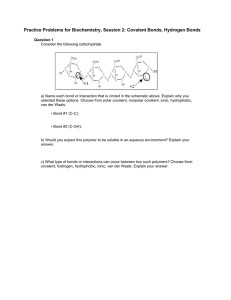
A) Breaking the H–H bond releases energy B) Breaking the Cl–Cl
advertisement

1. Which best describes the energy change during the reaction? 5. Consider the sets of charged objects shown in the diagram: H2(g) + Cl2(g) ® 2 HCl(g) A) B) C) D) E) Breaking the H–H bond releases energy Breaking the Cl–Cl bond releases energy Forming the H–Cl bond absorbs energy Forming the H–Cl bond releases energy Breaking the H–CL bond releases energy 2. The attractive force between the protons of one molecule and the electrons of another molecule are strongest A) in the solid phase B) in the liquid phase C) in the gaseous phase D) during sublimation E) during fusion 3. Given the pure substances and their bond dissociation energies, which substance is the most difficult to decompose into its atoms? A) HI 295 kJ•mol–1 C) H2 432 kJ•mol–1 E) HF 570 kJ•mol –1 B) HCl 428 kJ•mol –1 D) O2 494 kJ•mol–1 4. Covalent bonds are the result of the A) B) C) D) E) attraction of electrons to each other attraction of an electron pair by two nuclei elevation of electrons to higher energy levels transfer of electrons from one atom to another the attraction of two nuclei to eachother Which is true? A) B) C) D) E) I and III are examples of attractive forces The largest attractive force is case II The largest repulsive force is case I The attractive force in II is twice that in IV The largest repulsive force is case II 6. Base your answer to the following question on the table below. Consider the shell electron configuration of five elements. Which will form covalent compounds? A) I and II C) III and V E) IV and V B) I and IV D) III and IV 7. A covalent bond is most likely to form between atoms of chlorine and A) iron C) phosphorus E) sodium B) magnesium D) potassium 8. Which is a fundamental definition of a chemical bond? A) Positive ions attracting negative ions. B) Transfer of electrons from one atom to another. C) Attraction between valence electrons from two atoms. D) Electrons simultaneously attracted by more than one nucleus. E) Nuclei simultaneously attracted to more than one electron. 9. The term electronegativity is used because A) some elements conduct electricity and others do not. B) an electric current is a stream of negative particles. C) it requires energy to remove electrons from neutral atoms. D) the nucleus is negatively charged. E) the attraction for electrons in a bond formed between two different atoms can be uneven. 10. The greater the electronegativity of an element, the greater the tendency of the element to A) gain electrons. C) gain protons. E) form cations. 16. What is the type of binding force between phosphorus and hydrogen in the compound PH 3? A) B) C) D) E) ionic bonding covalent bonding hydrogen bonding van der Waals forces metallic bonding 17. Which type of bond is present in CS 2? A) network B) electrovalent C) polar covalent D) metallic E) nonpolar covalent 18. Which compound contains covalent bonds? A) BeO B) MgF 2 C) NaCl D) SO 2 E) CaS 19. Which compound contains a covalent bond with the greatest polarity? A) HF B) H2O C) BBr3 D) CCl4 E) Cl 2 20. Which pair of elements forms the most polar bond? B) lose electrons. D) lose protons. 11. Which compound has the greatest ionic character in its bonds? A) KCl B) CaCl2 C) GaCl3 D) AsCl3 E) O2 12. Which element exists as diatomic molecules at STP? A) copper C) hydrogen E) chromium B) helium D) silicon 13. Which compound has double covalent bonds? A) CsCl B) CO 2 C) CCl4 D) H2O E) NaF 14. What force or bond holds the two nitrogen atoms together in a molecule of nitrogen gas, N 2? A) B) C) D) E) ionic bond hydrogen bond nonpolar covalent bond van der Waals force polar covalent bond 15. Which bond has the least ionic character? A) S–Cl C) Br–Cl E) Na–Cl B) H–Cl D) Cl–Cl A) O and Cl C) O and P E) Br and Cl B) Cl and Br D) P and Br 21. Which is the most polar bond? A) C–O B) C–N C) B–O D) B–N E) Cl–Cl 22. The bond formed between two nonmetallic atoms with different electronegativities is the A) ionic B) metallic C) polar covalent D) nonpolar covalent E) coordinate covalent 23. Which type of bonding is usually exhibited when the electronegativity difference between two atoms is 1.1? A) B) C) D) E) ionic covalent metallic network bonding will not occur 24. Which formula has bonds with the most ionic character? A) O–H B) O=O C) C=O D) B–Cl E) C–H 25. The bonding of H + to NH3 to form NH4+ is A) B) C) D) E) coordinate covalent ionic metallic van der Waals nonpolar covalent 26. A coordinate covalent bond is one in which A) two atoms are bonded by one electron B) one atom shares two of its electrons with another atom C) two atoms each contribute one electron to a common bond D) two atoms each contribute two electrons to a common bond E) two atoms with opposing charges attract each other 27. In the diagram of an ammonium ion to the right, why is bond A considered to be a coordinate covalent bond? A) Hydrogen provides a pair of electrons to be shared with nitrogen. B) Nitrogen provides a pair of electrons to be shared with hydrogen. C) Hydrogen transfers a pair of electrons to the nitrogen. D) Nitrogen transfers a pair of electrons to hydrogen. E) Hydrogen and nitrogen each provide an electron. 