Technical-, Ordering Data, Linear Guides Loads | Calculation
advertisement
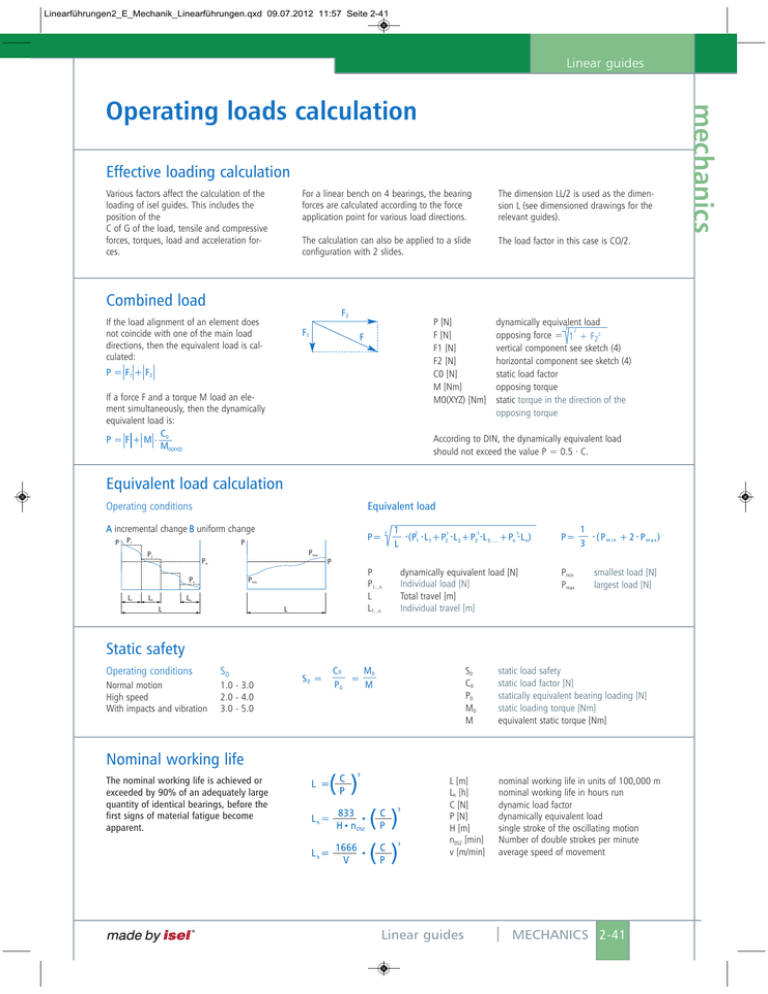
Linearführungen2_E_Mechanik_Linearführungen.qxd 09.07.2012 11:57 Seite 2-41 Linear guides Effective loading calculation Various factors affect the calculation of the loading of isel guides. This includes the position of the C of G of the load, tensile and compressive forces, torques, load and acceleration forces. For a linear bench on 4 bearings, the bearing forces are calculated according to the force application point for various load directions. The dimension LL/2 is used as the dimension L (see dimensioned drawings for the relevant guides). The calculation can also be applied to a slide configuration with 2 slides. The load factor in this case is CO/2. Combined load F2 If the load alignment of an element does not coincide with one of the main load directions, then the equivalent load is calculated: F1 P [N] F [N] F1 [N] F2 [N] C0 [N] M [Nm] M0(XYZ) [Nm] F P = F 1 + F2 If a force F and a torque M load an element simultaneously, then the dynamically equivalent load is: C P=F+M. 0 M0(XYZ) dynamically equivalent load F 2 opposing force = 1 + F22 vertical component see sketch (4) horizontal component see sketch (4) static load factor opposing torque static torque in the direction of the opposing torque According to DIN, the dynamically equivalent load should not exceed the value P = 0.5 . C. Equivalent load calculation Equivalent load Operating conditions A incremental change B uniform change P P1 3 1 . 3. 3 3 3 (P1 L 1+P2 . L 2+P3 . L 3.....+Pn . L n) L P= 1 . ( Pm i n + 2 . Pm a x ) 3 Pmax. P2 Pm P Pn L1 P= P P P1...n L L1...n Pmin. Ln L2 L L dynamically equivalent load [N] Individual load [N] Total travel [m] Individual travel [m] Pmin Pmax smallest load [N] largest load [N] Static safety Operating conditions S0 Normal motion High speed With impacts and vibration 1.0 - 3.0 2.0 - 4.0 3.0 - 5.0 S0 = M0 C0 = P0 M S0 C0 P0 M0 M static load safety static load factor [N] statically equivalent bearing loading [N] static loading torque [Nm] equivalent static torque [Nm] Nominal working life The nominal working life is achieved or exceeded by 90% of an adequately large quantity of identical bearings, before the first signs of material fatigue become apparent. made by isel ® L [m] Lh [h] C [N] P [N] H [m] n0SZ [min] v [m/min] Linear guides nominal working life in units of 100,000 m nominal working life in hours run dynamic load factor dynamically equivalent load single stroke of the oscillating motion Number of double strokes per minute average speed of movement MECHANICS 2-41 mechanics Operating loads calculation Linearführungen2_E_Mechanik_Linearführungen.qxd 09.07.2012 11:57 Seite 2-42 mechanics Linear guides Operating loads calculation Load vertical on the bench surface Loading Dimensioned figure Load on a trolley F F F P1= F F L1 F L2 + + 4 2L 2a P2= F 4 2 P3= F F L1 + 4 2L F L2 2a 4 P4= F 4 F L1 2L F L2 2a P2 P4 L a P1 P3 L a 1 F L2 3 L1 F L1 F L2 + 2L 2a Load in direction of motion Loading Dimensioned figure Load on a trolley F F L6 P2 F Pt1 P1 Pt3 Pt1 P PPPt1t1t1t1 PPt1 Pt1 Pt2 P3 t1 P4 Pt4 Pt2 Pt2Pt4 PP Pt2t2t2 Pt4 Pt2Pt2 PPt2P Pt4t4t4 PPt4 Pt4 a L P1 ... P4 = F L6 2L Pt1 ... Pt4= F L5 2L F t4 L5 1 2 3 4 Load at right angles to the direction of motion Loading Dimensioned figure F Load on a trolley F L4 P1 F Pt1 P3 P2 PPt33 P4 P3 Pt3 PPPP3 33 P Pt2 P3 3 3 P Pt44 Pt3 PP Pt3t3t3 PP4 Pt3Pt3 Pt3 Pt4 PPP4 44 P P4 4 4 Pt4 PP Pt4t4t4 Pt4Pt4 Pt4 2-42 MECHANICS a P1 ... P4 = F L4 2a L L3 F Linear guides 1 2 3 4 Pt1=Pt3= F 4 F L3 2L Pt2=Pt4= F 4 F L3 2L made by isel ®