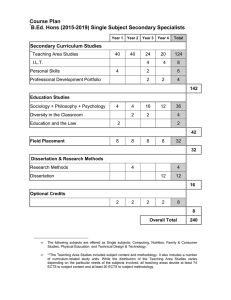
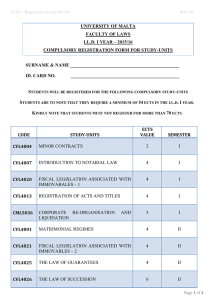
Riga Technical University Course list 2013/2014
advertisement

Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! Riga Technical University Course list 2013/2014 Autumn GENERAL COURSES HSP489 Organizational Psychology 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Psychological characteristics of a manager. Psychological characteristics of a worker. Psychological theories of management. Organizational culture and its levels. Staff selection. Team building. Organization development. English Language 2.00 CP (3.00 ECTS) upper Intermediate Basic English course that can be integrated with other subjects on the curriculum and that is based on acquisition of technical terminology in the particular field: 1) acquiring creative reading skills by working with professional texts; 2) mastering the fundamentals of relevant conversation and developing discussion skills; 3) improving listening comprehension skills to ensure effective participation in conferences, projects etc. 4) developing writing skills (essays, summaries, abstracts, conclusions). Mathematics Part II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Introduction. Analytical geometry: vectors, lines, and surfaces. Linear algebra: matrices, determinants, and systems of linear equations. Introduction to analysis: limits, continuity. Differential calculus: derivative, differentials and their applications. Integral calculus: indefinite and definite integrals, their applications. Ordinary differential equations. Series. Double and triple integrals. Physics Part II 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Introduction to physics. Fundamentals of mechanical motion. Molecular physics and thermodynamics. Electrostatics. Direct current. Electromagnetism. Oscilations and waves. Optics. Quantum physics. Structure of solid state. Nuclear physics and elementary particles. Latvian Language ( Part I; Part II; Part III) 1.00 CP (1.5 ECTS) (each part) The course is designed for foreigners. The aim of the course is to train and develop basic skills in communication, listening, reading and writing so that purpose in everyday situations. The course contains the most neccesary topics. History and Culture of Latvia 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Balts and Livs. Origin and development of their culture. The development of different culture phenomena in Latvia: books, theatre, cinema, music, fine art etc. Latvian folklore and mythology, Dievturība, the search for Latvian identity. Computer Studies (basic course) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Kinds of computers. An overview of the modern computer. The fundamentals of the data processing theory. Alghorimization. Iteration, recursion processes and loops. The fundamentals of programming language: variables, arrays, records, files, input/output operations, subroutines. Introduction in the programming. Modules of the program. Libraries. Previous courses: Informatics of socondary school. FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING BĢE331 Cartography 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The nature of mapping. Language of map: projections, coordinates and map scales. Mathematical bases of maps. The classes of maps and atlases. Projection, compilation and production of maps and atlases. Using of maps in science and practice. BĢE315 Engineering Geodesy 2.00 CP ( 3.0 ECTS) Geodetic methods for construction projects. Building grip line layout methods. Special networks. Measurement of angles, distances and heights. Deformation and subsidence of buildings. Geodetic instruments. Structure and regulation of optical-mechanical instruments. BĢE427 Fundamentals of Land Management 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Substance and process of land management. Real property and its definition. Land management parties and its interrelation. Background information. Urban and rural land planning and development, implementation. The results of land reform. Rural land use, building and environmental protection. Urbanization, urban planning and implementation. Spatial planning and implementation processes. DIM203 Supplementary Mathematics (for construction engineering) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Fourier series. Elements of partial differential equations. Line and surface integrals. Elements of the theory of vector fields. Probability theory: algebra of events, discrete and continuous random variables. Normal, exponential, and Poisson distribution. Elements of mathematical statistics. Conjecture testing. Two-dimensional random variables. BĢE428 Geodetic Control of Transportation Structures 2.00 CP ( 3.0 ECTS) Geodetical control elements, instruments, methods. Settling of foundations. Deformations of bridges. High inacessible buildings, their verticality. Deformations of sea port buildings. Global positioning systems for roads Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! BĢE114 Fundamentals of Geomatics 2.00 CP ( 3.0 ECTS) Geomatics - common part of geodesy, cartography and land management. Introduction in geodesy, photogrammetry, global positioning systems,digital mapping, cartography, geographical information systems, property valuation, land cadastre, land development and planning. BĢE407 Surveying Instruments 2.00 CP ( 3.0 ECTS) The course "Geodetic Instruments" presents with instruments used in Geomatics and their measurement principles. Instruments and measurement systems become more complex and complicated, it is necessary to know routine field inspections and also the necessary verification checks on a regular basis collimation stands. Geodetic instruments are grouped by application functions, structure, accuracy classes, and other factors. Subject dealt metrological measurements and geometric reduction. Meteorological and geometrical reductions. FACULTY OF ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT IET127 Microeconomics 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The subject matter of the course is Microeconomics. Demand. Supply. Utility and demand. Comparison of prospective and current value. Discounting. Production, productivity. Maximization of corporate profits in the conditions of perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition and oligopoly. Market of production factors: labour market; market of production resources; land market. Theory of public choice. IUE218 Computers (basic course) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Fundamental concepts of information. Computers and their types. Text editors. Program Word. Logical functions. Concept and structural scheme of an algorithm. Use of algorithms in problem solving. Program MathCad. Mathematical calculations - statistical processing of data. Approximation, assessment of errors, forecast, optimization. Resolution of problems by applying MathCad. Presentation of the laboratory work by using Powerpoint. IUV106 Business Communication 2.00 CP ( 3.0 ECTS) Characteristics of information. Verbal and non-verbal information. Process of communication. Written communication. Oral communication. Talking to the point. IUE334 Business Economics 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Evaluation of production and financial resources of an enterprise, incl. intangible assets, accounting of fixed assets, specifics of evaluation, revaluation, depreciation, exclusion; long-term financial assets; methods of valuation of current assets; accounting in production, incl. calculation of total production prime cost, process prime cost, models of profit and loss account, annual report. IĀS111 National Economy of Latvia 2.00 CP ( 3.0 ECTS) The course gives an insight in the major indicators of Latvia's economy and trends, as well as the position of Latvia within the European Union and in the world. IUE219 Marketing 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Definitions and essence of marketing. Detailed focus on marketing environment. Marketing mix elements and their interrelationship. Consumer behavior in the consumer and business market, the place of consumers within the marketing system. Segmentation, product and pricing policy, organization of marketing and control, development of a system of marketing information, competition, product life cycle, distribution, promotion in the market etc. MFZ104 Physical Basics of Technology 2.00 CP ( 3.0 ECTS) Physics is closely related to natural sciences, leads to new trends of the multidisciplinary research – biophysics, material science, physical chemistry. Physics is also the basis for engineering. The technical level of production directly depends on the development of physics. All these point to the fact that the course of physics at technical universities has a special significance. A course of physics for engineers is a fundamental theoretical training base, without which the further success of an engineer is not possible. The course of study based on the School of Mathematics provides the theoretical basic knowledge of mechanics, molecular physics and thermodynamics, electromagnetism, wave and quantum optics, quantum mechanics, solid state physics, atomic physics, nuclear, and particle physics. The course consists of lectures with practical examples. DIM207 Mathematics for Economists 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Partial derivatives and elasticities for several argument functions. Substitution rate and elasticity. Optimization problems and application in economics. Elements of probability theory: algebra of events, discrete and continuous random variables. Normal, exponential and Poisson's distributions. Elements of mathematical statistics. IUE330 Planning of Entrepreneurship 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Role of planning and forecasting in business and key aspects of planning methodology: principles, methods, types, sequence. Business plan for a successful operation of a business, contents, requirements for development and presentation. Key issues of production planning: planning of sales, production volumes, required resources and their sources, costs and performance results. ITE319 Fundamentals of Business Logistics 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The main components of the study course "Fundamentals of Business Logistics” are supply, production and distribution, i.e. how to ensure the flow of materials, semi-finished or finished products from the supplier to the end user that involves a physical flow of orders, information and goods. The subject is based on the knowledge acquired during the first study year, i.e. in microeconomics, marketing, entrepreneurship economics, and is a separate business sphere for the subjects to be acquired additionally in the second study year. The subject consists of lectures and practical classes, the topics of which include the most important spheres of logistics. The teaching staff act as mediators helping students acquire the theory and conducting practical classes. Students independently acquire the theoretical material independently Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! using textbooks and special literature. Students independently analyse and evaluate case studies, make decisions and substantiate their choice and take part in discussions. IMP201 Taxes and Duties 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Structure and elements of the taxation system: state taxes and duties, state dues, duties imposed by local governments. State taxes and duties forming the taxation system. Tax and duty payers, entities subject to taxation, tax and duty rates, payment procedure. Tax payers' rights, responsibilities and liability. IET104 Macroeconomics 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The subject matter of the course is Macroeconomics. Main economic indicators. GDP and its calculation. Cycles in national economy. Macroeconomic equilibrium. Money, banking, inflation. Employment, unemployment. Fiscal policy and national budget. Monetary policy. Keynesian theory and monetarism. Model IS-LM. International economic relations. IUE133 Introduction to Study Field 1.00 CP (1.5 ECTS) Organization of the study process. Methods of studies: reading, listening, writing, exposition of the material, preparation for examinations. Use of literature and other sources of information. Problems of national and regional economic development. Entrepreneurship and its role in the development of Latvian national economy. Organization of international relations and fundamentals of customs. IUE329 Economics of Innovations 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Essence, concepts, goals of innovations. Classification of innovations. Operation of innovation. Indicators of science intensitivity of a product. Innovation enterprises, types, organizational structures. Sphere of marketing innovation: strategic and tactical marketing innovations in enterprises. Innovation infrastructure, its core elements. Planning of the innovation process. Economic substantiation of innovations. IĀS515 Quantitative Methods in Management (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Quantitative methods, economic-mathematical models and decisionmaking process. Specific models of linear programming. Integer programming tasks. Models of development scenario choice. Transportation problems and optimization of transshipment. Goal programming. Specific methods for time series analyses and forecasting. Econometric modelling. Multiple and dynamic regression. Nonlinear econometric models. Parameter estimation methods. Matrixtype (input-output) models. Game theory elements. IĀS515 Quantitative Methods in Management (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Quantitative methods, economic-mathematical models and decisionmaking process. Specific models of linear programming. Integer programming tasks. Models of development scenario choice. Transportation problems and optimization of transshipment. Goal programming. Specific methods for time series analyses and forecasting. Econometric modelling. Multiple and dynamic regression. Nonlinear econometric models. Parameter estimation methods. Matrixtype (input-output) models. Game theory elements. IEU540 Electronic Commerce and E-business (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) E-commerce within the context of the information society. Role of technology and telecommunuications in the e-commerce. Focus on the issues related with enhancement of efficiency of economic performance and safety of information in open networks. Legisalation and normatives governing e-commerce. Issues of internet marketing. IUE591 Marketing Theory (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Goals and objectives of the course. Product policy. Marketing models. Theory of marketing management. Marketing theory and its current development. Development of marketing concept for upgrading business starategy. Costs and product quality, tendencies of change taking into account satisfaction of consumer requirements. Practical implementation of marketing theory, its development. System of marketing calculations. Marketing models and methodology of economic substantiation of marketing solutions. IET526 Economic Theory (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The subject provides in-depth knowledge in microeconomics and macroeconomics. Particular attention is paid to a deeper understanding of demand and supply, consumer choice and public choice theories. The types of economic development policy and economic development problems under conditions of globalization and international integration are analysed. IUV524 Business Process Management (graduate) 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) Theories of business process management. Organizational forms of management systems. The types of management organization. Effectiveness and productivity. Modeling of personnel. Management teambuilding. FACULTY OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DMI201 Basics of Computer Simulation and Modelling 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The course ‘Basics of System Modelling and Simulation’ considers basic concepts of system modelling, i.e. the concept of computer modelling and standard procedure, modelling motivation and main principles, and model development and application aspects. The essentials of analytical modelling and types of analytical models used in practice, such as differential equations, difference equations are discussed, Boolean functions, logical expressions, finite automats, network models and Petri nets, are considered. The fundamentals and applications of system statistical modelling are considered. The structure of a computer simulation model and its main components are defined. Discrete event simulation methods for input modelling, time handling and process simulation, simulation on spreadsheets and simulation output analysis are considered. Systems dynamics approach is discussed. Main principles and methods for model testing and validation are given. Modelling software and tools ad-on are reviewed. