Discussion 6 Notes: Common Gate Amplifier (10/22/05) 1. Draw the
advertisement

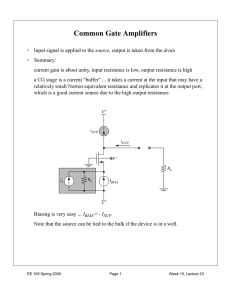
Discussion 6 Notes: Common Gate Amplifier (10/22/05) 1. Draw the DC biased Common Gate (CG) Amplifier as in Fig 8.38a, page 513 2. Discuss the skills of drawing small-signal model of the circuit as in Fig 8.39, page 514 • Meaning of constant voltage and current source in small signal circuit (grounded and open circuit respectively. Why? No change of voltage and current at those nodes!) • Discuss the orders of magnitude of gm, gmb, ro , roc, RL, RS (gm = 10 gmb, gm ~ 1mS, ro ~1MΩ , ro << roc (because we can use cascade etc. for current source), RL =>0 RS => inf for current amp and RL =>inf RS => 0, for voltage amplifier) • Discuss the meaning of gmb (change VSB => change VT h => change ID) 3. Draw the small signal circuit for deriving AV = vout / vin . Don’t have to derive. Reinforce the concepts of drawing small signal circuits and also the definition of AV. Remember to include series RS and parallel RL. Give the answer: AV = (RL//roc//ro )(gm+gmb+1/ro )/(1+RS(gm+gmb+1/ro ) (RL//roc//ro )/(RL//roc)). Simplification: Let Rs=>0, RL=> inf, also 1/ro << gm, roc >> ro AV = roc (gm+gmb) (This simplified version has been derived in Lecture note) 4. Another way to find AV • AV = vout /vin = (vout /iout ) (iout /iin ) (iin /vin ) (what are these? Rout AI 1/Rin ) • So, we have to find Rout, AI and Rin • We know that the CG amplifier is a unity current gain amplifier if everything is ideal. Therefore, we can model it as the 2-port network shown in Fig. 8.42, page 517 (Draw the circuit, don’t give the exact value of Rin and Rout yet) • Apply a current source (with RS in parallel) and parallel RL as the output, find AI = iout /iin . • Apply current divider concept and get AI = RS/(Rin +RS) * Rout / (Rout + RL) • Find Rin and Rout . Draw both Figures 8.41 and 8.40. Explain the definitions and when RS, RL have to be attached. • Both derived in lecture note already. But repeat either one of them to reinforce the concept and show them the skill of derivation. (KCL, KVL) • Rin = (1+(roc//RL)/ro )/(1/ro +gm+gmb) ~ 1/(gm+gmb) (which approximations have we used?) • Rout = roc// (R S (ro /RS + gmro + gmbro +1)) ~ roc // (ro (1+gmRs)) 5. Finding AV: • AV = Rout /Rin * RS/(Rin +RS) * Rout / (Rout + RL) • Substitute Rout and Rin into AV Use the assumption we used to derive AV (Let Rs=>0, RL=> inf, also 1/ro << gm, roc >> ro ), AV = roc (gm + gmb) 6. The second method provides another path to calculate AV. This is especially useful when we are only interested in approximated values.