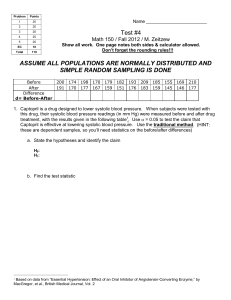
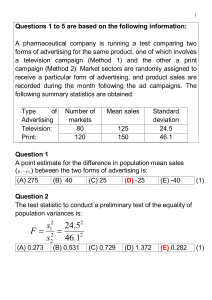
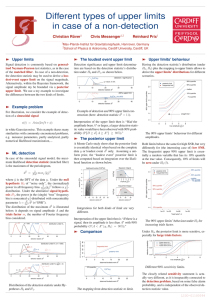
Introduction To Statistics Chapter 1 I Two Kinds Of Statistics A. Descriptive Statistics
advertisement

Chapter 1 Introduction To Statistics I Two Kinds Of Statistics A. Descriptive Statistics 1. Measures of central tendency 2. Measures of dispersion 3. Measures of association B. Inferential Statistics 1 II What Are You Expected To Learn? A. The What, When, and How of Statistics 1. What statistics are available? 2. When each statistic should be used? 3. How each statistic should be computed? B. Reasons For Studying Statistics 1. Read and understand statistical presentations in your field 2 2. Design experiments 3. Learn how to use a statistical package to analyze data 4. Detect fallacies in the presentations of statistical results III Describing Characteristics By Numbers A. Variable: A Symbol That Is Used to Stand for an Unspecified Element of a Set 1. Range of the variable: set of elements for which the variable stands 2. Value: an element in the variable’s range 3 B. Classification Of Variables In Mathematics 1. Qualitative variable: range consists of attributes or non-quantitative characteristics of people, objects, or events Unordered Ordered 2. Quantitative variable: range consists of a count or a numerical measurement of a characteristic Discrete Continuous 4 C. Measurement in the Behavioral Sciences, Health Science, and Education D. Four Levels of Measurement and Transformations 1. Nominal: one-to-one 2. Ordinal: strictly increasing monotonic 3. Interval: positive linear X a bX , where b 0 4. Ratio: multiplication by a positive constant X bX , where b 0 5 E. Importance of Level of Measurement 6