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! DSP701 Knowledge Management Systems 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) n this course students will learn about the concepts of organisational learning and knowledge, essential factors of organisational learning, knowledge flow and networks and technologies supporting them. Human-computer interaction and interface design will be discussed. Students will learn to define knowledge management strategy, to design knowledge management systems, to plan the development of these systems and will be familiar with different knowledge management technologies. DSP702 Research Methods in Business Informatics 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Modern society is being moved towards a knowledge-based model within which innovative solutions are created that can be applied to enhancing the economy. However, innovative solutions can be created through synthesizing existing knowledge. Scientific methods have been designed and are applied specifically for this purpose, therefore being familiar with such methods should be of benefit to students of business informatics program. The main subject of the course is the introduction to and practical application of scientific methods that can be used in computer science research. Given that some of the students may not be familiar with the concept, the course presents the types of scientific methods and possibilities of application thereof. Quantitative and qualitative scientific methods are considered, the research process and its various steps are analyzed, and the stages of drafting a scientific publication are set out. To ensure a more efficient learning process, theoretical studies are complemented with a realistic research project of a nominal volume; the results of this project shall be presented in a written report. A number of lectures are dedicated to honing technical writing skills that can be applied to drafting course and final papers. DSP707 Service Science, Management, and Engineering 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course is about service oriented approach in business and information systems and software engineering. It concerns vertical (inside the enterprise) and horizontal (inter-organisational) service provision situations. The emphasis is put on new innovative service development. The course comprises service design methods, basics of building service oriented architectures (SOA), and other topics of service engineering. Students will experiment with various service development and running technologies. They will learn approaches to service governance according to most popular service management methods and standards. Students are expected to have basic knowledge in business process modelling, systems theory and portfolio management. The course concerns also research advances in SOA. DPI721 Business Analytics 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Companies are making decisions across all functional areas. The role of information technology specialists is to develop infrastructure to provide decision makers with precise information at the right time and the right place. First part of the course deals with the value chain and analyzes information sources of the main business processes. Accent will be put on the quality management and cost accounting. Second part of the course deals with business intelligence architectures and tools available for enterprise information utilization. Students will have to do a case study to analyze business processes of a particular company and develop metrics and specifications of business intelligence solution. DPI704 Quality, Risk and Security Technologies 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) 4.0A modern enterprise's operations are closely related to the application of information and communications technology. For the most part, enterprises cannot remain competitive and viable without resorting to ICT. However, selecting the most appropriate technologies for a specific company requires an understanding of ICT. Some of the most crucial prerequisites for successful deployment of ICT in an enterprise is the quality of technologies chosen, understanding of the risks associated with such technologies and security of the selected technologies. The main topic of the course is an overview of the existing quality, risk and security technologies from the following viewpoints: 1) Process; 2) Activities; 3) Standards; 4) Methods applied; and 5) Best practice examples. To ensure that the aim of the course is successfully attained, theoretical studies are complemented with practical deployment and analysis of the technologies discussed. During the practical part of the course, narratives of quality, risk and security management processes are created, existing methods and standards are applied to real-life enterprises' situation examples and existing technologies are applied in practice.0 CP (6.0 ECTS) DSP708 Advanced data technologies 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) In the course above-mentioned models are combined with well-known and very wide used relational database models. The course includes main groups of query languages used in advanced database systems, such as SQL and its object and temporal extensions; multidimensional query languages for data warehousing systems and artificial intelligence languages. The course concerns also issues on information systems architecture for large variety of possibilities to organize storing, searching and presenting data, information and knowledge: different client/server architectures with application servers and web servers, distributed database architectures and multibase architectures. Databases are not only for data storage and retrieval, they can perform different algorithms to provide needed information and knowledge. To illustrate this database capability deductive databases, data mining, and intelligent databases are considered. DOP700 Enterprise Information Technology Architecture, Applications and Integration 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Commercially available enterprise information systems are often used in implementation and automation of enterprise business processes. The objective of the course is to master main principles of enterprise information systems, their deployment and modification. Main topics covered in the course are business process modeling, application of ERP, workflow and other enterprise systems in process automation, modification and deployment of enterprise information systems, integration of enterprise information systems and adoption service- Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! oriented computing in enterprise systems. Technologies for the modification of enterprise systems are explored in laboratories. DPI700 Storage Networking 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The course covers concepts, features, design and applications of storage area networking (SAN) including SAN management challenges, requirements, and solutions’ advantages and disadvantages. Storage consolidation, management, virtualization, scalability, performance, backup and restore, and replication are explained from the relevance to business continuity and high-availability. Lectures present intermediate to expert-level knowledge of intelligent storage solutions with multiple transport options over long distances. The course also includes such topics as storage network architectures, Fibre Channel and other emerging technologies, and storage networking management applications and their market. Hands-on labs and projects are based on IBM Lotus Notes Domino and Workplace Services or alternative applications. After completing the course students can propose solutions to set up and run SANs. DSP703 Systems Theory 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The goal of systems theory is to develop general description methods of systems, based on systems thinking, providing inclusion of all critical factors that have influence on systems performance. In this course students acquire foundations of systems theory. The focus is on specific systems theories which represent relevant factors for business development. Students obtain understanding of principles of systems classification and system classes. Foundations of cybernetics are included into the course as well as theories of living systems and viable systems. Students learn to use set theory and graph theory which are needed for systems modelling and are used in other courses. DSP700 Enterprise Architecture and Requirements Engineering 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course presents basic approaches to requirements engineering. Students learn to identify and design enterprise/business architectures and specify requirements for organisational information systems viewing people and computer systems as nodes of information processing. They learn to analyse and design information flows in organisations and organisational networks and how to develop the information logistics model. IBM requirements identification and management tools are used in the course. Acquired knowledge is beneficial not only for requirements identification for information and communication technology solutions; it is applicable also for the design of products and services in general. DSP105 Introduction to Study Field 1.00 CP (1.5 ECTS) During first year studies at the university former pupils meet a rather different style of teaching and learning, do not know each other and have unclear idea about their future profession. All mentioned facts influence their motivation to continue studies in future. The objective of the course is to stimulate students’ early adoption to university requirements and their motivation to study seriously and systematically meeting the stated requirements. This is achieved by making them acquainted with the specificity of university studies (faculty’s structure, requirements of the study process, pedagogical and scientific activities) during the first 3 lectures, as well as presenting the essence and perspectives of the chosen profession in the labour market on the basis of a business game during remaining lectures. In the context of the business game students are divided into several groups and each group, guided by its supervisor, develops a specific system by going through all stages in a system development process and identifying activities, working specialists and preparing documents at each stage. At the end of the course each group demonstrates achieved results and acquires feedback from the supervisor. DIP106 Algorithmization and Programming of Solutions I 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Students receive academic knowledge in computer applications, as well as pragmatic skills in development of algorithms, software development and debugging. The acquired knowledge and skills provide further successful mastering of computer science courses. DAA300 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics and Image Processing 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Today, working with computer is connected to graphical objects creation in 2D and 3D space, as well as image processing. In this course students learn about different methods of graphical primitives construction as well as graphical objects transformation and visualization methods. Students are also acquainted with various image processing methods, including image quality enhancement and image compression. DIP217 Applied Software 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Integrated application programs development principles overview on the base of MS Office. Different components usage methods. Text editor (MS Word), spreadsheet (MS Excel), presentation tool (MS Power Point), workflow support (MS Outlook), graphical editor (VISIO). Collaboration of different components. Web-technology basic. DST203 Introduction to Computer Architecture 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Data representation; minimization and technical implementation of logical functions; basic functional elements in computers and then synthesis; organization and architecture of computers; control unit; memory audits addressing modes; input - output subsystem; direct memory; virtual memory; RISC and CISC architectures; implementation examples. DIP208 Programming Languages 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) rogramming language concept, standard and versions, alphabet, syntax and semantics. Classifications, characteristics and usage possibilities of programming languages. Technology of program preparing for running. Program structure. Example of simple program. Basic objects of programming languages, operators and data, review of control statements. Functions. Objects and storage classes. Pointers, arrays, string processing. Structures. Files. Graphics. Programming languages progress tendencies. