Unit 5 – Resistors
advertisement

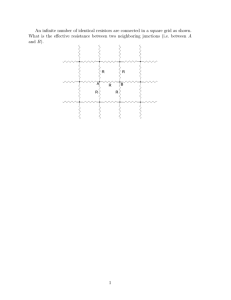
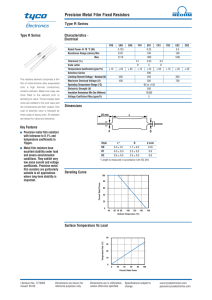
DELMAR’S Standard Textbook of Electricity - 5th Edition Unit 5 – Resistors 1) Uses of Resistors a) Limit the flow of current in a circuit b) Form a voltage divider network 2) Fixed Resistors a) One ohmic value which cannot be varied i) Determined at the time of manufacture b) Types i) Carbon composition (1) Inexpensive (2) Available in a wide range of values (a) < 1 Ω - 22 MΩ (b) Power ratings 1/8 – 2 Watts (3) Change value over time or if overheated (4) Tolerance 10% - 20% ii) Metal film (1) Resistance determined by the type of metal used to form the film and its thickness (2) Capable of high tolerance .1% - 2% (3) Stable (4) More expensive iii) Carbon film (1) Less expensive than metal film (2) Better tolerance than carbon composition 5% iv) Metal glaze (1) Similar to metal film (a) Metal combined with glass (2) High tolerance 1% - 2% v) Wire-wound Notes (1) Resistance determined by: (a) Wire material (b) Diameter of the wire (c) Length of the wire (2) Capable of high power operation 5W - >200W (3) Disadvantages (a) Physically large (b) More expensive (c) Because of the coiled construction cannot be used in high frequency circuits (i) Added inductance (d) Relatively low tolerance 3) Color Code a) 4-band color code b) 5-band color code 4) Standard Resistance Values of Fixed Resistors 5) Power Ratings a) Ohm’s Law describes the relationship of voltage, current, and power for a resistor i) P = IE, P = E2/R, P = I2R ii) If exceeded, resistor will be damaged 6) Variable Resistors a) Ohmic value can be changed or varied over a range b) Potentiometer i) Fixed resistive track with a movable contact ii) May be linear or logarithmic response c) Typically carbon – low power applications or wire-wound for higher power applications d) May be available as a multi-turn device for precision adjustment e) Potentiometers vs. rheostats i) Potentiometer – Three terminals ii) Rheostat – two terminals (1) A potentiometer can be configured as a rheostat by connecting the wiper to one end of the resistive track 7) Schematic Symbols a) Fixed resistor b) Variable resistor i) Potentiometer ii) Rheostat