FDR's Isolationism -1932 "Good Neighbor Policy" w/Latin America
advertisement

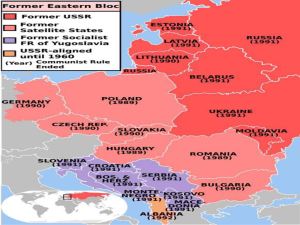
FDR's Isolationism -1932 "Good Neighbor Policy" w/Latin America -troops from DR & Haiti -Cuba: supported rebels by lowering tariff on sugar for new government -Mex: stopped silver purchases after Mex government nationalized oil until negotiations took place -Nye hearings led to suspicion of business' pushing for WWI -Neutrality Acts in 1935-37 outlawed arms sales to nations at war; stopped US travel to "belligerent powers" -N. Acts used in Spanish civil war -1940: banned sale of aviation fuel & scrap metal to Japan; after Tripartite Pact more metals were embargoed The New Deal Changes Course Challenges from Right & Left -American Liberty League formed by Al Smith and other Democrats, arguing that Deal restricted individual freedom and hinted at socialism -rich felt FDR had "abandoned class" -Charles Coughlin won people over with radio and pressing for his ideas such as nationalization of banks followers, mostly of urban lower-class and small businessmen, organized as "National Union of Social Justice" -Francis Townsend appealed to older Americans by suggesting that $2 thousand be paid to all retired citizens over 60 as long as they spent it - idea would have bankrupted nation -Huey Long, a Louisiana governor & senator: "Share Our Wealth" program: 100% income tax on incomes >$1 million & appropriate all fortunes >$5 million to redistribute to lesser off: "every man is a king" -Emergency Relief Appropriation Act gave FDR $5 billion to spend -FDR set up Works Progress Administration led by Harry Hopkins -WPA gave work: employed 8 million + people, put $11 billion into economy and built many bridges, schools, etc -Federal Writers' and Theatre Projects -government was deficit spending: no effect because money used to fund public works was taxed from citizens -AAA unconstitutional - Soil Conservation and Domestic Allotment Act paid farmers to cut production of "soil-depleting" crops such as wheat and cotton -National Labor Relations Act supported by NY senator Robert Wagner, guaranteed collective bargaining rights, protected "closed shops" (all employees join union as condition of employment), and outlawed spying on unions, union "agitators" - called Wagner Act -Social Security Act (1935) drafted by committee led by Secretary of Labor Frances Perkins, gave system of old-age pensions to workers, some workers' compensation, and aid for handicapped and dependent mothers -Revenue Act raised income taxes for higher income levels, increased corporate taxes and boosted levies on gifts and estates FDR's departure from isolationism -didn't invoke N. Acts in 1937 when Japan invaded China - neither side had formally declared war - NA's didn't separate aggressors from victims & could encourage conquest -1940: gave British 50 destroyers in return for lease of British bases in W. Hemisphere -Lend-Lease Act (1941): US could lend war materials to nations deumed "vital to the defense of the US" let FDR help Britain (and USSR later) -US ships protected Lend-Lease shipments -met w/Churchill to discuss joint military strategy: Atlantic Charter -German U-Boat attacks; FDR gave authority to fire on sight; Reuben James sunk -Pearl Harbor - declare war on Japan -Hitler & Mussolini declare war WWII v. WWI: Postwar & Truman Truman & Foreign Policy -economic boom: GI Bill, reconverting industry, tax cut -Nuclear Arms Race: Atomic Energy Commission focused on military weapons -Britain gave US responsibility for thwarting Communism in Mediterranean -Marshall Plan: $17 billion to Europe for recovery (in return for alliance) - Greece & Turkey -1947 declaration about Marshall Plan; "Truman Doctrine" to let US police world -Truman Doctrine / containment: US come to defense of countries in danger of Soviet invasion -Berlin air lifts -North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO): 10 European nations, US and Canada; attack on one is attack on all; formal end of isolationism; Truman gave $1.3 billion to NATO nations; stationed 4 army divisions in Europe -H-bomb; NSC-68 report on USSR aggression & pressed for military buildup Domestic Policy -veterans, industry, spending led to llnflation -1946: inflation; Truman made New Deal-style solutions; conservatism in government rejected plans -UMW coal mine strike: Truman threatened to sieze mines & in RR strike threatened to draft strikers; alienated labor -President's Committee on Civil Rights alienated South; Korean War - Issues -"Greece of Far East": would US enforce containment -Truman Doctrine & "policing" -NSC-68 utilization -peace talks: armictice Foreign Policy: Dulles v. Truman -"liberation" & "massive retaliation": threaten to use nuclear force; liberate East Europe; "New Look" military of bombs & planes -wanted full support from US allies -believed in "brinksmanship" to push USSR to war with US -Eisenhower didn't act on Dulles' ardent ideas -mutual defense pacts with 43 nationg under Dulles -Nikita Khrushchev called for "peaceful coexistence" internationally -Quemoy & Matsu: Taiwanese islands used for raids on China; US defend them and hinted nuclear attack on China; brinkmanship -CIA: led by Allen Dulles; made by National Security Act of 1947; influenced countries using bribes & disinformation; helped overthrow anti-US governments in Iran and Guatemala -Vietnam: French trapped at Dienbienphu by Vietminh; Eisenhower decides not to help -Geneva Peace Accords: split Vietnam; Eisenhower not sign due to domino theory -Third World: US & USSR tried to get TW countries; nationalism from recent freedom; Aswan Dam in Egypt: Nasser denies US due to subterfuge suspicions & not liking Israel -Suez crisis: US not happy at Britain, France & Israel for attacking Egypt for nationalizing Suez; thought USSR might use nukes; made anti-West feeling in 3rd World & made US dominant over Britain & France -U-2 plane shot over Russia US in 1950's -nuclear power (AEC) -technology: plastics, pesticides, computers -