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! DSP202 Discrete Structures of Computer Science 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) During studies students acquire the practical applications of discrete mathematics concepts, graph algorithms and mathematical foundations of data base. Students acquire the properties of binary relations by detailed examination of equivalence and ordering. Students acquire key elements of graph theory, ways of graph representations. Theoretical knowledge has to be used by practical calculations with shortest path algorithm; algorithm for minimal spanning tree and algorithm for maximum flow problem. The course also observes basic concepts of relational database, operations of relational algebra and basics elements of Structured Query Language (SQL). While studying the subject students have to work out course work; they have to write program that solves the defined task by using algorithms and concepts given in lectures. DSP303 Technology of Large Databases 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The main differences of large databases (LDB) and desk-top databases. Data models of LDB. Architecture of LDB logical and physical data organization. On-line transaction management and On-line Analytical processing database systems. Instance and its structure. Database dictionary and configuration parameters. Optimisation of SQL queries. Tuning and audit. The most popular large database management systems: Oracle, MS SQL Server, DB2, Progress, Postgress. The future trends. DPI343 Computer Organization and Assembly Language 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) This course covers organization principles of CPU, main memory, external devices and basics of Assembly language programming. Students will obtain skills and knowledge to operate computer components using low level programming techniques. DIP320 Adaptive Data Processing Systems 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Basic Principles of ADPS Design. Application of Business System Planning Method and LIS Technology. Adaptive user dialogue design on the basis of mathematical and lingvistical models. Different examples of Adaptive Data Processing Systems are considered: Financial, Banks, Insurance Information Systems. DSP342 Methods of Systems Theory 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Job of a system analyst is directly related to the analysis of different business and technical systems. For this purpose a system analyst must know methods and tools for the identification and describing of characteristics and operating principles of different systems. The main attention of the course is devoted to the development of students' systems thinking by considering the use of system theory methods in the analysis of different kinds of systems. The following topics are considered during the course: origin of systems science and its specific methods, basic elements of systems thinking, principles of systems classification, cybernetic approach to systems thinking, principles and elements of system control and management, evaluation of system complexity, the role of information and communication in system management, system laws and principles, as well as life cycles. By developing an individual work students must apply theoretical knowledge to the analysis of real world systems. DPI349 Software Evolution Technologies 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) 1968 is a year of identification of software crisis and software engineering was recognized as an engineering discipline, which enabls to view software development as an engineering process. The course deals with modern software development techniques and technologies used in different stages of software development process. In general, software development can be divided into the following components: life cycle, process, analysis and design tools, programming environment, quality assurance, project management, team work. These components are discussed during the course, showing their evolution, solved and unsolved problems. DSP347 System Engineering 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Professional responsibilities of systems analyst require to have a good knowledge of methods and tools for identification of characteristics and operation principles of various types of systems. This course is focused on the specific method of systems theory – systems engineering, touching also main issues of systems theory and systems analysis. In the course the following topics are considered: systems notion, key concepts of systems thinking, systems engineering process and principles, systems models, modeling methods, techniques and languages, systems development life cycle, structured techniques, process of systems analysis and design and its support by SSADM methodology. DOP204 Numerical Methods 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Solution of linear equation systems by direct, iterative and variation methods. Solution of nonlinear equations and systems. Interpolation, aproximation, mean square method, its applications. Noncorrect problems. Regularization with Tihonov method. DAI241 Fundamentals of Automation 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Stabilization, monitoring and program-driven control systems. Structure of systems. Obtaining methods of control systems equations, transmission functions, time and frequency characteristics. Stability of the system. Analysis of control systems quality. Pulse control. Non linear control. Simulation of systems. Identification of systems. DSP451 Large Databases (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The problems of large database (DB) design. Multibases systems. Homogeneous and heterogeneous DB systems. The data models of large DB. Optimization of DB structure. Client/server technologies. DB and transaction servers. The adminstration problems of large DB. Security policy of DB. Auditing DB use. Tuning process of DB. Recovering and backing up a DB. DIP485 Software Metrology and Planning Models (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Software project management: development process models, task planning and assignment, project calendar, human management models, cost estimation models, software metrics, quality management models, Testing and risk management. Management of “Mission Impossible” projects. Variety of software engineering.Tasks distribution. Tasks realization graphic. Software costs estimation. Analytic, algorithmic, COCOMO models. Maintenance costs. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! DPI503 Evolution of Object-Oriented Software (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Students acquire implementation of object-oriented approach (OOA) principles in several programming languages. There are discussed both fundamental OOA principles (abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism) and some additional principles (parallelism, typing). At the centre of attention there are three object-oriented programming languages: Ada, Java, Python. The course includes a survey of some specific questions: applet development, server script development, creation of complex data structure and others. DSP555 Requirements Engineering (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course explains the role of requirements engineering in organizational development and information systems design. During the course students learn several requirements engineering methods, such as soft systems methodology, process oriented methods, and architecture, service, decision analysis, business rules, and agent oriented methods. The main emphasis in the course is on training the ability to understand in which situations which requirements engineering methods and tools are to be used and how they are to be combined to achieve desired level of requirements acquisition detail and manageability. DIP415 Network Software (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) In lecture course the basics of network architecture and development of computer network software using different programming approaches are discussed. DSP411 Theory of Systems and Processes (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The goal of systems and process theory is to develop general system structure and functioning description methods which are founded on systems thinking that allows to consider all relevant factors for system operation. In this course students get acquainted with philosophical foundations of systems theory as well as with general and specific system theories. They also acquire basic conceptions of system structure, system classification, system laws, rules and principles, general characteristics of system functioning, mathematical models and analysis of system structure, and basics of structural modeling and multilevel flow modeling. DPI502 Object-Oriented System Analysis (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) At the beginning of course an introduction to organizing of system requirements is given. The forms of presentation of requirements are shown to explain possible input information at the stage of system analysis. Further process of system analysis and design is presented from use case view and system modeling is based on system use case analysis. System analysis and design is performed used UML diagrams. System conceptual modeling and analysis of using the system is shown in the course. The great attention is devoted to analysis of object interaction and identification and description of system classes. Practical system modeling in UML is shown based on usage of CASE tool Sparx Enterprise Architect. System design process and the term of system architecture are also mentioned in the course content. At the end of course several methodologies of object oriented system analysis and the role of system analysis in general software development process are shown. FACULTY OF TRANSPORT AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MSE305 Hydro- and Gas Dynamics 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The subject contains consideration of properties of liquids and gases, hydrostatic forces, pressure definition. The Fluid Dynamics course is based on motion equations of liquids and gases. Real flows described in terms of border layer equations and turbulence length. Non dimensional methods used for process modeling. Heat losses and flow types are analyzed. Methods of pipe, valve, pump and fan selection. Flow parameters described in nozzles, channels, around the body. MAB205 Basics of Production Engineering 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Engineering process and it's components. Methods of production (machining, cold plastic treatment, electrophysical treatment and other methods). Design of engineering processes. Engineering processes of product assembly. MAB114 Introduction to Study Field 1.0 CP (1.5 ECTS) MTM516 Analysis and Optimization of Machines, Structures and Technological Processes (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Strategy of experiment organization. Basic statistical concepts. Classical experimental designs (Factorial design, Box-Behnken, D-optimal). Space filling designs. V.Eglajs experimental design. Latin Hypercube Design. Regression analysis. Parametric and non-parametric approximation methods. Radial basis functions. Response surface methodology. Experimental Designs for fitting of Response surfaces. Filtration of Outliers. Classification of optimization problems. Handling of nonlinear constraints. Deterministic and stochastic global optimization methods (Taboo search, simulated annealing, genetic algorithms, multistart methods). Virtual prototyping of mechanical systems. Metamodelling and optimization by using EDAOpt, ANSYS and ADAMS programs. MSE432 Thermodynamics and Gas Dynamics (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The subject “Thermodynamics and Gas Dynamics” covers different thermodynamic systems and their characteristics. Energy transition types. Simple and complicated thermodynamic systems. MTH503 Computer-Aided Analysis of Mechanical Systems of Machines (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Matrix methods in mechanism kinematics and dynamics. The method of constraints for planar kinematic analysis. Revolute, prismatic, gear and cam pairs are considered together with other 2 degrees-of-freedom types of constraints. Formal description of kinematic diagrams. The automatic assembly of the systems of equations for position, velocity and acceleration analysis. Geometry of masses. Forward and inverse tasks of geometric, statistic, kinematic and dynamic analysis. Dynamics Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! of planar systems. Computation of planar generalized forces for external forces and for actuator-spring-damper element. Relations between transfer velocity, angular velocity of rigid body and generalized velocities: analogue matrices. Simple applications of inverse and forward dynamic analysis. Numerical integration of first-order initialvalue problems. Accuracy and stability of integration methods. Kinematics of rigid bodies in space. Reference frames for the location of a body in space. Euler angles and Euler parameters. Velocity, acceleration and angular velocity. Relationship between the angular velocity vector and the time derivatives of Euler parameters. Kinematic analysis of spatial systems. Basic kinematic constraints. Joint definition frames. Denavit-Hartenberg notation. The constraints required for the description in space of common kinematic pairs (revolute, prismatic, cylindrical, spherical). Equations of motion of constrained spatial systems. Computation of spatial generalized forces for external forces and for actuator-springdamper element. Computation of reaction forces from Lagrange’s multipliers. Dynamical models of AC and DC electromotors, internal-combustion and diesel engines. Dynamical models of control systems: PID controllers. 2D simulation packages: Working model 2D. 3D simulation packages MSC ADAMS: ADAMS View. Parametric optimization.Programs ADAMS Insight, EDAOpt. MSE541 Theory of Boundary Layer (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Study course ``Theory of Boundary Layer `` is planned for extended studies of heat and mass transfer, fluid mechanics and aerodynamic theory and practical applications. The main emphasis is on the convective heat exchange and the related phenomena of flow mechanics. Basic topics: Hydrodynamic and thermal boundary layers. Laminar, transient and turbulent flows. Viscosity, compressible and incompressible flows. Differential equations of flow dynamics and heat mass transfer. Boundary layer evaluation and empirical relationships. Analytical and numerical methods for solving equations. Modeling and simulation methods. Empirical methods of heat exchange and flow mechanics. MTH507 Lifting and Transporting Machines (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Ways of transferring/shifting hard objects, liguids, loose and other materials, the physical and mechanical issues of their transfer. Desing and exploitation of the machines used in the agriculture, processing industries (mainly food, woodprocessing, construction materials) and service industries (mainly cargo transit, transport, seaport ). FACULTY OF POWER AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DAI201 Electrical Measuring 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Measuring process,ways and methods.Measuring errors and estimation ofmeasurement result. Characterostics and structures of means of measuring.Measures, measure transducters and electromechanical measuring instruments.Bridge and conpensational chemes.Electronic,analog and digital measuring instruments.Measuring of resistance, inductivity, capacity,current,voltage,power,energy,phase shift,frequency and signal parametres. EEP475 Electronic Equipment 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Typical power supply unit topologies of electronic equipment. Linear and switching mode voltage regulators - principles of operation and common integrated circuits. Overcurrent protection circuits. Power amplifiers, their classification and the main characteristics. The structure and basic properties of operational amplifiers. Typical operational amplifier circuits, signal generators and active filters. Logic gates and their manipulation. Typical combinational logic – decoders, encoders, multiplexers, adders, programmable logic devices. Typical sequential logic – triggers, binary counters, parallel and shift registers. Semiconductor ROM and RAM memories, their structure and parameters. Integrated logic circuit families - DTL, TTL, CMOS, BiCMOS, ECL, GaAs devices, their structure and parameters. ADCs and DACs. Converters „voltage – frequency” and „frequency – voltage”. Timer circuits and applications. EEP201 Theoretical Basis of