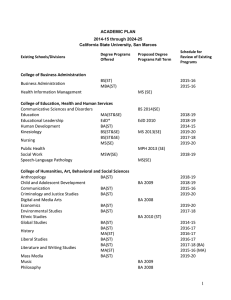
KENNESAW STATE UNIVERSITY GRADUATE PROGRAM/CONCENTRATION PROPOSAL
advertisement

KENNESAW STATE UNIVERSITY GRADUATE PROGRAM/CONCENTRATION PROPOSAL FORM 11/04/02 PROGRAM OR CONCENTRATION NAME: Doctor of Education (EdD) Program DEPARTMENT: Educational Leadership Early Childhood and Elementary Education Secondary and Middle Grades Education Special Education PROPOSED EFFECTIVE DATE: August 1, 2006 Check One or More of the Following and Complete the Appropriate Sections Sections to be Completed __X___New Program Proposal** All _____Change in Program/Concentration/Degree Requirements _____New Concentration Proposal III - VII I - VII **A new course proposal is required for each new course that is part of the new program Submitted by: ______________________________________________________ Faculty Member ___ Approved ___ Not Approved ______________________________________________________ Department Curriculum Committee ___ Approved ___ Not Approved Date ______________________________________________________ Department Chair ___ Approved ___ Not Approved Date Date ______________________________________________________ 11/18/2005 School Curriculum Committee ___ Approved ___ Not Approved ______________________________________________________ School Dean ___ Approved ___ Not Approved Date ______________________________________________________ President Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Date ______________________________________________________ Vice President for Academic Affairs ___ Approved ___ Not Approved Date ______________________________________________________ Dean, Graduate Studies ___ Approved ___ Not Approved Date ______________________________________________________ GPCC Chair ___ Approved ___ Not Approved Date Page 2 of 53 Date 11/18/2005 UNIVERSITY SYSTEM OF GEORGIA NEW GRADUATE PROGRAM PROPOSAL Doctor of Education (EdD) Program (With embedded EdS) Kennesaw State University October 2005 Department of Educational Leadership Department of Early Childhood Education Department of Secondary and Middle Grades Education Department of Special Education BAGWELL COLLEGE OF EDUCTION Proposed Start Date: August 1, 2006 CIP:______ Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 3 of 53 11/18/2005 Table of Contents I. Page Program Description Unique Aspects of the Program………………………………………………… 6 Institutional Importance of the Program………………………………………... 8 KSU’s Mission and Strategic Plan……………………………………………… 9 System and State of Georgia Goals…………………………………………….. 10 Staffing and Enrollment …………………………………………………………10 Plans for Launching Program…………………………………………………… 11 II. Objectives of the Program ……………………………………………………… 12 III. Justification and Need for the Program Overview……………………………..…………………………………………. 14 Appropriate Specialization ………………………………………….………….. 17 Productivity……………………………………………………………………... 23 Partnering……………………………………………………………………….. 23 Placement ………………………………………………………………………. 24 IV. Procedures Used to Develop the Program………………………………………… 24 V. Curriculum: Degree Program Requirements Program Admission/Residency Requirements…………………………………. 25 Course Offering Schedule and Plan-of-Study …………………………………. 27 Growth and Flexibility …………………………………………………………. 39 Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 4 of 53 11/18/2005 VI. Inventory of Faculty Directly Involved Course/Instructor Support……………………………………………………… 40 Faculty Development…………………………………………………………… 43 VII. Outstanding Programs of This Nature at Other Institutions……………………… 43 VIII. Inventory of Pertinent Library Resources………………………………………. 44 IX. Facilities ………………………………………………………………………... 45 X. Administration ………………………………………………………………….. 47 XI. Assessment ……………………………………………………………………... 47 XII. Accreditation …………………………………………………………………… 48 XIII. Affirmative Action Impact ……………………………………………………... 48 XIV. Degree Inscription ……………………………………………………………… 48 XV. Fiscal and Enrollment Impact and Estimated Budget Enrollment Projections…………………………………………………………. 48 Costs …………………………………………………………………………… 48 XVI. Appendices Distributed School Leadership Model ………………………………………… 51 KSDs Linked to Standards………………………………………………………52 Survey of Faculty Qualifications………………………………………………..53 Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 5 of 53 11/18/2005 I. PROGRAM DESCRIPTION Unique Aspects of Program Consistent with the Board of Regents P-16 Initiatives and the Georgia Leadership Institute for School Improvement (GLISI), the Bagwell College of Education’s (BCOE) Doctorate of Education (EdD) degree in Teacher and Administrator Leadership will produce teachers and administrators who will serve effectively as leaders of learning in P-12 schools in a variety of Distributed Leadership (GLISI) roles. The Distributed Leadership Model (Appendix A) as envisioned by the University System of Georgia Board of Regents prepares teachers and administrators to effectively serve in a variety of leadership roles in schools and school