EXPERIMENT 2: Shunt Wound Machine as a Motor
advertisement

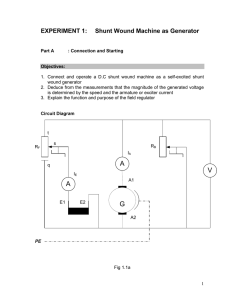
EXPERIMENT 2: Part A Shunt Wound Machine as a Motor : Connection and Starting Objectives: 1. Connect and operate a D.C shunt wound machine as a D.C shunt wound motor with and without starter 2. Measure the starting current and the armature voltages 3. Deduce that the starter reduces the starting Circuit Diagram 1. Without starter L+ A A1 E1 E2 V M A2 LPE Fig 2.1 1 L1 I 0 L2 L3 MOTOR PROTECTION SWITCH 3 POLE I DANGER 415 Volts ROTATION REVERSING SWITCH 1 W L3 0 V L2 2 U L1 L1 L2 L3 2 TORQUE Nm M OL n x1 x2 x3 CONTROL UNIT FOR MAGNETIC POWDER BRAKE CONTR. MODE BRAKE MOTORS min-1 REVOLUTIONS 0 Nm SET/START VALUE 0 min -1 X 1000 POWER R M STARTER 100W Ω A1 E1 A2 E2 L UAUSG 0 1 A2 M/G A1 START SE2662-3A E2 E1 ST7007-5A - + - + 2. With starter L+ A RA A1 E1 E2 V M A2 LPE Fig 2.1 Instrument/Component 1 D.C shunt wound machine 1 Magnetic powder brake 1 Control unit for brake 2 Rubber coupling sleeves 2 Coupling guard 1 Shaft end guard 1 Starter for D.C motors 1 Field regulator for D.C generators 1 Load resistance 2 Multimeter 1 Set of connection cables 3 Exercise 1. Copy the following detailed information from the ratings label of the D.C shunt wound machine, which apply when operated as a shunt wound motor: a) b) c) d) e) Type U I UE IE :………………………. :……………………….V :……………………….A :……………………….V :……………………….A 2. Connect the machine without starter, according to circuit diagram in Fig 2.1 3. Set the control unit as follows: a) Speed n b) Torque M c) Operating mode n = 3000 rpm = 1Nm = constant Range on multimeters a) Voltage b) Armature current, IA c) Exciter current, IE = 300 V =1A = 0.3 A 4. Operate the motor and set the torque on the control unit to M=0.3 Nm. Measure the starting current and the armature voltage. Enter the measured values into Table 2.1 5. Connect the machine with starter, according to circuit diagram in fig. 2.2. The settings on the control unit remain unchanged. Set the starting resistor to 100% (47 Ω) Measure the starting current and the armature voltage. Enter the measured values into Table 2.1 Starter Load Starter Current Ia (A) Armature Voltage UA (V) R = 0Ω M = 0.3 Nm R = 47Ω M = 0.3 Nm Table 2.1 Questions 1. What is the purpose of the starter? 4 Part B : Load Characteristics Objectives 1. Connect and operate a D.C shunt wound machine as a shunt wound motor for recording the load characteristics 2. Draw the load characteristic curve from the values obtained by measurement and by calculations 3. Deduce from the load characteristics that the motor is most efficient at its nominal speed and check the deduction by calculations 4. Describe the response of the shunt wound motor under various load conditions Circuit Diagram L+ A A A1 E1 E2 V M A2 LPE Fig 2.3 5 Instrument/Components 1 D.C shunt wound machine 1 Magnetic powder brake 1 Control unit for brake 2 Rubber coupling sleeves 2 Coupling guard 1 Shaft end guard 1 Starter for D.C motors 1 Field regulator for D.C generators 1 Load resistance 2 Multimeter 1 Set of connection cables Exercise 1. Connect the circuit diagram shown in Fig 2.3 2. Set the control unit as follows: a) Speed b) Torque c) Operating mode n M M = 3000 rpm = 1Nm = constant Range on multimeters a) Voltage b) Armature current, IA c) Exciter current, IE = 300 V =1A = 0.3 A 3. Operate the generator. Set the D.C power supply to 220V 4. Set the control unit to the torque values given in the table, commencing at 0.3 Nm. Measure the speed, armature current and the exciter current. Enter the values into table 2.2 below 5. Calculate the consumed electrical power P1 = UA x Itot Itot = IA + IE 6. Calculate the delivered mechanical power P2 = 2πMN/60 this simplify to P2 = M.N/9.55 7. Calculate the efficiency of the motor, η = P2 / P1 Enter the calculated values into the table 2.2 6 8. From the results, measured and calculated, plot the graph of the load characteristics. a) N (rpm) vs M (Nm) b) IA (A) vs M (Nm) c) P2 (W) vs M (Nm) d) ŋ vs M (Nm) 220 U (V) M (Nm) 0.3 0.5 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 N (rpm) IA (A) IE (A) Itot (A) P1 (W) P2 (W) ŋ Table 2.2 Question 1. From the characteristics result, describe the response of the speed of the motor under load condition. 2. State the best efficiency with the corresponding values of torque and speed 7