Getting to Know: Electricity and Magnetism Relationship
advertisement

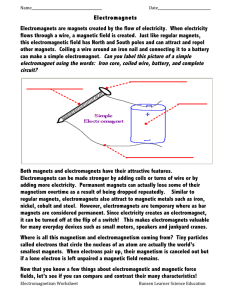
Getting to Know: Electricity and Magnetism Relationship On the bus ride to school, you may enjoy listening to some of your favorite music through your headphones. You might be surprised to learn that the speakers in your headphones work because of the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Tiny magnets inside a speaker make the speaker vibrate as the magnetic field in the speaker changes. The vibrations of the speaker create sound waves that travel to your ears. So, how does the magnetic field inside the speaker change? That is the work of devices called electromagnets. Electromagnets use electricity to create a magnetic field and are used for many functions. For example, electromagnets are used in doorbells, garage door openers, electric cars, and trains. They are also used in all sorts of electric motors and generators. Speakers, like the ones inside headphones, contain electromagnets. How do electromagnets work? In general, electric current is the movement of charged particles through a conducting wire. The flow of electric current through a wire creates a magnetic field around the wire. If the wire is wrapped around a metal core, the magnetic field created by the flowing current strengthens. A simple electromagnet is a wire wrapped around a metal core that is connected to a power supply. When electricity flows through the wire, the metal core becomes magnetized. I understand how electromagnets make tiny headphones work. How can they make an entire train move? Electromagnets can vary greatly in strength. The electromagnets inside electric trains are much stronger than the electromagnets inside your headphones. Misconception 1: I get it! The larger the electromagnet, the stronger it is. That’s why electromagnets in trains are so much stronger than the ones in headphones. That’s not quite correct. Electromagnets come in different sizes and strengths, but the two properties are not always directly related. Stronger electromagnets have a stronger magnetic field. They are not necessarily larger than weaker electromagnets. Two electromagnets of the same size can differ in strength. Concept: Electricity and Magnetism Relationship Getting to Know www.discoveryeducation.com 1 © Discovery Education. All rights reserved. Discovery Education is a subsidiary of Discovery Communications, LLC. What factors affect the strength of an electromagnet? We can change the strength of an electromagnet by changing the number of wire loops wrapped around the metal core. More loops produce a stronger magnetic field. Fewer loops produce a weaker magnetic field. The voltage supplied to the electric current in the system also affects the strength of an electromagnet. For example, you can produce a stronger electromagnet by using a higher- voltage battery. What is a generator? The number of times wire is wrapped A generator is a device that uses magnets around the core changes an electromagnet’s strength. to produce an electric current. Recall that with electromagnets, electric current flows through a wire and creates a magnetic field around the wire. For a generator, the opposite is true; a magnet that moves next to a wire causes electric current to flow through the wire! This electrical current is carried through large wires from large generators in a power plant all the way to your home and school and then through smaller wires to the outlets inside. Misconception 2: An object can become positively charged if its electrons are destroyed, right? No, charge is never created nor destroyed. If an object becomes positively charged, it is because electrons have been transferred away from it. Misconception 3: Electricity can produce a magnetic field, but magnetism can’t really create an electric current. Actually, a magnetic field really can create an electric current! A moving magnetic field can cause electrical charges to flow inside a wire, creating electrical current. This is how power plants change the energy of spinning turbines into electricity. In most power plants, generators produce large amounts of electricity by spinning a long coil of wire around a strong magnet. The kinetic energy used to spin the wire may come from wind energy, the energy of flowing water, nuclear energy, or energy from burning fossil fuels. You will learn much more about the workings of electromagnets and generators as you explore the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Concept: Electricity and Magnetism Relationship Getting to Know www.discoveryeducation.com 2 © Discovery Education. All rights reserved. Discovery Education is a subsidiary of Discovery Communications, LLC.