Electrical Drives 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Mechanic of electrical drives (ED), static and dynamic properties of electrical motors, its characteristics and regimes, transient processes of ED, adjustment of speed, torque and position in ED, energetic of ED, choice of motors power, a special modes of ED, basics of automatic regulation and control: classification, mathematical representation, dynamic links and structure schemes, criteria of stability. EEP345 Unconventional Systems of Energy Conversion and Accumulation 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Wind power stations, turbines, adjusting, connections to the Main, small power hydraulic plants, its adjusting, electric machines of the special construction, photovoltaics, piezo generators, piezo motors, motion and movement sensors, low voltage inverters, adjusting, regulation, batteries, UPS. EEP582 Control Technique with Microprocessor Controllers (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Process control systems with one and two tanks of capacities. Control loops. Industrial measurement equipment for flow, pressure, level and temperature. Controlled valves, programmable controllers, functions, P, PI, PID control loops, optimal setting techniques. EEP570 Elements of Automatics (graduate) 9.00 CP (13.5 ECTS) Sensors for measurement of electrical and non-electric parameters. Measurements schemes. Synthesis of logical parts of measurement schemes. Functional converters. Characteristics of technical parameters. Indicators of reliability level of the schemes. FACULTY OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS RAE362 Digital Devices and Systems 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Pulse signals and their impact on linear electrical circuits. Pulse signals transformer. Digital switches. Logic families, their parameters and electrical structures. Limiters. Pulse generators. Analogue and digital Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! comparators. Digital to Analogue and Analogue to Digital Converters. Timers. Computer memories. Computer internal and external interfaces. circuits. Resonances in RLC series and parallel circuits. Three-phase power systems analysis. RAE361 Digital Devices of Telecommunications Systems 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Addressing modes in processor systems. Systems of commands of onebyte microprocessors and programming basics. Floating comma number formatting and the subprocessor. External memory and its addressing and protection. Pipeline processing commands and the data. Alarm processors, their use. REA204 Electron Devices 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Electron devices as two and four terminal devices, their current-voltage characteristics. Small signal parameters of two and four terminal devices and corresponding equivalent circuits. Electron energy spectrum of solids, their division in metals, dielectrics and semiconductors. Intrinsic semiconductors and semiconductors with impurities. Electron statistics in semiconductors. P-n junction, its equilibrium and non-equilibrium properties. Heterojunction and contact metal-semiconductor. Rectifier, p-i-n, high frequency, pulse, tunnel, reverse, Zener, variable capacitance and Schottky diodes. Bipolar junction transistors, thyristors, field effect transistors and charge coupled devices. Structure, operation principles, current-voltage characteristics, parameters, mathematical models, advantages and drawbacks of devices considered. Influence of temperature on operation of electron devices. RDE301 Telecommunications Theory 5.00 CP (7.5 ECTS) The aim of electro-communications theory is to provide students with the basic knowledge of principles, structure and operation of communication systems. The following questions are covered: the history of telecommunication systems, their development, classification; signal and noise as random processes; geometrical interpretation of signals; sampling theorem, discretization of continuous signals; modulation and detection; the models of communication channels, information theory; codes, their classification and application; Shannon's theorems, theory of optimal reception of digital and continuous signals; signal filtering. Laboratory work and practical work are also envisaged. RDE302 Transmission Media 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) Communication line design. Classification of cable, insulating materials, protective covers. Electromagnetic processes in symmetrical, coaxial cable, waveguides. Design optimization. Electromagnetic compatibility. Mutual influence, rationing, protection. Shielding theory. Corrosion. Line construction, design, operation. The course includes both theory and communication lines measurements in the laboratory study. The international standards relating to the use of communication lines have been dealt with. Students are prepared both for practical work with lines of communication, and further studies in Master Course. RDE302 Transmission Media 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) Communication line design. Classification of cable, insulating materials, protective covers. Electromagnetic processes in symmetrical, coaxial cable, waveguides. Design optimization. Electromagnetic compatibility. Mutual influence, rationing, protection. Shielding theory. Corrosion. Line construction, design, operation. The course includes both theory and communication lines measurements in the laboratory study. The international standards relating to the use of communication lines have been dealt with. Students are prepared both for practical work with lines of communication, and further studies in Master Course. RTR223 Electrical Engineering Theory 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) Circuits elements, parameters and fundamental laws: current, voltage, resistance, power, energy, ideally linear elements R, L, C, ideal and real current and voltage sources, Ohm`s and Kirchoff`s laws. Resistive circuits, their analysis methods: current and voltage division rule, Thevenin, Norton and superpozition theorems. Sinusoidal steady state theory and analysis in frequency domain: complex impedance and admittance, phasors and phasor diagrams. Magnetically coupled RAE261 Digital Electronics and Computer Architecture 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Types of electrical signals. Arithmetic and algebra of binary counting system. Logic algebra and its functions. Minimization of logical functions. Combinational logic circuit analysis and synthesis. Sequential logic basic elements. Basic structure of computers, general concepts: algorithm, command, program, operand, address, operational system, computer memory, central processor, arithmetic-logic-unit. REA202 Electrical Measurements 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Introduction into foundations of measurement. Energy parameters of signals. Signal time parameter measurement. Measurement of shape and spectrum of signals. Concentrated and distributed parameter circuits. Measurement of non-electrical values. Fundamentals of Metrology. Automatization of measurement process. DIM205 Supplementary Mathematics (for electrical engineering) 2.00 CP (4.0 ECTS) Line integrals and surface integrals. Scalar and vectorial fields. Derivative in the direction, gradient, flux, circulation, divergence, rotor, Gauss and Stokes theorems. Laplace operator in curvilinear coordinates. Function of complex variable. Cauchy's theorem and integral formula. Taylor and Laurent series. Residues. Laplace transform., its basic properties and applications. Bessel functions. MAT104 Structures and Properties of Engineering Materials 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The role of engineering materials in technology. Types of materials: metals, polymers, ceramics, glass and composites. Structural levels of materials. Interconnection of structure and properties. Mechanical testing. Engineering properties of materials and methods of processing. Recycling. Principles of material selection. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! RAE306 Digital Switching Systems 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Introduction to telecommunication systems and services. Basics of digital circuit switching, time and space switches. Digital networks: component and multiplexing systems, main types of lines and trunks. Digital switching systems: comparison of EWSD and S12. Basics of packet switching and transmission. Difference between circuit and packet switching. Open system interface. ATM. Compromise between circuit and packet switching. RAE555 Teletraffic Theory (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The course covers the experimental systems in relation to telecommunications network systems. Within the framework of the course students will discuss the network management and control methods. Students will be enabled to promote their understanding of the performance of real systems. Important part of the course is evaluation methods as well as current trends and problems in the context of Internet, mobile and broadband communications. RDE432 Transmission Systems (special course) (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course deals with transmission systems (TS) at an advanced level. It includes the theoretical analysis of TS, as well as their practical implementation. In the laboratory students are trained in the practical skills in the area of TS. The following topics are discussed: noise and its influence on transmission quality, regeneration of digital signals, baseband line codes, passband line codes, clock extraction and timing, xDSL technologies. RAE541 Encoding and Encryption (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Characteristics of codes. Simple codes for error detection and error correction. Prefix and suffix codes. Cyclic codes, swapped codes. Applications. Filtering of digital signals. Synchronizaton in TV and message transmission. Methods of encryption. RAE472 Digital Switching Systems (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) This course is partly based on CCNP SWITCH 642-813 Official Certification Guide. Introduction to OSI system Layer 2 and multilayer switch operation. Basic VLAN concepts. End-to-end VLAN. VLAN channel. Ethernet application in campus network. Inter VLAN communication through Layer 3 routing. Switch port aggregation with EtherChannel. Spanning tree protocol. Multilayer switching with CEF. Voice VLAN. Catalyst and ASR switches. Enterprise network, Ethernet carrier environment. Switching in optical networks. RAE556 Mobile Communications Systems (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The course covers the following topics: propagation of waves in multipath environment, loss mechanisms and numerous methods of estimating the median value in mobile and cellular environment, technical parameters of such systems and methods of ensuring communication between cellular and base stations, as well as management of cellular and backbone networks. RDE425 Research Seminars (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Scientific workshops cover the following themes: presentation and discussion of the problems in the next generation telecommunications networks based on the analysis of the scientific literature, presentation and discussion of MSc analytical and experimental research results, the latest reviews on communications and measurement methodology, the latest telecommunications software for the analysis and their application reviews, taking part in scientific seminars, and work on the master thesis discussions. INSTITUTE OF APPLIED LINGUISTICS VIL167 Introduction to Linguistics 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The content of subject: In the lectures and seminars the essence of language is considered, as well as its structure and functioning, the origin and development of language, the diversity of world languages, their classification and methods of research. HVD118 English Speaking Countries I 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Geography, history, culture, traditions, holidays, political and economic situation, applied information on customs and way of life in the USA and UK are covered within the framework of the course. Students complete oral and written tasks. Students work individually, in pairs, in groups, present their achievements to their colleagues. Regular work with different tasks; individual, independent work with the textbooks; analysis of the new material. Students discuss situations in any sphere of life, compare processes and problems in the USA, Europe and Latvia. Discussions, reports and essays on the course topics. VIA161 Analytical Reading I 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course provides extensive reading and text analysis of professional literature in engineering, culture, economics, etc. Integration of communicative situations to master different skills of work with a text as well as professional situations thereby modelling students’ professional activity. HVD144 Basic Grammar Course I 5.00 CP (7.5 ECTS) Acquisition of basic English grammar skills by applying them in written and oral speech (in reports, conversations, summaries, essays). Knowledge of English grammar is acquired through the study of theory and practical drills. HVD123 Functional Communication I 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Development of students skills in speaking and making presentations on professional subjects at conferences. Communication in a foreign language at a conversational level. The content of the course includes developing competence in spoken business language. Presentations are made on the following subjects: professional, economic, cultural, and historical issues. