The Sun is the source of most visible light.
advertisement

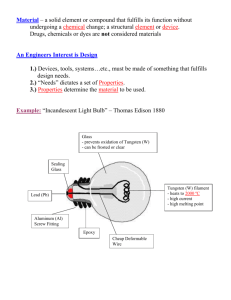
Page 1 of 5 KEY CONCEPT The Sun is the source of most visible light. BEFORE, you learned NOW, you will learn • Visible light is part of the EM spectrum • EM waves are produced both in nature and by technology • How visible light is produced by materials at high temperatures • How some living organisms produce light • How humans produce light artificially VOCABULARY THINK ABOUT incandescence p. 569 luminescence p. 569 bioluminescence p. 569 fluorescence p. 571 Why is light important? This railroad worm has eleven pairs of green lights on its sides and a red light on its head. The animal probably uses these lights for illumination and to frighten away predators. Almost every living organism, including humans, depends on visible light. Think of as many different ways as you can that plants, animals, and people use light. Then, think of all the sources of visible light that you know of, both natural and artificial. Why is light important to living organisms? Light comes from the Sun and other natural sources. RESOURCE CENTER CLASSZONE.COM Learn more about visible light. It is hard to imagine life without light. Human beings depend on vision in countless ways, and they depend on light for vision. Light is the only form of EM radiation for which human bodies have specialized sensory organs. The human eye is extremely sensitive to light and color and the many kinds of information they convey. Most animals depend on visible light to find food and to do other things necessary for their survival. Green plants need light to make their own food. Plants, in turn, supply food directly or indirectly for nearly all other living creatures. With very few exceptions, living creatures depend on light for their existence. check your reading 568 Unit 4: Waves, Sound, and Light How is plants’ use of light important to animals? Page 2 of 5 Most of the visible light waves in the environment come from the Sun. The Sun’s high temperature produces light of every wavelength. The production of light by materials at high temperatures is called incandescence (IHN-kuhnDEHS-uhns). When a material gets hot enough, it gives off light by glowing or by bursting into flames. Other than the Sun, few natural sources of incandescent light strongly affect life on Earth. Most other stars give off as much light as the Sun, or even more, but little light from stars reaches Earth because they are so far away. Lightning produces bright, short-lived bursts of light. Fire, which can occur naturally, is a lower-level, longerlasting source of visible light. The ability to make and use fire was one of the first light technologies, making it possible for human beings to see on a dark night or inside a cave. check your reading Why does little light reach Earth from stars other than the Sun? Some living things produce visible light. Many organisms produce their own visible light, which they use in a variety of ways. They produce this light through luminescence. Luminescence is the production of light without the high temperatures needed for incandescence. The production of light by living organisms is called bioluminescence. Bioluminescent organisms produce light from chemical reactions rather than from intense heat. Bioluminescence enables organisms to produce light inside their tissues without being harmed. VOCABULARY Don’t forget to make word frames for the terms luminescence and bioluminescence. Bioluminescent organisms include insects, worms, fish, squid, jellyfish, bacteria, and fungi. Some of these creatures have lightproducing organs that are highly complex. These organs might include light-producing cells but also reflectors, lenses, and even color filters. The firefly, a type of beetle, uses bioluminescence to attract mates. A chemical reaction in its abdomen allows the firefly to glow at specific intervals. The pattern of glowing helps fireflies of the same species identify each other at night. Most often, the male flashes a signal while flying, and the female responds with a flash. After they have identified each other, the fireflies may continue to exchange flashes until the male has located the female. Chapter 17: Electromagnetic Waves 569 Page 3 of 5 The process of bioluminescence is very efficient. Almost all of the energy released by the chemical reactions of bioluminescence is converted into light. Very little heat is produced. Researchers in lighting technology wanted for years to imitate this efficiency, and that became possible with the development of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LEDs produce little heat, converting almost all of the incoming electrical energy into light. `check your reading A female firefly responds to a male’s signal. How is bioluminescence different from incandescence? Human technologies produce visible light. Human beings invented the first artificial lighting when they learned to make and control fire. For most of human history, people have made light with devices that use fire in some form, such as oil lamps, candles, and natural gas lamps. After the discovery of electricity, people began to make light through a means other than fire. However, the technique of using a very hot material as a light source stayed the same until the invention of fluorescent lighting. In recent years, “cool” lighting has become much more common. Artificial Lighting Is all artificial light the same? Many types of artificial light sources are available. These sources differ in the amount of light they produce, the way the light beams are directed, and the characteristics of the light itself. SKILL FOCUS Designing experiments MATERIALS PROCEDURE 1 Design a procedure to discover and record differences among several different types of artificial lighting. Your procedure should test how different colored materials appear in different types of lighting. You should compare the results with how these materials appear in direct sunlight. 