Example: Analysis of a Complex Diode Circuit
advertisement

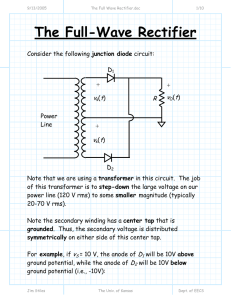
8/18/2005 Example_Analysis of a Complex Diode Circuit.doc 1/5 Example: Analysis of a Complex Diode Circuit Consider this circuit with two ideal diodes: 10.0 V + vDi 2 R1 =10K + iDi 1 vDi 1 − iDi 2 R2 =5K − -10.0 V Let’s analyze this circuit and find vDi 1 , iDi 1 , vDi 2 , and iDi 2 ! Remember, we must accomplish each of the five steps: Step 1: ASSUME that both D1 and D2 are “on” (might as well!). Step 2: ENFORCE the equalities vDi 1 = 0 = vDi 2 , by replacing each ideal diode with a short circuit. Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS 8/18/2005 Example_Analysis of a Complex Diode Circuit.doc 2/5 Step 3: ANALYZE the resulting circuit, and find iDi 1 and iDi 2 . + vDi 2 =0 − R1 =10K 10.0 V i i i D1 + vDi 1 =0 iDi 2 R2 =5K − -10.0 V Begin with KCL: i = iDi 1 + iDi 2 where i = and iDi 2 = Therefore, iDi 1 = Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS 8/18/2005 Example_Analysis of a Complex Diode Circuit.doc 3/5 Step 4: Now we must CHECK inequalities to see if our assumptions are correct! iDi 1 = iDi 2 = One assumption is therefore INCORRECT. We must proceed to step 5—change our assumptions and completely start again! Q: Wait a second! We don’t have to completely start from the beginning, do we? After all, our assumption about diode D2 turned out to be true—so we and already know that iDi 2 = vDi 2 = 0 , right? A: NO! The solution for diode D2 is dependent on the state of both diodes D1 and D2. If the assumption of just one diode turns out to be incorrect, then the solutions for all diodes are wrong! So, let’s change our assumption and start all over again! Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS 8/18/2005 Example_Analysis of a Complex Diode Circuit.doc 4/5 Step 1: Now ASSUME that D1 is “off” and D2 is “on”. Step 2: ENFORCE iDi 1 = 0 (D1 open) and vDi 2 = 0 (D2 short). Step 3: ANALYZE resulting circuit, and find vDi 1 and iDi 2 . 10.0 V + vDi 2 =0 − R1 =10K i + iDi 1 =0 iDi 2 vDi 1 R2 =5K − -10.0 V Note i = iDi 2 = and from KVL: ∴ vDi = Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS 8/18/2005 Example_Analysis of a Complex Diode Circuit.doc 5/5 4) CHECK our assumptions. iDi 2 = vDi 1 = ∴ Assumptions are correct! We are finished! Jim Stiles vDi 1 = iDi 1 = 0 vDi 2 = 0 iDi 2 = The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS