Common Emitter Amplifier Design & Simulation
advertisement

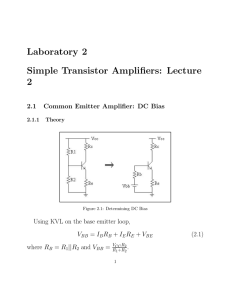
CHAPTER 8 COMMON EMITTER AMPLIFIER 8.1 Overview You will design, simulate, build the circuit, and measure the voltage gain of the amplifier. 8.2 Cadence Simulation 1. The specifications for the common-emitter amplifier are shown below gm =19.2 mS VRE =0.3 V I1 = 40IB VCC = 9V Vin,m = 10 mV 2. Assume that the 2N3904 transistor have a β = 150 and an IS of 6.734 fA. Electronics I Laboratory Manual, First Edition. c 2014 ,J. Ou. Copyright 41 42 COMMON EMITTER AMPLIFIER RC R1 + 9V − VCC 2N 3904 1kHz 100mVpp C1 R2 Vs RE Figure 8.1: Common-emitter amplifier 3. Determine IC from gm . gm = IC /VT (8.1) 4. Determine RE from the VRE specification. RE = VRE /IC 5. Calculate VBE . (8.2) IC ) IS (8.3) VB = VBE + VRE (8.4) VBE = VT ln( 6. Calculate the voltage at VB . 7. Determine IB from β and IC . 8. Determine I1 given IB . 9. Determine R1 + R2 from VCC and I1 . I1 = VCC /(R1 + R2 ) (8.5) 10. Determine R2 from VB . VB = R2 VCC R1 + R2 11. Determine R1 from R1 + R2 and R2 . (8.6) IMPLEMENTATION 43 12. Choose RC so as to have a collector voltage of VCC /2. VCC − RC IC = VCC /2 (8.7) 13. Design the value of coupling capacitor so that the impedance of the capacitor is less than 5 Ohms. 1 | (8.8) |Zc | = | ωC1 14. Calculate the gain of the amplifier. AV = − RC 1/gm + RE (8.9) 15. Simulate the circuit in Cadence. 16. Submission checklist A table summarizing calculated and simulated values of IC , VBE , VB , IB , I1 , VRE , and AV . Simulated Vin and Vout . 8.3 Implementation 1. Build the circuit in the lab. 2. Measure the current in the RC by dividing VRC by RC . 3. Measure the DC voltage at the base of the transistor. 4. Measure VRE 5. Measure the peak-to-peak voltage of Vin and Vout on the oscilloscope. 6. Submission checklist A table summarizing simulated and measured values of IC , VBE , VB , IB , I1 , VRE , and AV . Measured plots of Vin and Vout (hint: save the oscilloscope image onto a USB drive).