Digital Multimeter (DMM) and Resistor Color Code
advertisement
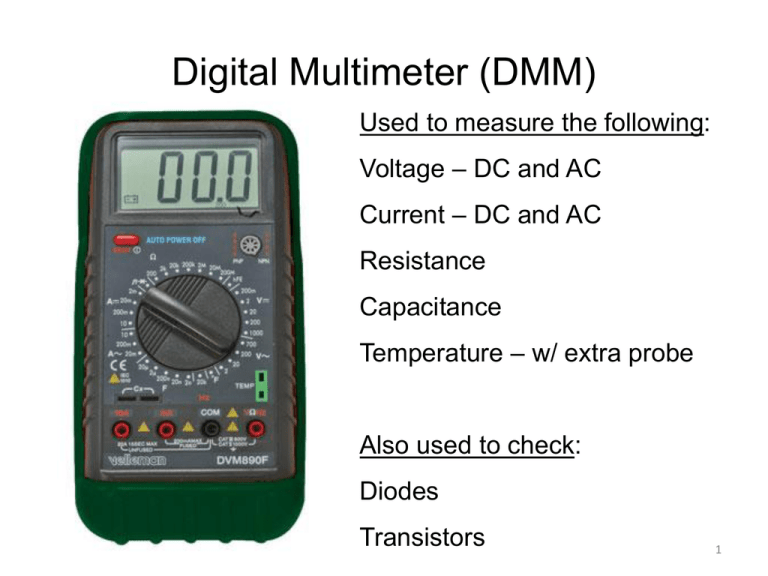
Digital Multimeter (DMM) Used to measure the following: Voltage – DC and AC Current – DC and AC Resistance Capacitance Temperature – w/ extra probe Also used to check: Diodes Transistors 1 We’ll Use the DMM to Measure Resistance • Resistors restrict the flow of current, given a fixed voltage • Unit = Ohms, Ω • They come in different packages 2 Color Code • The resistors we’ll test have a color code to identify their resistance and tolerance. 3 Resistor Color Band Code Band 1 (closest to the end) – first digit Band 2 – second digit Band 3 – power of ten multiplier (most cases simply the number of zeros) Band 4 – tolerance (Red = 2%, Gold = 5%, Silver = 10%, none = 20%) Color Value Color Value Black Brown Red Orange Yellow 0 1 2 3 4 Green Blue Violet Gray White 5 6 7 8 9 4 What is “Tolerance” about? • If a resistor has a nominal value of 1000 Ω and a tolerance of ± 10 % then individual resistors with the same nominal value are allowed to vary in their actual values from 900 Ω to 1100 Ω and still be considered acceptable. • Any resistor fabricated with an actual value outside that range should be rejected as “not meeting specifications”. 5 Practice Problems Determine the nominal value of resistance and the tolerance for resistors having the following color codes. • Brown Green Red Silver • Yellow Violet Orange Gold • Red Red Red Determine the color code to specify each of the following resistors • 1 kΩ • 390 kΩ • 56Ω 6