districts. The roles include, but are not limited to: a) learning and development leader, b) change leader, c) performance leader, d) curriculum, instruction and assessment leader and e) relationship development leader. Graduates of the KSU EdD program will be equipped to support and inspire colleagues to achieve higher levels of student learning in P-12 schools. Furthermore, the degree is explicitly designed to assist the Board of Regents in meeting the demands of the Double the Number and Double the Diversity Of Teachers plan. For example, the degree is designed to accomplish the following: a) reduce attrition rate of new teachers. As part of their program of study, candidates in the teacher leadership concentrations of the EdD program will serve as master teachers and mentors to pre-service teachers and novice teachers from the BS and MAT programs at KSU. In a similar manner, practicum students in the administrator leadership field of study will serve as mentors and/or supervisors to preservice and novice teachers as well. b) prepare teachers and administrators to lead effectively through a distributed leadership model. Graduates will be prepared to function effectively in each of the eight distributed leadership roles identified by the Georgia Leadership Institute for School Improvement c) have a sustained emphasis on quality by building a community of leaders for learning in schools who have the knowledge, skills, and dispositions to impact positively student learning for all and to assist their colleagues in doing the same. The degree is unique in other ways as well. Candidates in the program will take a common core of 27 hours regardless of their concentrations. These 27 hours are designed to prepare graduates of this program to be boundary crossers and network builders--extremely knowledgeable about their own specialty areas, as well as other related areas of teacher and administrator leadership that have the potential to positively impact student learning in P-12 schools. The EdD degree in Teacher and Administrator Leadership is a comprehensive doctoral degree with an embedded Educational Specialist (EdS) degree. In addition, at both the EdD and EdS levels candidates select from one of two fields of study with a major in one of ten concentrations as outlined below. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 6 of 53 11/18/2005 I. Administrator Leadership Concentrations: A. Educational Leadership & Policy B. Diversity Track: Special Education Administration C. Technology Leadership II. Teacher Leadership Concentrations: A. Adolescent Education Tracks: Mathematics Reading Future Tracks in English/Language Arts, Science B. Diversity Track: Literacy C. Elementary & Early Childhood Tracks: Teacher Advocate Teacher Education Reading D. Instructional Technology Finally, another unique aspect of the degree is that it has been developed through a collaborative process, bringing faculty and administrators from across the university together to design a program that is distinctive in the state, region, and country. The collaborative process of design, development, and delivery of the program is consistent with the Regent’s Principles and Actions for the Preparation of Educational Leaders for the Schools (Principle #3). Clearly, the Doctorate of Education degree at KSU is distinctive and will significantly strengthen the Board of Regents (BOR) position and reputation in the region. The Doctor of Education Program (EdD) in Teacher and Administrative Leadership builds on the philosophical foundation laid by Kennesaw Statue University’s intense focus on ethics, leadership, Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 7 of 53 11/18/2005 and community engagement. These values emerge naturally from KSU’s long-standing, successful commitment to Invitational Leadership, an ethical theory of practice whereby leaders intentionally summon others to realize their potential in all areas of human endeavor. In this thinking, it is not enough that leaders of learning concern themselves merely with organization and management; rather, they must inspire and instruct by example. In the Bagwell College of Education, we recognize the explicit relationship between Invitational Leadership and Distributed Leadership in educational settings. The proposed Doctor of Education Program in Teacher and Administrator Leadership builds on this tradition by bringing together professional, experienced educational leaders for advanced, collaborative study in leadership practice and theory. The proposed program will provide a forum for further development of distributed leadership skills for those individuals who form the foundation of strong school communities. Another uniqueness of the proposed Doctorate of Education program is the international focus that is designed to foster the growth of global educators who, armed with comparative educational experiences, understand the international implications of high