Capacitance Exercise: Series & Parallel Capacitors

CAPACITANCE EXERCISE
COMBINATION OF CAPACITORS
1.
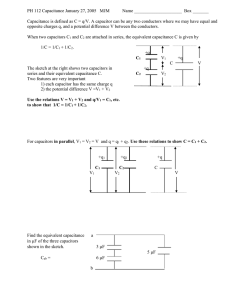
In this exercise you are to find the voltage across each capacitor and the charge on each capacitor in the circuit below.
Use V = 12 volts, C
1
= 3
μ
F, C
2
= 2
μ
F, and C
3
= 4
μ
F.
1.1.
Before solving the problem, answer the following:
(a) Do you expect the voltages across each capacitor to be the same?
Are there any capacitors that you know will have the same voltage across them?
Solution:
Parallel capacitors have the same voltage V – here C
2
and C
3
are parallel.
(b) Do you expect the charges on each capacitor to be the same?
Are there any capacitors that you know will have the same charge?
Solution:
Series capacitors have the same charge q – here C
1
and C p
, the equivalent capacitor for C
2
and C
3
, are in series.
1.2.
Draw a simplification of the circuit by reducing the parallel combination of C
2
and C
3
to a single capacitor C p
.
What is the value of C p
?
Solution:
2 3
6
1.3.
Now, are the charges the same on C
1
and C p
?
What about the voltages?
Solution:
As stated above – the charges are, but not the voltages.
1.4.
Now reduce the series combination C
1
and C p
to the equivalent C s
.
Find C s
and redraw the simplified circuit.
Solution:
1
1
1
thus
1
·
1
or
1
·
1
3·6
3 6
18
9
2
1.5.
Find the charge on C s
using Q = CV.
Explain why this is the same as the charge on C
1
and C p
.
Solution: capacitor C s
.
24
‐ the charge on the series capacitors C
1
and C p
is the same as on the equivalent
1.6.
Use the relationship V = Q/C to find the voltages across C
1
and C p
.
Is V
1
+ V p
= 12 volts?
Solution:
8 and 4
Yes, V
1
+ V p
= 12 V.
1.7.
Use the relationship Q = CV to find the charges on C
2
and C
3
.
Does Q
2
+ Q
3
= Q s
?
Solution:
2
2
2 · 4
Yes, Q
2
+ Q
3
= Q s
.
8
and
4 · 4 16
CAPACITOR CONNECTED TO A SPRING
2.
Consider an air ‐ filled parallel ‐ plate capacitor with one plate (labeled a ) connected to a spring having a force constant k , and another plate ( b ) held fixed as shown in the figure .
If the charges placed on plates a and b are + Q and ‐ Q , respectively, how much does the spring expand from the position
( x 0 ) with no charges present?
Hint: What is the electric field generated by the charges on plate b ?
Solution:
The spring force F acting on plate a is given by
F
The electrostatic force F due to the electric field created by plate b is:
F for the total electric field in the capacitor we found E
=
σ
ε
0 this can be viewed as the sum of the fields from plate a and b :
=
Q
ε
0
A
(where A is the area of the plate)
as both plates contribute equally we have 2 or result as one would get for a single plate with charge Q and area A).
With this we get: F
Q
2
ε
0
A
(which is the same
In equilibrium the two forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction thus:
or
2
CAPACITOR NETWORK
3.
Evaluate the equivalent capacitance of the configuration shown in the figure.
All the capacitors are identical, each with a capacitance C.
Solution:
First calculate the equivalent capacitance of the capacitors connected in series:
C
C
C
C
C
C
, and
2
those are connected in parallel to give the total equivalent capacitance
3
6 3 2
6
11
6
IMPOSSIBLE NETWORK
C 2C
4.
Determine the equivalent capacitance of the combination of capacitors shown in the figure.
Hint: You will have to take advantage of the symmetry of the problem!
3C
C 2C
Solution:
Based on the symmetry of the problem the voltage drop over the two capacitors with capacitance C is the same.
Similarly the voltage drop over the two capacitors with capacitance 2C is the same.
This means that the potential at both ends of the capacitor with capacitance 3C is the same – or in other words, there is no potential difference across the capacitor with capacitance 3C!
Therefore this capacitor does not add to
the total capacitance of the circuit – there are no charges on it.
Therefore the circuit is equivalent to the following circuit:
C 2C
C 2C
For which one can easily calculate the equivalent capacitance:
or
These two equivalent capacitances are connected in parallel to give the overall equivalent capacitance:
4
3
SPHERICAL CAPACITOR
5.
A conducting solid sphere of radius a, carrying a charge +Q is surrounded by a thin conducting spherical shell with radius b (b>a) carrying a charge of –
Q.
This is a spherical capacitor.
a b a) What is the direction and magnitude of the electric field in the following regions:
+Q
1.) r<a 2.) a<r<b and 3.) r>b
Solution: ‐ Q
1.) For r<a there is no electric field (inside conductor).
2.) For a<r<b one has a spherical charge distribution with a total charge of +Q, so the electric field is:
1
4
3.) For r>b the net charge enclosed is zero, thus there is no electric field outside the spherical capacitor.
b) What is the potential difference ∆ between the spherical shell and the solid sphere?
What is the capacitance of the spherical capacitor?
Solution:
For a<r<b we have for the potential V(r):
∆ (which is a positive quantity because b>a)
Thus the capacitance of a spherical capacitor is:
∆
4