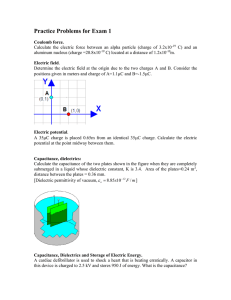
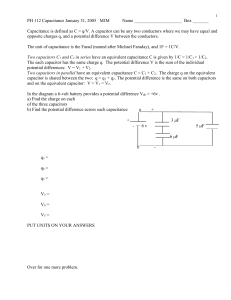
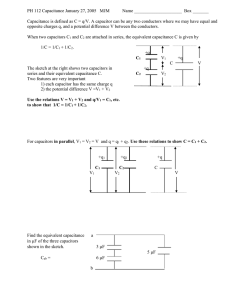
Capacitance, C (F) - Norwell Public Schools
advertisement

Capacitance Notes March 20 Today: • Questions re: text Q's/P's • Questions re: Electrostatics Problems 5 • Capacitance, C (F) • HW for Friday: Online Honors Physics 1 Capacitance Notes Honors Physics March 20 2 Capacitance Notes March 20 Capacitor: A device that stores energy by holding a net charge at a certain voltage. Most common type is referred to as a "parallel-plate capacitor". Capacitors have a lot of applications in modern electronics; just about any physical button (e.g., on a remote control) has a capacitor that governs its function. Honors Physics 3 Capacitance Notes March 20 Capacitance, C (F): Any capacitor has a Capacitance, C, that describes the amount of charge it can store for a certain voltage. By definition, C=Q V where Q is the amount of charge it will store (note: a capacitor stores an equal amount of + and - charge, so the overall net charge is zero; Q is the amount of + and - charge it holds), and V is the voltage difference across the two plates. The unit of Capacitance is the Farad (F), named for Michael Faraday. A capacitance of 1 F means the capacitor will hold 1 C (a huge amount) of charge at a voltage of 1 V (less than a AAA battery). Most capacitors are micro-Farad (E-6 F) or nano-Farad (E-9 F). Honors Physics 4 Capacitance Notes March 20 Example 1: When a certain capacitor is connected to a 12 V potential, it can store 2.4 E-10 C of charge. What is its capacitance? Example 2: A 3 E-8 F capacitor is connected to a 6 V potential. How much charge will it store? Example 3: What voltage is required to store 6 E-10 C of charge on a 3 E-9 F capacitor? Honors Physics 5 Capacitance Notes March 20 Parallel-plate capacitors: The most common form of capacitor is a parallelplate capacitor. It features two parallel plates (pieces) of metal that are separated by a distance d (m). The two plates generally have the same surface area A (m2). For this, we can determine the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor based solely on geometry: with representing the "Dielectric Constant", and representing the "Permittivity of Free Space", a constant equal to 8.85 E-12 C2/Nm2. The term "Dielectric" refers to an insulator; essentially, if you slip an insulator between the two parallel plates, you will improve its ability to hold charges; in effect, you increase its capacitance. Honors Physics 6 Capacitance Notes March 20 Example: A parallel plate capacitor is formed from plates with a surface area of 0.0025 m2 that are separated a distance of 0.005 m. If there is only air between the plates (dielectric constant = 1), what is the capacitance of these plates? If connected to a 20 V power source, how much charge would be stored on the plates? What is the strength of the Electric Field between the plates? Honors Physics 7