The magnetic force on a charged particle
advertisement

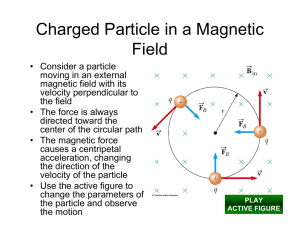
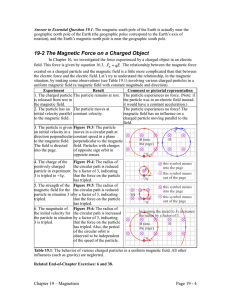
The magnetic force on a charged particle 1) depends on the sign of the charge on the particle. 2) depends on the velocity of the particle. 3) depends on the magnetic field at the particle's instantaneous position. 4) is at right angles to both the velocity and the direction of the magnetic field. 5) is described by all of these. Electric Force: FE qE Magnetic Force: FB qv B Figure 27.17 Cyclotron motion • Radius of orbit mv R qB • Period – time for one complete orbit. 2 R v T Velocity Selector Figure 27.21a Mass Spectrometer mv r qB Figure 27.33 A positively charged particle moves with speed v in the positive x direction. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude B exists in the negative z direction. You want to balance the magnetic force with an electric field so that the particle will continue along a straight line. The electric field should be in the 1) positive x direction. 2) positive z direction. 3) negative y direction. 4) negative x direction. 5) negative z direction. Currents in Magnetic Fields • Current: I qnvd A FB qv B – Each charge q feels a magnetic force: – Force on a wire segment of length dl is the force on all of the charges in that segment: dQ qn(Vol ) qn( Adl ) dF dQv d B qn( Adl ) v d B Idl B A current I flows in a wire that is oriented as shown. Which of the vectors represent the magnetic field that results in a maximum force on the wire?