Transformer Short-Circuit & Open-Circuit Tests Lab Report
advertisement

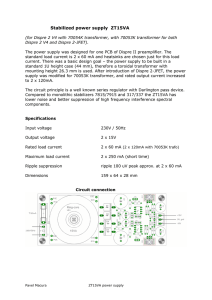
Short-Circuit and Open-Circuit Tests of A Transformer Lab #7 Chris Visser Mike Diliberto Ray Rioux November 1, 2006 Wentworth Institute of Technology ELEC465-01/02 Department of Electronics and Mechanical Prof. Ali Khabari 1 Abstract: The purpose of this lab was to study the operating characteristics of a single-phase transformer. The most important results were the resistance and coil values for both short-circuit and open-circuit tests. Introduction: The objective of this experiment was to measure the power, voltage and current of both a short-circuit and open-circuit transformer. We also calculated the corresponding resistance and inductance values along with the efficiency of the transformer. Experimental: Figure 1: The transformer circuit used for the short-circuit test. Starting this experiment, we wired the transformer for a short-circuit test as seen in Figure 1. We calculated the equivalent reactance on the high side. In order to calculate Reqhs, we used the power and current readings from the short-circuit test. We used the formula: Psc = Isc^2 * Reqhs Next in order to calculate the resistance in the inductor we had to find the total reactance first. This was done using the current and voltage from the short-circuit test. We used the equation: Isc = Vsc / Zeqhs We then used the calculated value and Reqhs in the following equation: Zeqhs = √(Reqhs^2 + Xeqhs^2) 2 Figure 2: The transformer circuit used in the open-circuit test part of the lab. In part 2 we performed an open-circuit test on the transformer as seen in Figure 2 and recorded the values for power, voltage and current. First, we calculated the core resistance on the low side Rfels. We did this by first finding Ifels with the equation: Poc = Voc * Ifels Using the calculated value for Ife, we then used the equation: Rfels = Voc / Ifels Next we calculated the magnetizing reactance Xm. We did this by first finding the current Im with the equation: Ioc = √(Ifels^2 + Imls^2) We used the current value of Im to calculate Xmls as seen below: Xmls = Voc / Im In order to calculate the efficiency, we first needed to find the power loss. We did this by adding the short circuit power and the open circuit power. Lastly, we calculated the efficiency of the transformer. This was done using the following equation: η = [(Pinput – Ploss) / Pinput] * 100 Results and Discussion: Below are our results and findings for the short-circuit test: Psc = 70 W Vsc = 6.8 V Isc = 16.6 A 3 Reqhs = 254 mΩ Xeqhs = 324.96 mΩ Open-circuit test: Poc = 20 W Voc = 120 V Ioc = 1.2 A Rfels = 720 Ω Xmls = 100.98 Ω The efficiency calculated for the transformer was 95.5%. Conclusion: By doing this experiment, we better know how to perform both a short-circuit and open-circuit test on a single-phase transformer. We now know how to find the equivalent winding impedance and core loss component of a transformer by taking measurements of power, voltage and current. We also understand how to calculate the efficiency using the power levels measured and given. We found our transformer to have very little loss which is a good thing. 4