performing schools and have the skills to lead others to that understanding. All of the students in the EdD will be required to take the Comparative International Education as part of the core course sequence. One concentration in the in Teacher Leadership is devoted strictly to diversity. Finally, as the program’s unique focus and design become known regionally and nationally, the distinctive nature of the program will also be attractive to candidates from other states. Furthermore, as Kennesaw’s reputation in international arenas continues to grow, we fully anticipate attracting strongly qualified international candidates to this unique program. Institutional Importance of the Program The proposed Doctor of Education Program in Teacher and Administrator Leadership will prepare education professionals for a variety of educational leadership positions. This program furthers Kennesaw State University’s mission by providing a facilitative collegiate environment that fosters high quality academic preparation with a focus on critical analysis skills, global and multicultural perspectives, leadership development, social responsibility, and lifelong learning. Kennesaw State University’s mission will be fully reflected in this unique and distinctive Doctor of Education in Teacher and Administrator Leadership program. The proposed program is a natural extension of KSU’s academic priorities as articulated in KSU’s Strategic Plan. Further, it provides an opportunity for KSU to build on an established foundation of its successful Master of Education degree programs. Specifically, the proposed program will help KSU meet the priorities and goals of the university’s strategic plan in the following ways: 1. The program provides an in-demand forum for individuals preparing for high-level leadership positions in the critical-need area of education. The proposed Doctor of Education Program in Teacher and Administrator Leadership is responsive to a welldocumented shortage of highly qualified professional educators with the knowledge, skills, and abilities necessary to lead educational organizations. 2. Kennesaw State University has placed an increasing emphasis on leadership development over the past decade, and specifically in graduate programs in Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 8 of 53 11/18/2005 education, nursing, business, information systems, professional writing, conflict management, and public administration. KSU’s commitment to and the importance of preparing leaders will only increase in coming years. The proposed program will provide professional educators with in-depth training and experiences in the concentrations of Leadership and Policy, Special Education Administration, Technology Leadership, Adolescent Education, Diversity, Elementary and Early Childhood Education, and Instructional Technology. In addition, the program’s emphasis on teacher and administrator leadership in a diverse, global environment furthers KSU’s mission as a university devoted to preparing graduates to have a positive impact on diverse learners in schools and classrooms of Georgia. Kennesaw State University is in an ideal position to offer this dynamic Doctor of Education Program. Graduate programs in Accounting, Business, Conflict Management, Education, Information Systems, Nursing, Public Administration, and Professional Writing currently draw over 1,800 highly qualified students seeking advanced degrees to our campus annually. The graduate programs in the Bagwell College of Education have grown by 142% in the past year alone. Kennesaw State University is uniquely qualified to offer this highly professional program based on its long history of collaboration both with the local school districts and with numerous community constituents. These ongoing partnerships have resulted in the community’s trust in the programs and graduates of Kennesaw State University. KSU's Mission and Strategic Plan Facilitating the development of leadership knowledge, skills, and dispositions in our graduates is central to Kennesaw State’s mission. KSU is well known for programs devoted to leadership development for administrators, faculty, staff, students, and community members. The emphasis placed on professional graduate education, collaborative learning, community involvement, and applied research provides a realistic and exciting context for adult learners. Kennesaw fulfills its mission and strategic plans by not only designing and delivering distinctive practitioner degree programs, but also through a network of institutes and centers. For example, KSU’s Institute for Leadership, Ethics and Character, one of very few institutes in the country with a focus on ethical leadership, will serve as a unique resource for students and faculty of the EdD program. As an educational institute, it offers leadership, stewardship, ethics, and character development curricula; comparative studies in leadership theory and practice; and