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! HVD141 Studies of State Language I 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Revision of the main grammar themes and improvement of knowledge in connection with the themes being studied. Acquiring of vocabulary and speech skills on the basis of the topics about the history, economy, politics and culture of Latvia. Special attention is being paid to spelling and elimination of mistakes characteristic for Russian language speakers both in written and oral speech. Basic business writing skills. HVD142 Translation Practice:Latvian-Russian and Russian-Latvian 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Integrated state language and Russian language skills improvement in connection with the are a of work 1) text comprehension and problem analysis development of discussion skills, listening comprehension; 2) development of oral speech comprehension in order to participate in meeting, conferences, etc. for consecutive interpreting; 3) written translation of a text, style and vocabulary improvement, document layout and written translation. IUV216 Technical Means for Office Work 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) A office work advanced technology. Technical means forms, characterrise and choise. The technical office in Latvia. VIA150 Development of Listening Comprehension of Monologues, Dialogues and Professional Texts II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Students listen to interviews, reports, and surveys. Business and professional situations in English are used in order to develop listening comprehension skills. Students make oral summaries of the texts they have listened to, comment on them, and perform various communicative tasks. Students use the skills and competences acquired to express their opinion, argue for and against, as well as present information. VIA151 Introduction to Translation Theory 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The course aims at familiarizing students with theoretical fundamentals of translation theory; introduction of the basic concepts of translation, which also involves the application of these to authentic translation assignments. The course provides opportunity to analyze and study the characteristic features of operational languages (Latvians, Russian, English, German), provides knowledge of culture, competence in the communicative aspects of translation, knowledge of language for special purposes, as well as knowledge of translation theory and linguistics. VIA203 Machine Translation (Basics of Computer Translation) 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Students study stylistic, semantic and other features of informative, descriptive, evaluative texts on the theme “Machine Translation”. Within the framework of the course students translate texts in various special fields aimed at different target groups (young adults, students, nonspecialists, people interested in the field). They analyze communicative situations in the written form, examine mistakes in machine translated texts. Students present their portfolios, ask and answer questions of various degrees of complexity, work in pairs and groups evaluating personal and other students’ performance. HVD156 Fundamentals of Written Speech II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) This course provides an introduction to writing clear, accurate messages and to understanding basic writing strategies. It is designed to help students to be more proficient at the kind of writing they need to do. This course will acquaint students with some typical techniques used for effective writing and will give them practice in writing various kinds of business letters, reports, summaries, reviews, abstracts and essays. Students will master vocabulary and terminology of business correspondence. Practical classes at which different types of letters, pieces of academic writing are analyzed, new vocabulary is mastered, writing and translating skills are developed. A short introduction into different types of business letters is given. Both individual and group work is implemented. Independent work of students is encouraged. VIV202 Practical German Course I 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) Pronunciation, reading and grammar, idioms and vocabulary. Classes are conducted in the respective foreign language. VIV143 Practical Course of a Second Foreign Language (Spanish) I 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) The course is intended to develop proficiency and to integrate students’ Spanish language skills as a second foreign language. Practical Spanish course comprises survey of theoretical and practical materials, including grammar and lexical tasks. The students are required to be actively involved in conversations and discussions in pairs and in groups on different subject areas. Students are asked to do several lexical and grammatical tasks and express ideas in composition on a given topic. Evaluation of reading and understanding skills by using methods of text analysis, as well as by answering questions. VIA201 Practical Course of a Second Foreign Language (French) I 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) The course is intended to develop proficiency and to integrate students’ French language skills as a second foreign language. Practical French course comprises survey of theoretical and practical materials, including grammar and lexical tasks. The students are required to be actively involved in conversations and discussions in pairs and in groups on different subject areas. Students are asked to do several lexical and grammatical tasks and express ideas in composition on a given topic. Evaluation of reading and understanding skills by using methods of text analysis, as well as by answering questions. VIA310 Development of Listening Comprehension Skills I 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) Development of speaking, reading, and listening skills. Situational communicative, pseudo-professional and professional communicative situations are used to develop listening skills in the English language. Students study definite issues developing oral and written speech, as well as listening skills. Discussion topics: professional, popular scientific, social economic, scientific technical issues. Practical classes based on various tests, communicative – situational tasks, pair / group work, discussions, denotative graphs (logical schemes of the text), brainstorming, regular listening practice, etc. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! HSP380 United Europe and Latvia 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) 1. Essence of a joint Europe. 2. Joint European institutions. 3. Secure integration of economic, social and political aspects. 4. Latvia and the European Union: perspectives and problems. 5. What the Lisbon Treaty means in the development of the EU with VIA165 Practice in Consecutive Interpreting I 8.00 CP (12.0 ECTS) Students get acquainted with the course of Consecutive Interpretation, its aim and specific character of consecutive interpreting as well as with the work of an interpreter. They acquire the note-taking technique, perform different tasks, participate in role-plays and interpret simulated seminars, conferences, etc. Communicative and interactive study method. Independent and responsible learning, cooperative learning. Pair work at practical classes. VIA164 Translation of Specialization Texts I 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Students read and analyse the source text (ST) paying attention to the following translatological categories: topic (the place and the year of publishing of the ST, the publishing house, formal features of the ST, specific features of language pairs; composition of the ST, status of the ST); semantics (word meaning, synonymy, polysemy, idiomatic meaning, functions of a linguistic sign, connotations, associations); lexis (terminology); pragmatics (the function of the target text (TT), translation tasks, the recipient, cross-cultural differences), and stylistics (the style of the ST, stylistic analysis, syntax, functional styles, cohesion etc.). Students learn to determine the text type of the ST, identify translation problems and solve them, develop translation strategies, and select appropriate translation methods. Students work with dictionaries, glossaries and other reference literature. They translate the text, revise and assess the translation editing it if necessary. VIA166 Political and Economical System of English Speaking Coutries 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The course aims at providing students with information and extending their knowledge on political and economic systems of English speaking countries, UK in particular. Simulations, role plays and case studies are used so as to develop students’ communicative skills in English. To develop reading and listening skills students are provided with a definite amount of authentic texts for reading and a list of special topics for speaking practice and listening comprehension. Practical classes using pair/group work, discussions, reports, denotative graphs (Mind Mapping), brainstorming, etc. Topics discussed: Structure of governments, parliament, electoral and party systems, media, major sectors of economy, etc. VIA311 Academic Writing II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course provides students with practice they need in order to incorporate new knowledge and skills. The first part of the course introduces students into comprehensive rhetoric, conventions and style of English academic writing. It intends to develop the basic skills of paragraph organisation, sentence structure and specific strategies of English academic writing. The second part of the course provides samples of academic writing and appropriate practice materials for students who need to write exam essays, abstracts, summaries, reports etc. in English. The aim of the course – to enable students to write better for academic purposes — is achieved through applying a process-genre approach to writing, using authentic source texts, and a step-by-step method of teaching academic writing. All the classes in the course are conducted in the form of student-centred collaborative writing workshops to allow maximum time for writing, to foster students' independence and to facilitate meaningful written communication. VIA186 Patents and Intellectual Property Protection 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Students practice to use the acquired knowledge taking part in simulations and role-plays both as copyright holders and copyright users, thus modelling situations, conflicts and the ways to solve them. Planned discussions: 1) Court trials on copyright and intellectual property rights protection in Latvia 2) Copyright and neighbouring rights from opposite perspectives: copyright holders vs. copyright users. 3) Translation as copyright medium. VIA170 Terminology of Business and Law 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) On completion of the course, participants will have enhanced their knowledge of international business and legal systems and have developed their ability to use English language effectively in a professional, business, legal and social context. In addition, students will have developed an extensive range of appropriate English language skills, as well as having produced a very useful portfolio of commercial correspondence and written work. Language skills are developed through many stimulating, realistic communicative activities. VIV306 General German I 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) The study course continues to develop reading, listening, speaking and writing skills in German as a second foreign language. Within the framework of the course translation skills are developed working with intermediate informative texts, translating from German into the mother tongue. VIA308 General Spanish I 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) The course is designed for Spanish as a second foreign language. The study continues a more detailed study of the subject commenced in the elementary Spanish language course. Students study input materials, perform various communicative tasks and exercises, analyze personal performance working in the class and independently. Students perform oral and written tasks and answer different questions. They work both individually and in small groups. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! VIA306 General French I 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) The course is designed for French as a second foreign language. The study continues a more detailed study of the subject commenced in the elementary course. Students study input materials, perform various communicative tasks and exercises, analyze personal performance working in the class and independently. Students perform oral and written tasks and answer different questions. They work both individually and in small groups. Spring HSP489 Organizational Psychology 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Psychological characteristics of a manager. Psychological characteristics of a worker. Psychological theories of management. Organizational culture and its levels. Staff selection. Team building. Organization development. English Language 2.00 CP (3.00 ECTS) upper Intermediate Basic English course that can be integrated with other subjects on the curriculum and that is based on acquisition of technical terminology in the particular field: 1) acquiring creative reading skills by working with professional texts; 2) mastering the fundamentals of relevant conversation and developing discussion skills; 3) improving listening comprehension skills to ensure effective participation in conferences, projects etc. 4) developing writing skills (essays, summaries, abstracts, conclusions). Mathematics Part II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Introduction. Analytical geometry: vectors, lines, and surfaces. Linear algebra: matrices, determinants, and systems of linear equations. Introduction to analysis: limits, continuity. Differential calculus: derivative, differentials and their applications. Integral calculus: indefinite and definite integrals, their applications. Ordinary differential equations. Series. Double and triple integrals. Physics Part II 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Introduction to physics. Fundamentals of mechanical motion. Molecular physics and thermodynamics. Electrostatics. Direct current. Electromagnetism. Oscilations and waves. Optics. Quantum physics. Structure of solid state. Nuclear physics and elementary particles. Latvian Language ( Part I; Part II; Part III) 1.00 CP (1.5 ECTS) (each part) The course is designed for foreigners. The aim of the course is to train and develop basic skills in communication, listening, reading and writing so that purpose in everyday situations. The course contains the most neccesary topics. History and Culture of Latvia 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Balts and Livs. Origin and development of their culture. The development of different culture phenomena in Latvia: books, theatre, cinema, music, fine art etc. Latvian folklore and mythology, Dievturība, the search for Latvian identity. Computer Studies (basic course) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Kinds of computers. An overview of the modern computer. The fundamentals of the data processing theory. Alghorimization. Iteration, recursion processes and loops. The fundamentals of programming language: variables, arrays, records, files, input/output operations, subroutines. Introduction in the programming. Modules of the program. Libraries. Previous courses: Informatics of socondary school. FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING BBM110 Introduction to Structural Analysis 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) General notions and axioms of statics. Forces, systems of forces and operations with them. Ties (supports) and their reactions. Equilibrium of bar systems. Calculations of forces under tension, compression, bending. Mechanical properties of materials. Geometric specifications of bar sections. Strength estimation of bar systems in case of static loading. Kinematic and structural analysis of systems. BĢE291 Global Positioning Systems (study project) 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Global positioning systems are dynamic in space and time, they provide a range of backgrounds and industry activities. The course "Global Positioning System Study Project" is the solution of practical tasks and research-based academic and theoretical knowledge. Study design challenge include geodetic, astronomical, etc. coordinates and time systems, satellite conformation, their orbits, the constellation of satellites, and the perception of signals. BĢE206 Global Positioning Systems 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Global positioning systems are dynamic in space and time, they provide a range of backgrounds and industry activities. The course "Global Positioning System" presents the terms of coordinates and time systems, satellites and their orbits, signals and satellite constellation. Global Positioning practical side involves different methods of measuring the performance of analytic processing and analysis of the results. BĢE329 Basics of Geoinformation Systems 