A battery is used to charge a parallel-plate capacitor, after which it is

Phys102 Term: 123 Online HW-Ch25-Lec02
Q1:
A battery is used to charge a parallel-plate capacitor, after which it is disconnected. Then the plates are pulled apart to twice their original separation. This process will double the:
A.
surface charge density on each plate
B.
stored energy
C.
capacitance
D.
charge on each plate
E.
electric field between the two plates
Ans:
B
Q2:
Given a 6.0 pF air-filled capacitor, you are asked to convert it to a capacitor that can store 30.0
µ J,
with a potential of 600 V. What is the dielectric constant of the material that you must insert between the plates of the capacitor?
Ans:
U =
1
2 C
′ V 2 =
1
2
κ CV 2
30.0 × 10 −6 =
1
2 ×
κ × 6 × 10 −12 × (600) 2
κ = 27.8
KFUPM-Physics Department 1
Phys102 Term: 123 Online HW-Ch25-Lec02
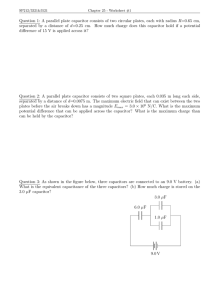
Q3:
A capacitor C
1
= 4.00
µ F
and another capacitor C
2
= 3.00
µ F
are connected in series across a 800 V supply line. The charged capacitors are disconnected from the supply line then reconnected to each other with terminals of like sign together. Find the final
Ans: charge on C
1
.
C
2
+
+
+ q
-
-
-
C eq
=
C
1
C
1
C
2
+ C
2
C
1
+
+
+ q
-
-
-
+
+
+ q
-
-
-
V
+
+
+
C
1
-
-
- q = C eq
V
0
=
C
1
C
1
C
2
+ C
2
× V
0
+
+
+
C
2
-
-
-
=
4 × 10 −6 × 3 × 10 −6
4 × 10 −6 + 3 × 10 −6
× 800 q = 1.37 × 10 −6 C so total charge on C
1
and C
2
is 2q when they are connected together, the potential difference across them is the same. q
1
C
1
= V q
2
C
2
= V so q q
1
1
C
1
= q
= q
2
C
2
2
C
2 also so q q
1
�
1 q
1
+ q
= (2q
1 +
C
C
2
1
�
2
C
1
= 2q ⇒ q
− q
1
) ×
= 2q ×
C
C
C
2
C
1
2
1 q
1
= 2q
2 C
1
C
2
+ C
2
2
= 2q
= 1.17 × 10 −3
−
C
q
1
KFUPM-Physics Department 2