General Education Annual Course Assessment Form
advertisement

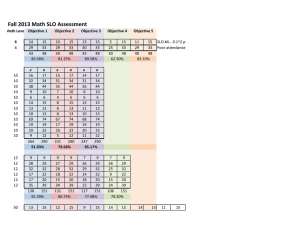
General Education Annual Course Assessment Form Course Number/Title KIN 69 – Stress Management Results reported for AY: 2012-2013 GE Area: E # of sections: 13 (Fall ’12 = 6, W’13 = 1, Sp’13 = 6 sections) # of instructors: 5 (1 section co-taught) Data are reported for 12 of 13 sections Course Coordinator: Peggy Plato E-mail: Peggy.Plato@sjsu.edu Department Chair: Shirley Reekie College: CASA Instructions: Each year, the department will prepare a brief (two page maximum) report that documents the assessment of the course during the year. This report will be electronically submitted, by the department chair, to the Office of Undergraduate Studies, with an electronic copy to the home college by September 1 of the following academic year. Part 1 -To be completed by the course coordinator: (1) What SLO(s) were assessed for the course during the AY? Fall 2012 & Winter 2013: SLO #2 – Students will be able to recognize the interrelation of the physiological, social/cultural, and psychological factors on their development across the lifespan. Spring 2013: SLO#3 – Students will be able to use appropriate social skills to enhance learning and develop positive interpersonal relationships with diverse groups and individuals. (2) What were the results of the assessment of this course? What were the lessons learned from the assessment? SLO #2: 55% of students demonstrated achievement of this SLO at a high level (B+ or higher), 29% at an average level (B to C), and 16% at a marginal level, or failed to demonstrate achievement of this SLO (C- or lower). Of the 31 students who scored a C- or lower on the assignment used to assess student achievement of this SLO, 11 students did not submit the assignment. SLO#3 - 75% of students demonstrated achievement of this SLO at a high level (B+ or higher), 21% at an average level (B to C), and 4% at a marginal level, or failed to demonstrate achievement of this SLO (C- or lower). Several instructors used the occupational stress paper to assess student achievement of SLO#2. In this paper, students interview someone working in their chosen career and use library resources to evaluate occupational stressors and solutions for those stressors. In analyzing occupational stress, students learn that when unmanaged, excessive stress can impact their health, social-cultural interactions, and psychological well-being. Additionally, students discuss sources of stress encountered at different stages of life (i.e., childhood, as college students, young adults beginning their careers/families, during middle age and older adulthood) and methods that can be used to effectively manage those stressors. The primary method used to assess SLO#3 was a group project (e.g., University Resources assignment) that required students to work in groups to research, then present information to the class on resources available on campus that may enhance students’ academic, social, or personal wellbeing and/or reduce stress. One purpose of this assignment is to teach students how to work in diverse groups, including communicating with team members, delegating the work, and coordinating their class presentation. In a reflection paper, students discussed how their groups worked together. If the group worked well together, they were asked to discuss what facilitated that process. If the group did not work well together, they discussed what they did to try and resolve the problems. An additional assessment method included pairing up students from different backgrounds (e.g., majors, gender, age) and having them engage in active listening throughout the semester. Students were given a theme to discuss and asked to use active listening skills during their discussions. Lessons Learned: The instructor who had students engage in active listening throughout the semester reported that students knew one another fairly well by the end of the semester, and that social skills and self-esteem were greatly enhanced. Social skills and interpersonal communication are essential tools needed throughout life. An instructor who used the university resources assignment to assess SLO#3 reported that the majority of students took responsibility to do an excellent job on the project and not let down their group members. What modifications to the course, or its assessment activities or schedule, are planned for the upcoming year? (If no modifications are planned, the course coordinator should indicate this.) Faculty teaching the course feel the university resources assignment is effective for helping students develop interpersonal skills while working within a group to accomplish a task, as well as learning about the numerous resources available on campus to help students manage stress and/or enhance their academic life. Generally, faculty feel that we need to put more emphasis on stress across the lifespan and improve on the assessment of SLO#2. Ideas that were discussed include interviewing family members or friends to learn about stressors they’re encountering (e.g., younger or older siblings, parents, grandparents) and how those stressors affect their well-being. In class, students can then discuss what they found and brainstorm strategies to reduce these stressors or mimimize the negative impacts of stress across the lifespan. Part 2 - To be completed by the department chair (with input from course coordinator as appropriate): (4) Are all sections of the course still aligned with the area Goals, Student Learning Objectives (SLOs), Content, Support, and Assessment? If they are not, what actions are planned? Yes, all sections of the course are aligned with the Area E goals, SLOs, content, support, and assessment. This is facilitated by using a common green sheet and textbook. Three assignments, Stress Log, Occupational Stress or Mini-Review Paper (requiring use of library resources), and University Resources, are linked to the SLOs and required in all sections of the course. New faculty meet with the course coordinator before teaching this course, and faculty teaching the course meet regularly during a duty day to discuss and share best practices, resources used (e.g., videos, biofeedback), teaching methodologies, assignments, and assessment.