invitational opportunities for service and community engagement. Other on-campus centers and institutes in a variety of fields and disciplines will provide valuable support for the EdD candidates and faculty. Some of these include the Educational Technology Training Center, International Center, A. L. Burruss Institute of Public Service, and the Center for Nonprofit and Public Leadership. The proposed Doctor of Education Program fully supports and embodies the mission of Kennesaw State University. As leaders of learning graduates of the EdD program will possess knowledge, skills and dispositions that reflect many of Kennesaw’s distinctive features. Kennesaw and its graduates are unique in that they Possess a substantive commitment to collaboration within the university and with others outside the university. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 9 of 53 11/18/2005 Are intentionally inviting. Are committed and strongly dedicated toward service and applied scholarship. Are focused on student learning and success. Value the importance of and practice ethical, principle-centered, and moral leadership. Value the importance of and implement innovative and interdisciplinary curricula, responsive to the individual and to current and future societal needs. Are committed to high quality, distinctive professional degree programs. Focus on global and multicultural perspectives with a commitment to international education. System and State of Georgia Goals As previously delineated in the first section of this proposal (Unique Aspects of the Degree) the EdD in Teacher and Administrative Leadership directly addresses system-level and state-level goals through linking with the Board of Regents’ P-16 Initiatives and the Georgia Leadership Institute for School Improvement (GLISI), the Regent’s Principles and Actions for the Preparation of Educational Leaders for the Schools and the Double the Number and Double the Diversity Of Teachers plan. In addition, the proposed program is closely aligned with the following University System of Georgia/Board of Regents’ strategic goals: USGBOR Goal 1. Educate graduates who are intellectually and ethically informed individuals with well-defined skills and knowledge who are capable leaders, creative thinkers and contributing citizens. USGBOR Goal 2. Expand participation by increasing access, enhancing diversity, improving service to nontraditional students, expanding use of distance education, advancing public library usage, and marketing the advantages of postsecondary education. USGBOR Goal 3. Increase academic productivity through improved recruitment, increased retention, accelerated graduation and expanded credit generation. USGBOR Goal 5. Help accelerate Georgia’s economic development by providing needed graduates, offering appropriate academic programs, and marketing the System and its institutions as economic assets of the state. USGBOR Goal 9. Increase, diversify, and strategically allocate resources. Staffing and Enrollment The results of a recent faculty survey (Appendix B) indicate that there is broad faculty expertise across the participating departments to move forward with this comprehensive doctoral proposal. The umbrella format of the program with equal contributions from a common core area and Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 10 of 53 11/18/2005 extending study in the respective areas of concentration with support from related cognate areas within and outside the Bagwell College of Education will spread the instructional demands of the program across departments and faculty. More specifically, the faculty in each of the program areas has many years of service at the graduate faculty level, have taught a full range of courses through the doctoral level, have experience as members of doctoral committees, and have chaired/directed doctoral dissertations to completion. Additionally, at least two faculty members in each program have special academic background and experience in research design and statistics. Most of them have taught in doctoral level research classes and served on doctoral committees as methodologists. This group of eight faculty members has a strong publication record in applied research and has contributed to developing the sequence of educational research courses from Master’s to Doctoral levels. Plans for Launching the Program The umbrella format of the program with equal contributions from a common core area and extending study in the respective areas of concentration with support from related cognate areas within and outside the Bagwell College of Education will ease initiation of the proposed EdS/EdD. For example, in the Department of Special Education, there are currently faculty with doctoral degrees who have the expertise to teach the research and comparative education courses in the common core. Given the number of requests for advanced preparation in special education administration, it