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The acquisition of Geo-Information Systems Basics (GIS) is essential for the formation of conception how to create the digital data sets in form of files describing the spatial information of surrounding us environment. These data sets • may be visualized on the computer screen or printed out by using specialized computer software, • may be used to form the thematic maps with a graphical, numerical and textual information, Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! • may be analysed the stored information for decision making in management, • may be accumulated in various layers of graphical and attribute information of many topics. BĢE402 Real Estate Valuation (for engineers) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Regulations of real estate appraisal, real estate value influencing factors, process of real estate appraisal, use of appraisal methods. Regulations of cadastral valuation, use of methods of cadastral valuation, real estate tax. BĢE313 Astronomy 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Spherical astronomy: coordinate systems, coordinate transformations, time and time measurement, motion of the coordinate systems, Fundamentals of celestial mechanics: equations of motion, Kepler’s Laws, Newton’s Laws, Two-body Equation. Applied astronomy. Astronomy of stars. BĢE300 Photogrammetry 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Scientific basis of the photogrammetry. Methods of the photogrammetry and instruments. Analytic and terrestrial photogrammetry. Orientational elements, measuring of the coordinates. Photomaps. Aerotriangulation. FACULTY OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DOP702 Customer Relationship Management and Social Network Technologies 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Customer relationship management systems together with social networking enable reaching a large number of customers and potential customers as well as gathering and distributing information using electronic channels. The course explores typical characteristics of customer relationship management systems and social networking applications with emphasis on understanding dynamics interactions within networking systems. Specific features of different social networking technologies and their utilization in business process optimization are also reviewed. DSP706 Business Process Management and Engineering 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Business process management and engineering requires understanding of basic principles of business process modelling, management, improvement, and reengineering. During the course students will learn to develop business process models, assign performance identifiers to process elements, assess the correspondence of business process to its goal, and to develop business process change proposals and implement changes at the level of a business process model. DSP707 Service Science, Management, and Engineering 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course is about service oriented approach in business and information systems and software engineering. It concerns vertical (inside the enterprise) and horizontal (inter-organisational) service provision situations. The emphasis is put on new innovative service development. The course comprises service design methods, basics of building service oriented architectures (SOA), and other topics of service engineering. Students will experiment with various service development and running technologies. They will learn approaches to service governance according to most popular service management methods and standards. Students are expected to have basic knowledge in business process modelling, systems theory and portfolio management. The course concerns also research advances in SOA. DSP701 Knowledge Management Systems 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) In this course students will learn about the concepts of organisational learning and knowledge, essential factors of organisational learning, knowledge flow and networks and technologies supporting them. Human-computer interaction and interface design will be discussed. Students will learn to define knowledge management strategy, to design knowledge management systems, to plan the development of these systems and will be familiar with different knowledge management technologies. DOP319 Computer Networks 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Computer networks and computer technology. ISO OSI model. Global networks. Local networks and their communication. Organization of network working places, communication channels, modems. Basic network services. Electronic mailing systems. Addressing in electronic mailing systems, office management on their basis. Design of network working place. Network service basis. Mailing electronic systems. DIP381 Operating Systems 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Operating System conception. Tasking and processes. Process coordination and synchronization. Physical and virtual memory organization. OS performance evaluation. OS examples - MS DOS, UNIX, OS/2, Windows. DPI230 Object-Oriented Programming 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) This course covers object-oriented (OO) programming concepts and techniques using C++ language as an example. After completing the course students will understand the basic principles of OO programming and obtain OO programming skills. OO basic concepts - abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism are discussed as well as practical programming issues, including class hierarchy formation, an exception handling, templates, etc. Comparison of C++ with some other OO programming languages (eg C # or Java) is also given. During laboratory work students must demonstrate theoretical knowledge and acquire programming skills. DOP201 Introduction to Operations Research 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Operations Research is a very important area of study, which tracks its roots to business applications. It combines the three broad disciplines of Mathematics, Computer Science, and Business Applications. Course of study presents the most important operations research problems and diversity of the addressed methods; provides knowledge Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! about possibilities of using the theoretical models in real situations and systems quantitative analysis. DPI348 Introduction to Applied Computer Science 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Students became familiar with scientific research method and get an information about requirements and best practice of presentation of research results, which are used for development of first scientific research during bachelor studies - bachelor thesis. Lectures content an information about what is a scientific research, what are its main components, how to use sources of scientific bibliography, how to use scientific ideas and results of scientific research offered by another authors, how to apply scientific method for bachelor level research and how to present own results during assertion of bachelor thesis. Practical lessons give to students a possibility to report on the stage of bachelor level research and to present a new result of the research and/or updating of an old result. Tasks are directed to application of theoretical information for practical approbation of received knowledge to develop parts of pilot research and to present intermediary results of scientific research. DSP341 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Design 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Systems lyfe cycles and design. Stages of system design. Top down and bottom up design strategies. Traditional and advanced approaches to Subject helps to understand tasks of system designing and place in the system development' s process. Students form project team, led by a student. The group consists of subgroups which are also run(ned) by the students. Students' task is to establish requirements for designed system, design it and realize at least in the prototype' s level. The system has a real customer, and all student activities proceeds in natural conditions of the systems designing. Subject also includes the theoretical aspects of the systems designing: upward and downward designing, traditional and modern methods of the system designing, different types of the system designing. DIP203 Data Structures 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Data structures concept and classification. Abstract data structures. Basic data structures. Linear data structures: arrays, lists, tables, stacks, queues. Non-linear data structures: trees and graphs. Logic and physical data structures. Pointers and lists. Simple linked list specification, representation and design. Double linked lists and their usage. DIM204 Discrete Mathematics 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Sets, mappings, relations. Combinatorics. Boolean algebra; discrete circuits, automata. DIP106 Algorithmization and Programming of Solutions II 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Students receive academic knowledge in computer applications, as well as pragmatic skills in development of algorithms, software development and debugging. The acquired knowledge and skills provide further successful mastering of computer science courses. DSP201 Database Management Systems 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Concepts of database (DB) technology. DB management systems (DBMS) and their functionality. DBMS types. Possibilities and restrictions of relation DB. DB data definition languages. Query languages SQL and QbE. Application design in DB systems. Tools of programming automatization. DBMS programming languages. Data exchange standards. Main principles of DB design. DMS214 Random Processes 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Definition and application of random process. Multivariate distributions. Correlation theory. Classification of processes. Stationary processes. Markov chain with discrete and continuous time. Markov processes. Gussian processes. Imiitation of random processes. DSP422 Artificial Intelligence (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Artificial intelligence is developing towards four goals – to create systems that think or act like humans, as well as systems that think or act rationally. In this course students acquire knowledge about a modern approach to artificial intelligence – development of intelligent agents. The course is focused on properties, environment, architectures and programs of intelligent agents, logical agents, ontologies, planning, uncertain knowledge and reasoning, making simple and complex decisions, inductive learning, learning decision trees, neural networks and reinforcement learning. In development of a course work students must use their theoretical knowledge for implementation of agent based intelligent systems and analysis of their performance. DIP414 Computer Aided Solution Processing (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Supervised machine learning, regression modelling, linear regression, least-squares method, model evaluation, automatic model building, heuristic search, genetic algorithms, genetic programming, nearest neighbour methods, regression trees and their practical applications. DPI401 Programming of Processes (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) This course covers the process management, theoretical and practical aspects of scheduling and synchronization techniques, including the use of Petri net modeling process. Memory management, including virtual memory and page replacement algorithms, distributed systems management methods and algorithms are also included in the course. Students acquire skills for independent analysis and presentation of theoretical material. DIP484 Applied Software Systems (scientific seminar) (graduate) 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Advanced models, methods, technologies and tools used in application software systems developing are considered. The basis of research seminar: latest papers in software journals, conference proceedings, exibition catalogues etc. IDA117 Basics of Occupational Safety (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! The policy of the state and labour protections requirements. Harmful and dangerous factors of working environment, their influence on a human body, principles of standardization. Measures for elimination or reduction of this influence. The bases of fire protection. HSP489 Organizational Psychology (graduate) 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Psychological characteristics of a manager. Psychological characteristics of a worker. Psychological theories of management. Organizational culture and its levels. Staff selection. Team building. Organization development. FACULTY OF ENGINEERING ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT IET127 Microeconomics 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The subject matter of the course is Microeconomics. Demand. Supply. Utility and demand. Comparison of prospective and current value. Discounting. Production, productivity. Maximization of corporate profits in the conditions of perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition and oligopoly. Market of production factors: labour market; market of production resources; land market. Theory of public choice. IET104 Macroeconomics 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The subject matter of the course is Macroeconomics. Main economic indicators. GDP and its calculation. Cycles in national economy. Macroeconomic equilibrium. Money, banking, inflation. Employment, unemployment. Fiscal policy and national budget. Monetary policy. Keynesian theory and monetarism. Model IS-LM. International economic relations. IUE133 Introduction to Study Field 1.00 CP (1.5 ECTS) Organization of the study process. Methods of studies: reading, listening, writing, exposition of the material, preparation for examinations. Use of literature and other sources of information. Problems of national and regional economic development. Entrepreneurship and its role in the development of Latvian national economy. Organization of international relations and fundamentals of customs. IUE216 Computers for Economists 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Introduction to processing of economic information by means of the MS Excel program - Goal Seek, Data Analysis and functions installed in these programs. Statistical processing of data by using forecasting elements, graphical and analytical possibilities offered by MS Excel. Optimization of simplified economic tasks by MS Excel programs Solver and MathCad. Development of a data base. Powerpoint and its use for presentations. IĀS207 Economic Statistics 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The course obtains tasks and organization of statistics. The course covers the tasks which include statistical observation, grouping, tabulation, data plotting, absolute, relative and average variation parameters, dynamic time series and implementation of the theory in practice. IĀS215 Quantitative Methods for Economics 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The course includes characterisation of economic and mathematical methods and models and decision making process. Within the course, students learn forecasting methods by using time series, models for examining economic relationships, models of linear programming, simulation and elements of the queuing theory. IMP203 International Economic Relations 