 4 9. Teaching and Learning Activities The subject will be delivered using the following means: • Lecture hours = 36 • Supervised Tutorial Hours = 8 • Laboratory Hours = 6 Total Contact Hours = 50 10. Laboratory 1. 2. 11. Reading Material Equivalent circuit determination and load test on single-phase transformer Load test on induction motor Textbook 1. S.J. Chapman, “ Electric Machinery and Power System Fundamentals”, 1st edition McGraw Hill Higher Education, 2002 Reference Materials 1. T. Wildi, “Electrical Machines, Drives, and Power Systems”, Sixth edition, Prentice-Hall, Inc., 2005 2. B.S. Guru and H.R. Hiziroglu, “Elecgrcial Machinery and Transformers”, 3rd edition, Oxford University Press, 2001 3. J.J. Grainger and W.D. Stevenson, Jr. “Power System Analysis”, McGraw-Hill, 2004 4. B.M. Weedy and B.J. Cory, “Electric Power Systems”, Fifth edition, John Wiley & Sons, 2012