Revised Blooms and Webbs
advertisement

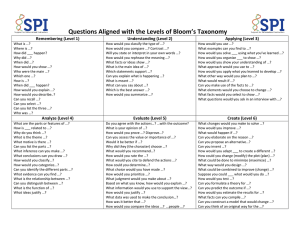
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy “Old” Bloom’s Taxonomy Synthesis *Was second highest level Evaluation *Was highest level Behaviors, Content, or Products Being Looked For Poem Play Invention Game Article Cartoon Experiment Song Conclusion Recommendation Self-Evaluation Court Trial Group Survey Discussion Editorial Analysis Survey Model Conclusion Graph Argument – Broken Down Questionnaire Report Application Diagram Sculpture Photograph Forecast List Project Puzzle Cartoon Comprehension Analogy Graph Outline Tape Recording Photograph Cartoon Speech Collage Knowledge People Events Recordings Dictionary Definition Text Reading Magazine Articles Highest Level Thinking Examples Of Question Words Creating Combine Compose Design Generate Invent Plan Formulate Originate Devise Revise Hypothesize Build Construct Produce Imagine Collect Evaluating Solve Critique Criticize Appraise Assess Conclude Justify Judge Check Experiment Hypothesis Test Detect Verify Recommend Debate Analyzing Analyze Sort Categorize Investigate Compare Estimate Differentiate Examine Organize Question Research Deconstruct Outline Attribute Divide Explain Applying Do Carry Out Complete Run Implement Apply Modify Build Construct Solve Report Illustrate Produce Execute Utilize Dramatize Understanding Explain Relate Describe Paraphrase Confirm Convert Match Infer Discuss Estimate Predict Summarize Interpret Rephrase Classify Compare Remembering Recall List Retrieve Find Name Recognize Identify Locate Describe Draw Label Select Outline Write Recite Record 4 Different Visual Guides To Bloom's Taxonomy | Edudemic (http://www.edudemic.com/blooms-taxonomy) Lepi, Katie et al. ' 4 Different Visual Guides To Bloom's Taxonomy | Edudemic '. Edudemic.com. N. p., 2014. Web. 16 Dec. 2014. The 6 Levels Of Bloom's Taxonomy, Explained With Active Verbs | Edudemic (http://www.edudemic.com/the-6-levels-of-blooms-taxonomy) Dunn, Jeff et al. ' The 6 Levels Of Bloom's Taxonomy, Explained With Active Verbs | Edudemic '. Edudemic.com. N. p., 2014. Web. 16 Dec. 2014. Webb’s Depth of Knowledge Arrange Calculate Define Draw Identify List Label Illustrate Measure Repeat State Memorize Who What When Where Why Name Report Recall Recite When was ___ ? Who was ___ ? What is ___ ? What is the formula for ___ ? How did ___ happen ? How would you write ___ ? How would you describe ___ ? Use evidence to support arguments Use appropriate voice for the audience Identify research questions Investigate problems Create a model for a situation Determine an author’s purpose Cognitive transfer of concepts Revise Differentiate Cite – Apprise Investigate Evidence Critique Compare Explain with Formulate Construct – Concepts Hypothesize Assess ProblemCite – Draw Solve Evidence Conclusions Argue Story element recall Mathematic calculations Map labeling Diagram relationships Measure objects Use punctuation Create descriptions Recall (Level 1) Graph Classify Separate Estimate Compare Relate Infer Can you explain how ___ affected ___ ? How would you compare ___ ? How would you contrast ___ ? How would you classify ___ ? What can you say about ___ ? When would you use an outline to ___ ? Skill / Concept (Level 2) Describe Explain Interpret Strategic Thinking (Level 3) How is ___ related to ___ ? How would you adapt ___ to create a different ___ ? Can you predict the outcome if ___ ? What would you use to support ___ ? Categorize Interpret Collect Distinguish Display Observations Organize Summarize Construct Show Modify Cause / Predict Effect Identify key events Summarize a story Use context to figure out word meaning Solve multi-step math problems Describe causes and effects Identify patterns Solve a problem Work with data Extended Thinking (Level 4) Create, test, and report on a hypothesis Apply an abstract model to a problem Use information from many sources Find similarities between different things Design an abstract model for a problem Using Webb's Depth of Knowledge to Increase Rigor (http://www.edutopia.org/blog/webbs-depth-knowledge-increase-rigor-gerald-aungst) Edutopia,. 'Using Webb's Depth Of Knowledge To Increase Rigor'. N. p., 2014. Web. 16 Dec. 2014. Write a research paper. Design and conduct an experiment. Apply information from one text to another to develop a persuasive argument. Design Connect Critique Create Analyze Prove Synthesize Apply – Concepts