WHAT DO THE LIGHT BULBS DO? Section 3: SUMMARY
advertisement

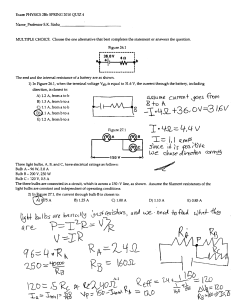
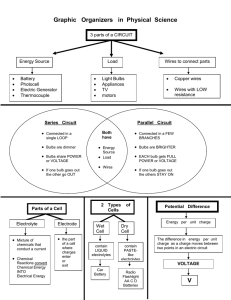
Name_____________________________ Date ________________ Hour _____ WHAT DO THE LIGHT BULBS DO? Section 3: SUMMARY 1. a. Does a light bulb filament control the amount of charge that passes through it or the rate at which charge flows? Rate b. What is your evidence? The amount of charge the capacitor stored/discharged was the same regardless of type of light bulb (or if any light bulb was) present in the circuit. The compass deflection however was different for each type of light bulb thus showing a different flow rate of charge. 2. a. Does the amount of charge stored in a charged capacitor depend on the type of bulbs through which it was charged? No b. What is your evidence? The behavior (brightness, light time) of the bulbs in a discharging capacitor circuit was the same regardless if it was charged with long, round or no bulbs. 3. Diagram the minimum parts of a circuit needed to charge a capacitor. Battery, two wires, and a capacitor. 4. a. Draw a complete circuit showing three bulbs in series. Connected loop with batteries, wires and 3 bulbs. No branches. b. What happens to the charge flow rate in a circuit as more bulbs are added in series? The charge flow rate decreased as more bulbs (resistance) were added. c. What is your evidence? The light bulbs got dimmer and the compass deflection decreased when more bulbs were added. 5. a. Draw a complete circuit showing three bulbs in parallel. Batteries connected with wires to 3 bulbs in branches (looks like a ladder) b. What happens to the charge flow rate of charge in a circuit as more bulbs are added in parallel? The charge flow rate increases as each bulb is added. c. What is your evidence? As more bulbs are added in parallel, the compass deflection increases. d. Why does this happen? Resistance in the circuit decreases 6. Suppose that a charged capacitor were discharged through each of the following combinations of bulbs: • a single long bulb • two long bulbs in series • two long bulbs in parallel Without doing the experiment, predict in which case the bulbs would be lit for: a. the longest time. Explain your reasoning Two long bulbs in series. We saw in lab that the series circuit increases resistance as its compass deflection is lower. b. the shortest time. Explain your reasoning Two long bulbs in parallel. We saw in lab that the round bulbs with low resistance light for the shortest time. Of the three options the lowest resistance scenario would be a parallel circuit. Compass deflection increases with every bulb added in parallel. Large deflections correspond to low resistance and high flow rate. 7. Given three of the same kind of bulbs, how could you combine them to get a. the maximum total resistance? Draw the circuit. Series b. The minimum total resistance? Draw the circuit. Parallel 8. Given two round bulbs and two long bulbs, how could you combine them to get: a. the maximum total resistance? All four bulbs in series b. the minimum total resistance? All four bulbs in parallel 9. State below as many facts about each of the following that you have concluded in this electricity unit. a. light bulbs Affect rate and not amount of charge. Provides resistance in a circuit. b. series circuits Loop. Increase number of resistors, decrease flow rate and increase resistance. c. parallel circuits Branches or ladder. Increase number of resistors, flow rate increases. d. wires Path in which charge can flow. Contains charge that a battery/gencon/capacitor can move or push.