28. Diamond and graphite both have bonds which are predominantly A) ionic C) covalent E) coordinate B) metallic D) network 29. Which of the following compounds is nonpolar? A) HCl C) CHCl 3 E) none of the above B) NH 3 D) AlCl 3 30. Which of the following molecules is nonpolar? A) H2O C) CO 2 E) CO B) NH 3 D) CHCl 3 31. Potassium chloride dissolved in pure water is an example of A) B) C) D) an ionic compound dissolved in a polar solvent an ionic compound dissolved in a nonpolar solvent a covalent compound dissolved in a polar solvent a covalent compound dissolved in a nonpolar solvent E) an ionic molecule mixed with a polar compound 32. The water molecule is A) ionic. C) electrovalent. E) linear. B) a dipole. D) a macromolecule. 33. Consider the elements and their first ionization energies. 37. Which molecule is nonpolar? A) C) B) D) E) 38. Which molecule is not a dipole? A) B) Three compounds are formed. Which statement concerning the three molecules is true? C) D) A) B) C) D) E) I and II are polar; III is nonpolar. I and II have the same degree of polarity. The bond angles in molecules I and II are identical. Electrons are attracted more strongly to B than to C. E) Electrons are attracted less to C than to B. 34. Which molecules are polar? 39. In ice, the molecules of H 2O(s) are held together by A) B) C) D) E) covalent bonds. hydrogen bonds. ionic bonds. oxygen bonds. Van der Waals forces. 40. Which statement best accounts for the boiling point of H2O being considerably higher than that of H 2S? A) B) C) D) A) I and IV only C) II, III and V only E) all of these The molecular mass of H2O is lower. Van der Waals forces are greater in H 2O. London dispersion forces are greater in H 2O. H2O molecules have more unshared pairs of valence electrons. E) Hydrogen bonding is more pronounced in H 2O. B) II and IV only D) III and V only 35. The compound that is a polar covalent molecule is A) CsCl B) CO 2 C) CCl4 D) SF6 36. Which is a polar molecule? A) B) C) D) E) H 2O 41. Why is the heat of vaporization of H 2O (2270 J) so much higher than that of C8H18 (590 J)? A) B) C) D) octane molecules are polar. molecules of water are less massive. octane gives off little energy when it vaporizes. the forces of attraction are stronger between water molecules. E) the forces of attraction are stronger within octane molecules. 42. Which substance has a high attraction for water molecules and a high solubility in water? A) I and IV only C) III and V only E) V only A) B) C) D) B) II and IV only D) IV and V only 43. The bonds between molecules in solid nitrogen are A) B) C) D) E) 48. Which diagram shows the orientation of the water molecules and the calcium ions when calcium chloride is dissolved in water? Van der Waals forces covalent bonds hydrogen bonds ionic bonds network bonds 49. Which Lewis electron dot diagram is correct? A) B) C) D) E) 44. Which molecular solid has only van der Waals forces as 50. The Lewis electron dot diagram for CO 2 is intermolecular bonding? A) B) A) KI B) HF C) H2S D) NH 3 E) CO 2 C) D) 45. Which substance in the solid state consists of particles E) held together by van der Waals forces only? A) Ge B) Rb C) KCl D) SiO2 E) CH 4 46. In which substance is the primary attraction van der Waals forces? 51. Which is the correct Lewis electron dot diagram for NH 3? A) B) C) D) E) A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V 47. Water and oil do not mix because A) B) C) D) E) their densities are different oil is a polar liquid water is a nonpolar liquid weak bonds form between oil and water no bonds form between oil and water 52. All of the following are resonance structures for NO3– except A) B) C) D) 53. The bonding orbitals on the central atom in a CF 4 molecule are A) s orbitals C) sp orbitals E) sp 3 orbitals B) p orbitals D) sp 2 orbitals 54. In which compound is bonding? A) BH 3 sp2 hybridization present in the B) C2H2 C) CH 4 D) H2O E) CO 55. Which hybridization of orbitals is present in the ammonium ion, NH 4+ ? A) sp B) sp 2 C) sp 3 D) dsp 3 56. Carbon dioxide is A) B) C) D) E) linear and polar linear and nonpolar bent and polar bent and nonpolar trigonal planar and polar 57. The shape of methane molecules, CH4, is A) bent C) tetrahedral E) planar B) triangular D) octahedral E) 58. The shape of an NH3 molecule is A) linear C) planar triangular E) bipyramidal B) tetrahedral D) trigonal pyramidal 59. The bonding orbitals on the boron atom in BF 3 molecule are A) s orbitals C) sp 2 orbitals E) p orbitals B) sp orbitals D) sp 3 orbitals 60. The shape of a water molecule is spd 3 A) bent C) pyramidal E) octahedral B) planar D) tetrahedral 61. The shape of CH2Cl 2 is A) linear C) pyramidal E) seesaw B) planar D) tetrahedral Answer Key Unit 8 Practice Test 1. D 37. B 2. A 38. D 3. E 39. B 4. B 40. E 5. B 41. D 6. A 42. C 7. C 43. A 8. D 44. E 9. E 45. E 10. A 46. C 11. A 47. D 12. C 48. B 13. B 49. B 14. C 50. C 15. D 51. C 16. B 52. C 17. E 53. E 18. D 54. A 19. A 55. C 20. C 56. B 21. C 57. C 22. C 58. D 23. B 59. C 24. A 60. A 25. A 61. D 26. B 27. B 28. D 29. E 30. C 31. A 32. B 33. A 34. C 35. E 36. B