2 Write up your experiment and carry it out. WHAT DO YOU THINK? • What differences did you discover among bulbs of different types and sizes? • How would you improve your design if you were to repeat your experiment? 570 Unit 4: Waves, Sound, and Light Artificial lighting with a variety of bulb types and sizes TIME 30 minutes Page 4 of 5 Incandescent and Fluorescent Lighting The development of the electric light bulb in the late 1800s made light available at a touch. An ordinary light bulb is a sealed glass tube with a thin tungsten wire running through it. This wire is called a filament. When electrical current passes through the filament, the tungsten gets hotter and begins to glow. Because these light bulbs use high temperatures to produce light, they are called incandescent bulbs. Tungsten can become very hot—about 3500 degrees Celsius (6300˚F)—without melting. At such high temperatures, tungsten gives off a bright light. However, the tungsten filament also produces much infrared radiation. In fact, the filament produces more infrared light than visible light. As a result, incandescent bulbs waste a lot of energy that ends up as heat. At such high temperatures, tungsten also slowly evaporates and collects on the inside of the bulb. Eventually, the filament weakens and breaks, and the bulb burns out. check your reading SUPPORTING MAIN IDEAS List the characteristics of incandescent lighting and the different types that are available. What causes ordinary light bulbs to burn out? Since the 1980s, halogen (HAL-uh-juhn) bulbs have come into wide use. Halogen bulbs have several advantages over ordinary incandescent bulbs. They contain a gas from the halogen group. This gas combines with evaporating tungsten atoms and deposits the tungsten back onto the filament. As a result, the filament lasts longer. The filament can also be raised to a higher temperature without damage, so it produces more light. Halogen bulbs, which are made of quartz, resist heat better than glass. Incandescent Light Bulb tungsten filament Halogen Light Bulb tungsten filament Fluorescent Light Bulb mercury vapor and other gases halogen gas mixture phosphor coating quartz bulb glass bulb electric current electrode Many electric lights in use today are fluorescent. Fluorescence (flu-REHS-uhns) occurs when a material absorbs EM radiation of one wavelength and gives off EM radiation of another. Fluorescent bulbs are filled with a mixture of mercury vapor and other gases that give off ultraviolet light when an electric current passes through them. Chapter 17: Electromagnetic Waves 571 Page 5 of 5 The insides of the bulbs are coated with a powder called phosphor that fluoresces. Phosphor absorbs ultraviolet light and gives off visible light. Because fluorescent lighting is cool and does not waste much energy as heat, it is more efficient and more economical than incandescent lighting. check your reading LEDs are being used more and more in place of incandescent bulbs. Why are fluorescent lights more efficient than incandescent lights? Other Types of Artificial Lighting Like fluorescent lights, many other artificial light sources use a gas in place of a filament. For example, neon lights use gas-filled tubes to produce light. However, instead of ultraviolet light, the gas gives off visible light directly. The colors of neon lights come from the particular mixtures of gases and filters used. Vapor lights, which are commonly used for street lights, work in a similar way. In a vapor light, a material such as sodium is heated until it becomes a gas, or vapor. The vapor responds to an electric current by glowing brightly. One of fastest-growing types of artificial lighting is the light emitting diode, or LED. LEDs do not involve bulbs, filaments, or gases. Instead, they produce light electronically. A diode is a type of semiconductor—a device that regulates electric current. An LED is a semiconductor that converts electric energy directly into visible light. LEDs have many advantages over traditional forms of lighting. They produce a very bright light, do not break easily, use little energy, produce little heat, and can last for decades. Some technologists believe that LEDs will eventually replace most traditional forms of artificial lighting. KEY CONCEPTS CRITICAL THINKING 1. Describe natural, nonliving sources of incandescent light. 4. Classify Make a chart summarizing the different types of artificial lighting discussed in this section. 2. What advantages does bioluminescence have over incandescence as a way for living organisms to produce light? 3. What are some advantages and disadvantages of artificial incandescent lighting? 572 Unit 4: Waves, Sound, and Light 5. Infer Why do you think moonlight does not warm you, even though the Moon reflects light from the hot Sun? CHALLENGE 6. Compare and Contrast What does LED lighting have in common with bioluminescence? How are the two different?