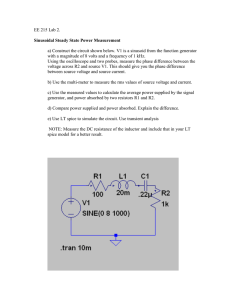
Chapter 1.nb

Physics 302/328 Homework
Chapter 1, #1,3,5,12,14,15,23,25,27,28
1.1 If 60 C of charge pass through an electric conductor in 30 seconds, determine the current in the conductor.
Solution: I = D Q/ D t = 60 C / 30 s = 2 C/s = 2 Amperes
1.3 If the current in an electric conductor is 1.5 A, how many coulombs of charge pass any point in a time interval of 1.5 minutes?
Solution: D Q = I D t = 1.5 C/s * 90 s
In[1]:=
Out[1]=
1.5
H Coulomb ê Second L * 90 Second
135. Coulomb
1.5 A lightning bolt carrying 20,000 A lasts for 70 microseconds. If the lightning strikes a tractor, what charge is deposited on the tractor it the tires are assumed to be perfect insulators?
Solution: D Q = I D t = 20,000 C/s * 70 m s
In[2]:=
20 000 H Coulomb ê Second L * I 70 * 10
6
Second M êê N
Out[2]=
1.4 Coulomb
2
1.12 Determine the missing quantity in the circuits below.
Chapter 1.nb
Solution: a) I = P/ V = 72 W / 24 V = + 3 b) P = 6 V * (-4 A) = - 24 (remember the passive sign convention?)
1.14 Determine the missing quantity in the circuits below.
Solution: a) I = P/ V = 12 W / (-6 V) = - 2 (Hint: redraw the circuit with the + sign at the top and V1
= +6V... The current must flow into the square box for P to be positive => I must be negative.) b) V = P / I = - (- 24 W) / (2 A) = -12 (Current entering the negative side of the square box, should produce negative power dissipated, according to the passive sign convention.
In this case, V * I = - P, V = - P / I.)
1.15 Two elements are connected in series, as shown below. Element 1 supplies 24 W of power. Is element 2 absorbing or supplying power, and how much?
Chapter 1.nb
1.15 Two elements are connected in series, as shown below. Element 1 supplies 24 W of power. Is element 2 absorbing or supplying power, and how much?
3
4 Chapter 1.nb
Solution:
Element 1 -> - 24 W of power => I = -24 W / 3 V = - 8 A. The current into the + terminal is -
8 A, which is equivalent to + 8 A going out of the + terminal.
This means that + 8 A is going into the + terminal of element 2. Element 2 is absorbing power (P is positive), and P = 6 V * 8 A = +48
1.23 Find the power that is absorbed or supplied by each of the circuit elements in the two circuits shown in the figure below.
Solution: a) P(voltage source) = 12V * (- 2 A) = - 24 W absorbed = + 24 supplied .
P(element 1) = 4 v * 2 A = + 8 absorbed
P(element 1) = 8 V * 2 A = + 16 absorbed.
Note that power absorbed = -24 W + 8 W + 16 W = 0 W
=> power absorbed = power supplied b) P(24 volt source) = 24V * (- 1 A) = - 24 W absorbed = + 24 supplied .
P(8 volt source) = 8 v * 1 A = + 8 absorbed
P(element 1) = 16 V * 1 A = + 16 absorbed.
Note that power absorbed = -24 W + 8 W + 16 W = 0 W
=> power absorbed = power supplied
1.25 Is the source V s
in the network below absorbing of supplying power, and how much?
Chapter 1.nb
1.25 Is the source V s and how much?
in the network below absorbing of supplying power,
5
6
Solution:
P(10 V element) = 10 V * (+3 A) absorbed = +30 absorbed
P(6 V element) = 6 V * 3 A = +18 absorbed
P(8 V element) = 8 V * 6 A = + 48 absorbed
P(current source) = 16 V * (-9 A) = 144 absorbed = +144 supplied
Adding up the powers: 30W + 18W + 48W + (-144W) = -48 W => the supply with V s absorbs +48 W.
Unknown supply: +48W / 6 A = +8 = V s
Chapter 1.nb
1.27 Find V x in the network shown below.
Chapter 1.nb
Solution:
In the next chapter, we will use Kirchhoff's currnet law to solve problems like this one. In this chapter, we will use power calculations.
12V (1 A) + 12 V (1 A) + 24 V (1 A) + 24 V(-4 A) + 16 V(2 A) + V x
V x
(2 A) = 0
7
1.28 Compute the power that is absorbed or supplied by each of the elements in the network shown below
Solution:
P(36 V) = 36 V (-4 A) = -144 W => +144 supplied.
P(element 1) = 12 V (4 A) = +48 absorbed
P(element 2) = 24 V (2 A) = +48 absorbed
P(element 3) = 28 V(2 A) = +56 absorbed
P(dependent source) = 4V (-2 A) = -8 W absorbed = +8 supplied .