iClicker Questions
advertisement

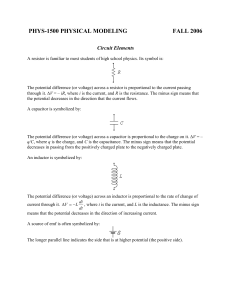
Clicker Question An inductance L and a resistance R are connected to a source of emf as shown. When switch S1 is closed, a current begins to flow. The final value of the current is A. directly proportional to RL. B. directly proportional to R/L. C. directly proportional to L/R. D. directly proportional to 1/ (RL). E. independent of L. Clicker Question An inductance L and a resistance R are connected to a source of emf as shown. When switch S1 is closed, a current begins to flow. The time required for the current to reach one-half its final value is A. directly proportional to RL. B. directly proportional to R/L. C. directly proportional to L/R. D. directly proportional to 1/(RL). E. independent of L. Clicker Question An inductance L and a resistance R are connected to a source of emf as shown. When switch S1 is closed, a current begins to flow. The time required for the current to reach one-half its final value is A. directly proportional to RL. B. directly proportional to R/L. C. directly proportional to L/R. D. directly proportional to 1/(RL). E. independent of L. Clicker Question Which curve shows the voltage drop across the inductor after S1 is closed and S2 is opened? A V(t) B C tswitch t D Clicker Question Which curve shows the voltage drop across the inductor after S1 is closed and S2 is opened? A V(t) B C tswitch t D Clicker Question Which curve shows the voltage drop across the Resistor after S1 is closed and S2 is opened? A V(t) B C tswitch t D Clicker Question Which curve shows the voltage drop across the Resistor after S1 is closed and S2 is opened? A V(t) B C tswitch t D Clicker Question After reaching a steady current, S1 is opened and S2 is closed, simultaneously. What curve shows the voltage drop across the resistor vs. time? A V(t) B C tswitch t D Clicker Question After reaching a steady current, S1 is opened and S2 is closed, simultaneously. What curve shows the voltage drop across the resistor vs. time? A V(t) B C tswitch t D Clicker Question After reaching a steady current, S1 is opened and S2 is closed, simultaneously. What curve shows the voltage drop across the resistor vs. time? A V(t) B C tswitch t D Clicker Question After reaching a steady current, S1 is opened and S2 is closed, simultaneously. What curve shows the voltage drop across the inductor vs. time? A V(t) B C tswitch t D Clicker Question After reaching a steady current, S1 is opened and S2 is closed, simultaneously. What curve shows the voltage drop across the inductor vs. time? A V(t) B C tswitch t D Figure 30.15 Clicker Question Right after switch S is closed, what will be the potential difference across the capacitor? A) 0 B) C) D) E) ε ε R2/(R1+ R2) ε /2 ε R1/(R1+ R2) Clicker Question Right after switch S is closed, what will be the potential difference across the capacitor? A) 0 B) C) D) E) ε ε R2/(R1+ R2) ε /2 ε R1/(R1+ R2) Clicker Question A long time after switch S is closed, what will be the charge on the capacitor? A) 0 B) Cε C) D) ε/C Cε /2 E) C/R2 Clicker Question A long time after switch S is closed, what will be the charge on the capacitor? A) 0 B) Cε C) D) ε/C Cε /2 E) C/R2 Table 30.1 Clicker Question An inductor (inductance L) and a capacitor (capacitance C) are connected as shown. If the values of both L and C are doubled, what happens to the time required for the capacitor charge to oscillate through a complete cycle? A. It becomes 4 times longer. B. It becomes twice as long. C. It is unchanged. D. It becomes 1/2 as long. E. It becomes 1/4 as long. Clicker Question An inductor (inductance L) and a capacitor (capacitance C) are connected as shown. If the values of both L and C are doubled, what happens to the time required for the capacitor charge to oscillate through a complete cycle? A. It becomes 4 times longer. B. It becomes twice as long. C. It is unchanged. D. It becomes 1/2 as long. E. It becomes 1/4 as long. Clicker Question An inductor (inductance L) and a capacitor (capacitance C) are connected as shown. The value of the capacitor charge q oscillates between positive and negative values. At any instant, the potential difference between the capacitor plates is A. proportional to q. C. proportional to d2q/dt2. E. all of A, B, and C. B. proportional to dq/dt. D. both A and C. Clicker Question An inductor (inductance L) and a capacitor (capacitance C) are connected as shown. The value of the capacitor charge q oscillates between positive and negative values. At any instant, the potential difference between the capacitor plates is A. proportional to q. C. proportional to d2q/dt2. E. all of A, B, and C. B. proportional to dq/dt. D. both A and C.