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Basic course on international movement of goods, services, labour and capital, regional economic integration and international economic organizations. The course is based on knowledge in theory of market economy and develops skills for its application IUV227 Business and Labour Law 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Concepts of Law theory, concepts of civil contractual relations, Family, Inheritance and Employment Law. Legal deal conception and its participants. Legal deal structure and forms. Main regulations of contract conclusion. Obligations and claimsfrom illegal activity. Guilt as the base of civiljudical responsibility. The degrees of guilt. IUV207 Fundamentals of Finances 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Elements of financial system. State finance management. Firm finance system and its goals. Credit system. System of banks. Securities market. Management of firm assets and capital. Investments management. Management of financial risk. Exchange market. System of insurance. Firm management in insolvency cases. IUV301 Business Management 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The targets and choice of management. Internal & external surroundingog the enterprise. The management of innovations. Management forms ofenterprise. The checking of process. Venture. The management of conflict. IUV302 Labor Management (basic course) 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) ILO, most important conventions. Systems of social safety. Industrialresource. Wages of employees. IUE335 Investment Economics 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Essence and relevance of investments in economy, macroeconomic factors affecting activity of investments, investment climate in the country and the role of the state in investment process. Types of investments, planning of capital investments and fundamental methodological principles of planning capital investments, formation of the price of capital. Principles of modeling calculations by using Excel. IUE705 Trade Enterprises Management 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The role of trading in the Latvian economy. Latvian economic relations with the EU countries. Trade enterprise types, features, functions, Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! planning and forecasting, organizational structure, management. Trade enterprise performance indicators, evaluation methods, performance records. IUV209 Accounting 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) An organization of book-keeping accounting. A financial economic action's balance and his analysis. IET516 Research Methodology (graduate) 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The course dealt with the concept of a scientific study, induction and deduction. Types of Research. Research methods. Research ethics and academic honesty. Cleared qualitative and quantitative research, research and data collection phases and their analysis. It means a research topic selection, justification and literature review studies. Are considered and evaluated academic publication databases and their use in the study process and conduct research. Discussion of the requirements of research design and presentation. Research organization on the Internet: The advantages and disadvantages. The course is given including research funding types and sources. IUE593 Theory of Economic Analysis (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Goals and objectives of economic analysis. Methodology of economic analysis. Provision of information for analysis of business peformance. Quantitative methods of analysis of business performance, their application. Methodology of analysis of indicators of business performance. Analysis of utilization of resources. Analysis of production prime cost. Analysis of profit and profitability. IEU538 Financial and Commercial Calculation Methods (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The objective of this course is principles and methods of financial and commercial calculations. The main attention of course is put to interest theory (simple and compound interest theory, force of interest, calculation methods of accumulation and present value of money). Additionally course covers calculation methods of annuities. Definition of cash flow, equivalence principle is introduced to students and all received knowledge is used to analyse different financial problems. Further course covers introduction in different types of risks in business, risk classification and risk estimation by applying statistical, expert and special coefficient methods, criteria for decision making and examples of their application. IUV528 Corporate Social Responsibility (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Theory of corporate social responsibility (CSR), classification and evaluation of CSR, role of stakeholder theory in CSR, CSR elements and initiatives, implementation of CSR program in company, worldwide practice of CSR, CSR practice in Latvia. IEU535 Project Planning and Control (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The goal of the subject is to provide necessary knowledge and skills about modern project management methods, project development phases planning, project structure creation, project tasks, durations, terms, resources and costs planning, coordination, controlling and correction, milestones plan creation, project plan performance monitoring and control. IUE585 Economics and Management of Innovations (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Classification of innovations. Role of innovations in the development of entrepreneurship. Planning, management, financing and forecasting of innovations in the market conditions. Economic evaluation of investment projects. Innovations and economic strategy in an enterprise. Management of innovations in the process of creating, making and realization. Model for selecting the options of innovations. Quality innovations and their competitiveness. Pricing in the sphere of innovations. FACULTY OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS RTR215 Circuit Theory 5.00 CP (7.5 ECTS) Transient analysis of electric circuits. First order circuits. Second order circuits. State variable analysis. Discrete-time convolution. Continuoustime convolution. Convolution algebra. Laplace transforms. Transfer function. Bode plots. Two-port networks. Two-port parameters. Two-port interconnections. Introduction into electric filter analysis. RTR220 Basics of Signal Theory 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Classification of signals, their characteristics, examples of use in communication systems. Continuous-time periodic and non-periodic signals, Fourier transforms, their properties. Discrete-time signals, Discrete Fourier Transforms, digital filtering, FIR and IIR filters. Modulation, AM, FM, PM signals, digital modulation, transformation of modulated signals by narrowband linear systems. Random signals, their main parameters, principles of measurement, noise in electronic systems. DMS212 Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Classical definition of probability. Axsiomatical definition of probability. Algebra of events. Bernully's schema. Formulas of full probability and Baijes. Continuous and discrete random variable. Distributive and density of functions. Large numbers law. Central limit theoreme. Elements of mathematical statistics. Combinatoric. Test of hypothesis. RAE305 TeletrafficTheory 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The course gives knowledge and skills of modelling, analysis and simulation of telecommunication networks as mass service systems. Dealing with M/M/1, M/M/k systems analytically. The use of Markov chains as mathematical models. Acquiring skills in simulation of systems with Petrie nets and other simple simulating tools (Java Simulation TOOLS). REA302 Materials, Components, Microelectronics 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) General characteristics of materials and components. Electroconductive materials and components. Dielectric materials. Resistors. Capacitors. Magnetic materials, inductive components. Semiconductors materials. Fundamentals of microelectronics technology. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! RAE359 Distributed Systems in Telecommunications 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The course deals with distributive systems in telecommunications. The goal of the course is to give an introduction to the distributive system problems, modelling of parallel processes and understanding of Open System Interconnection reference model (OSI - RM), functionality and architecture of telecommunications networks. FACULTY OF POWER AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING RDE425 Research Seminars (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Scientific workshops cover the following themes: presentation and discussion of the problems in the next generation telecommunications networks based on the analysis of the scientific literature, presentation and discussion of MSc analytical and experimental research results, the latest reviews on communications and measurement methodology, the latest telecommunications software for the analysis and their application reviews, taking part in scientific seminars, and work on the master thesis discussions. EEP203 Digital Electronics (basic level) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Digital quantities, number systems, logic functions, Boolean algebra and laws, Karnaugh map, analysis and design of combinational logic circuits, fixed function logic circuits, programmable logic and its description methods. RAE475 Telecomunications and Computer Networks (graduate) 5.00 CP (7.5 ECTS) Telecommunications networks and systems as a telecommunication business infrastructure are studied. Skills of using the network control and management technologies and tools, network planning skills, network simulation skills and tools are objectives of this course. RAE473 Computer Technologies in Telecommunications (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The objective of the course is to enable students to construct software by means of systematic object-oriented analysis and design. The course covers the methods for object-oriented analysis and modelling of application domains and software systems. The analysis includes description of objects and their structuring and functional specifications. The design will include the system modelling with layering and partitioning. RDE417 Physics of Optical Information Processing (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course is designed to introduce students to the fundamentals of optoelectronic and optical communications. Topics cover waveguide optics, nanophotonics, metamaterials, holography, optical information processing, laser technology and nonlinear optics, atmospheric laser communications, FOTS information multiplexing and computer simulation. RDE410 Design and Maintenance of Telecommunications Networks (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course deals with projecting of transmission systems. Students identify and define tasks, structure, and content of a project. Topics include principles of electricity supply and powering, maintenance tasks and management, parameters and methods, condition, control means and parameters of communication systems, remote control systems. EEI358 Intelligent Electronic Equipment in Robotic Systems 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Industrial electronic devices with self-educated and fuzzy logic control equipment on the basis of standard processors and special microchips. Artificial neural networks in motion control in the robotic control systems. Generic algorithms and artificial intelligent in the control of robots. EEP585 Simulation of Electrical Processes (graduate) 5.00 CP (7.5 ECTS) The subject is devoted to simulation of electrical circuits. Principles of composing of differential equation systems for electrical equipment, of their numerical calculation, and its features in MATLAB are given in the first significant part of the course. The second part is devoted to PSPICE circuit description language and to the features of its practical utilization. The theoretical part of the course deals with solutions of ordinary differential equation systems and basics principles of PSPICE. The practical (most important) part of the course includes various examples of simulation of electrical equipment. EEP583 Industrial Frequency Converters and Inverters (graduate) 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Historical overview of AC drive systems development. Mechanical and electrical characteristics of DC and AC drive systems with different speed control methods. Variable frequency AC drives, typical applications and characteristics. Inverters and frequency converters with pulse width modulation techniques. Scalar and vector-oriented control methods of frequency converters. EEP572 The Control Systems of Power Electronics Equipment (graduate) 5.00 CP (7.5 ECTS) Electronic elements of control systems. Saw-teeth mode voltage, forming of firing pulses. Achieving of the time delay in control systems, phase shifting control, synchronization with network, generators for clock pulses, diversification devices, Pulse Width Modulators, microprocessor based control systems for frequency converters. EEP524 Design of Power Electronics Systems (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The subject is proposed for full and part-time RTU academic master study program „Computerized Control of Electrical Technologies” students. The power electronics system main converter design and calculation are considered. It is desribed the design and calculation of controllable rectifier, net inverter, DC pulse converter and autonomous inverter power and control schemes. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! FACULTY OF TRANSPORT AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MMP532 Mechanics of Composite Materials (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Composite materials. Fibers. Matrix materials. Types of composite materials. Calculation of the streses and strains in composite materials. The methods and models of micromechanics of composites. The model of the unidirectional composite. The model of the composite, armed with short fibers. FEM apliccation in the micromechanics of composite materials. Macromechanics of composites. Strength and fracture in composites. MTH505 Rotary Machines (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Rotating parts of structures, shafts of energy and transportation machinery parts. A key initiative of the dynamic load factor, rotor disbalance. The dynamic calculation methods are analysed. The rotor balancing methods are considered. MMP539 Vibrotechnology and Vibromachines (graduate) 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Typical vibtotechnologies and machines. Fundamentals of the system. Nonlinear effects. Optimal design. Vibroisolation tasks. Optimal vibroprotection of machines and constructions. Complexes. Rotor dynamics. Design and calculations. MSE535 Non-Standard Sources of Energy (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) The subject gives basic knowledge in matters of non-standard and alternative energy sources, sustainable development theory, legislative acts and strategies on different levels that support and promote use of such energy sources and the modernization of utilization technologies. Huge attention is given to energy sources that have been used already for several centuries – solar, wind, running water (oceans, sees, rivers, tidal and ebb energy), biomass. The potential and the level of the utilization technology of every source is carefully evaluated according to technical, economic, environmental aspects. Emphasis is put on efficiency of energy conversion and total profitability. From the same aspects household and industrial waste, sludge from water treatment plants is considered. Interest is also built towards nuclear energy and hydrogen technologies. All sources are evaluated on the level of EU and the Republic of Latvia development plans. IDA117 Basics of Occupational Safety (graduate) 1.0 CP (1.5 ECTS) The policy of the state and labour protections requirements. Harmful and dangerous factors of working environment, their influence on a human body, principles of standardization. Measures for elimination or reduction of this influence. The bases of fire protection. MMP535 Fracture Theory (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Griffith ideas on cracks stability conditions. Irvin method. Stress concentration. Stress intensity factor. Fracture toughtness. Energy methods: J-integral, strain energy release rate parameter, R-curve. Damagemechanics. Cracks and debonding in composites. Cyclic loading and de-bonding in composites. Cyclic loading and cracks propagation conditi-ons. MMP533 Nonlinear Mechanics of Materials (graduate) 3.00 CP (4.5 ECTS) Material classification. Nonlinearity. Rheology. Plasticity. Stress distortion and nonlinear theory. Flow theory. Viscosity. Nonlinear creep theory. Mechanical models. Models with memory. Aging models. Flow models. The crack theory. Elastic properties of non-linear models. Technology. Calculation program. HSP446 Pedagogy (graduate) 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The course deals with important aspects of pedagogy such as subject of pedagogy, different philosophies of education, theories about teaching and learning. The students are introduced to basic concepts of learning and the current pedagogical ideas.During the course students are involved in different learning activities: group discussions, case studies, presentations . The aim of activities is to show how the theory relates to the pedagogical practice. Students will be able to develop the practical skills how to manage the education process. During the reflections promoted by lecturer students will get deeper understanding of main issues of teaching process: pedagogical style and motivation, interaction in pedagogical environment. Students will learn how to cooperate, how to share the ideas, how to describe, anayse and evaluate concrete pedagogical situations . INSTITUTE OF APPLIED LINGUISTICS HVD144 Basic Grammar Course II 5.00 CP (7.5 ECTS) Acquisition of basic English grammar skills by applying them in written and oral speech (in reports, conversations, summaries, essays). Knowledge of English grammar is acquired through the study of theory and practical drills. VIA161 Analytical Reading II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course provides extensive reading and text analysis of professional literature in engineering, culture, economics, etc. Integration of communicative situations to master different skills of work with a text as well as professional situations thereby modelling students’ professional activity. VIA150 Development of Listening Comprehension of Monologues, Dialogues and Professional Texts I 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Students listen to interviews, reports, and surveys. Business and professional situations in English are used in order to develop listening comprehension skills. Students make oral summaries of the texts they have listened to, comment on them, and perform various communicative tasks. Students use the skills and competences acquired to express their opinion, argue for and against, as well as present information. HVD123 Functional Communication II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Development of students skills in speaking and making presentations on professional subjects at conferences. Communication in a foreign language at a conversational level. The content of the course includes developing competence in spoken business language. Presentations Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! are made on the following subjects: professional, economic, cultural, and historical issues. HVD118 English Speaking Countries II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Geography, history, culture, traditions, holidays, political and economic situation, applied information on customs and way of life in the USA and UK are covered within the framework of the course. Students complete oral and written tasks. Students work individually, in pairs, in groups, present their achievements to their colleagues. Regular work with different tasks; individual, independent work with the textbooks; analysis of the new material. Students discuss situations in any sphere of life, compare processes and problems in the USA, Europe and Latvia. Discussions, reports and essays on the course topics. HVD156 Fundamentals of Written Speech I 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) This course provides an introduction to writing clear, accurate messages and to understanding basic writing strategies. It is designed to help students to be more proficient at the kind of writing they need to do. This course will acquaint students with some typical techniques used for effective writing and will give them practice in writing various kinds of business letters, reports, summaries, reviews, abstracts and essays. Students will master vocabulary and terminology of business correspondence. Practical classes at which different types of letters, pieces of academic writing are analyzed, new vocabulary is mastered, writing and translating skills are developed. A short introduction into different types of business letters is given. Both individual and group work is implemented. Independent work of students is encouraged. HVD141 Studies of State Language II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Revision of the main grammar themes and improvement of knowledge in connection with the themes being studied. Acquiring of vocabulary and speech skills on the basis of the topics about the history, economy, politics and culture of Latvia. Special attention is being paid to spelling and elimination of mistakes characteristic for Russian language speakers both in written and oral speech. Basic business writing skills. HVD142 Translation Practice:Latvian-Russian and Russian-Latvian II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Integrated state language and Russian language skills improvement in connection with the are a of work 1) text comprehension and problem analysis development of discussion skills, listening comprehension; 2) development of oral speech comprehension in order to participate in meeting, conferences, etc. for consecutive interpreting; 3) written translation of a text, style and vocabulary improvement, document layout and written translation. VIA185 Lexicology and Stylistics 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The course introduces the fundamental notions of Lexicology and Stylistics, it covers the main themes of modern English lexicology and stylistics: language units, word building, semantic changes, phraseology, borrowings, semasiology, neology, lexicography, methods of stylistic analysis, stylistic expressive means and their classification. It enables students to uncover the layers, patterns and levels that constitute stylistic description in the process of translation the texts from the source into the target ones. IET109 Fundamentals of National Economy 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The subject matter of economic theory. Market mechanism. Demand. Supply. Elasticity. Needs, utility. Production factors, productivity. Production costs. Profit. Microeconomic equilibrium and stability. Business cycles in national economy. Equilibrium in national economy. Money and inflation. Employment. Role of the government in economics. Forms of international economic relations and their development. IUV101 Fundamentals of Law 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) Abstract Concepts of Law theory, concepts of civil contractual relations, Family, Inheritance and Employment Law. Legal deal conception and its participants. Legal deal structure and forms. Main regulations of contract conclusion. Obligations and claims from illegal activity. Guilt as the base of civil judicial responsibility. The degrees of quilt. VIA311 Academic Writing I 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) The course provides students with practice they need in order to incorporate new knowledge and skills. The first part of the course introduces students into comprehensive rhetoric, conventions and style of English academic writing. It intends to develop the basic skills of paragraph organisation, sentence structure and specific strategies of English academic writing. The second part of the course provides samples of academic writing and appropriate practice materials for students who need to write exam essays, abstracts, summaries, reports etc. in English. The aim of the course – to enable students to write better for academic purposes — is achieved through applying a process-genre approach to writing, using authentic source texts, and a step-by-step method of teaching academic writing. All the classes in the course are conducted in the form of student-centred collaborative writing workshops to allow maximum time for writing, to foster students' independence and to facilitate meaningful written communication. VIA310 Development of Listening Comprehension Skills II 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) Development of speaking, reading, and listening skills. Situational communicative, pseudo-professional and professional communicative situations are used to develop listening skills in the English language. Students study definite issues developing oral and written speech, as well as listening skills. Discussion topics: professional, popular scientific, social economic, scientific technical issues. Practical classes based on various tests, communicative – situational tasks, pair / group work, discussions, denotative graphs (logical schemes of the text), brainstorming, regular listening practice, etc. VIA164 Translation of Specialization Texts II 4.00 CP (6.0 ECTS) Students read and analyse the source text (ST) paying attention to the following translatological categories: topic (the place and the year of publishing of the ST, the publishing house, formal features of the ST, Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement! specific features of language pairs; composition of the ST, status of the ST); semantics (word meaning, synonymy, polysemy, idiomatic meaning, functions of a linguistic sign, connotations, associations); lexis (terminology); pragmatics (the function of the target text (TT), translation tasks, the recipient, cross-cultural differences), and stylistics (the style of the ST, stylistic analysis, syntax, functional styles, cohesion etc.). Students learn to determine the text type of the ST, identify translation problems and solve them, develop translation strategies, and select appropriate translation methods. Students work with dictionaries, glossaries and other reference literature. They translate the text, revise and assess the translation editing it if necessary. VIA165 Practice in Consecutive Interpreting II 8.00 CP (12.0 ECTS) Students get acquainted with the course of Consecutive Interpretation, its aim and specific character of consecutive interpreting as well as with the work of an interpreter. They acquire the note-taking technique, perform different tasks, participate in role-plays and interpret simulated seminars, conferences, etc. Communicative and interactive study method. Independent and responsible learning, cooperative learning. Pair work at practical classes. VIA180 Translation of Legal Texts 2.00 CP (3.0 ECTS) The students master the use and definitions of legal terms. In practical classes they define and analyze terminology, present the ability to work with different types of legal documents, magazines, newspapers and books, using analytical skills and lexical knowledge in order to translate texts in Law from English into Latvian/Russian and vice versa. Students are taught to apply different sources and reference materials as well as dictionaries and glossaries. Students individually should create a glossary of legal terminology. VIA156 Translation and Comprehension of Professional Literature I 8.00 CP (12.0 ECTS) Students read and analyze different texts in the major in order to develop the following skills and competences: • Understanding meaning: deducing the meaning of unfamiliar words and word groups; relations within the sentence/complex sentences; implications - information not explicitly stated, conceptual meaning, e.g. comparison, purpose, cause, effect. • Understanding relationships in the text: - text structure; the communicative value of sentences; relations between the parts of a text through lexical and grammatical cohesion devices and indicators in discourse. • Understanding important points; distinguishing the main ideas from supporting detail; recognising unsupported claims and claims supported by evidence - fact from opinion; extracting salient points to summarise; following an argument; reading critically/evaluating the text. • Reading efficiently: surveying the text, chapter/article, paragraphs, skimming for gist/general impression; scanning to locate specifically required information; reading quickly. • Note taking. • Summarizing. Discussions on the following subjects: fundamental principles of text analysis; text types; semantic, syntactic and lexical characteristics of professional texts; communicative function of the text; structure of the text; semantic and pragmatic features of the text; content structure of the text; comprehension and interpretation of the text; efficient reading and interpretation of informative, narrative and descriptive texts in the major in English. VIV306 General German II 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) The study course continues to develop reading, listening, speaking and writing skills in German as a second foreign language. Within the framework of the course translation skills are developed working with intermediate informative texts, translating from German into the mother tongue. VIA308 General Spanish II 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) The course is designed for Spanish as a second foreign language. The study continues a more detailed study of the subject commenced in the elementary Spanish language course. Students study input materials, perform various communicative tasks and exercises, analyze personal performance working in the class and independently. Students perform oral and written tasks and answer different questions. They work both individually and in small groups. VIA306 General French II 6.00 CP (9.0 ECTS) The course is designed for French as a second foreign language. The study continues a more detailed study of the subject commenced in the elementary course. Students study input materials, perform various communicative tasks and exercises, analyze personal performance working in the class and independently. Students perform oral and written tasks and answer different questions. They work both individually and in small groups. Please see the rtuasd.lv before fill in learning agreement!