is anticipated that the department will be able to generate enough resources to offer a minimum of two new courses (e.g., EXC 8300 and EXC 8310) the second year of the program. The other courses required in this concentration are offered by the Department of Educational Leadership. Therefore, the graduate students will have the ability to take four new courses, but only two will be offered by the Department of Special Education. Similarly, beginning in the third year, the Department of Special Education will generate revenue to support two more new courses in literacy and will also require students to take courses offered by the Reading Institute housed within the BCOE. Finally, as the graduate students move more intensively into their doctoral study, they will take courses offered in the metropolitan area of Atlanta by the University of Spain or the University Monterey and ultimately complete corresponding internships in schools or universities in one of those respective countries. Thus the EdS/EdD will be phased-in systematically and conjointly with other departments (and universities) as resources and opportunities become available. It is anticipated that all of the concentrations will evolve similarly across all departments within the BCOE. According to our records, since 2002, the BCOE has increased the annual number of program completers from approximately 300 to 785. This growth pattern has allowed the college to add between six and eight new tenure track lines per year. To successfully launch the program, the Dean of the BCOE has agreed to devote four of these new lines to the EdS/EdD, one to each department. In addition, the Dean has committed to investigating the possibilities of funding non tenure track positions through the KSU Foundation or other sources of outside funding. One consideration is that the non-tenured lines will be reserved for individuals who are experienced researchers, willing to serve for two-three years as distinguished faculty and be primarily responsible for mentoring members of the PTEU who are inexperienced in chairing doctoral dissertations and/or serving on doctoral committees. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 11 of 53 11/18/2005 Faculty searches in the future will include as an essential employment criterion experience chairing or serving on doctoral dissertations. Salary adjustments will be made in future searches so that the offer of employment is attractive and competitive for senior faculty who are interested in becoming associated with an emerging, dynamic university and interested in becoming involved with this distinctive and unique doctoral program in Teacher and Administrator Leadership . Initially, the program will draw students locally from the Atlanta Metro Area, particularly from Cobb County, Fulton County, DeKalb County, Paulding County, Cherokee County and areas north of Atlanta. Many holders of the educational leadership L-5, T-5, L-6, and T-6 certificates are anxious to upgrade their certification to higher levels. The demand for an EdD/EdS program in the KSU service area is great. The departments have frequent contact with educators who have expressed interest an EdD/EdS program, particularly their own M.Ed. and Add-on Program graduates. Enrollment distribution across program areas will be based upon demand and the developing readiness to support advanced degrees in each program area. As noted above, the demand for further graduate study options in professional education has been developing for some time. Program planners will need to manage the number of candidates admitted to the program while delivering a high quality program. The proposed doctoral program will start in Fall 2006. The BCOE will focus on recruiting cohorts of 20-25 EdS candidates in each of the tracks. In addition to this group of EdS candidates, KSU will recruit a cohort of 30-35 doctoral candidates from across concentrations who have completed the EdS at other institutions. II. OBJECTIVES OF THE PROGRAM The purpose of this program is to prepare professional educators to become leaders for learning in P-12 schools. The program will prepare teacher and administrator leaders who can effectively function in distributed leadership roles with the express intent of positively impacting learning for all P-12 students. Drawing on the literature of distributed leadership, teacher leadership, and ethical leadership, the following list has been developed to indicate the knowledge, skills, and dispositions expected of graduates. Linkages to the USGBOR Distributed Leadership Roles and the NCATE and PSC standards are provided Appendix C of this proposal. Graduates from the Doctorate of Education program at Kennesaw State University 1. Demonstrate leadership as advocates for students and education. Candidates a. synthesize and apply the latest research on learning, leadership, and developmental theory, advocating for implementation of best practices and assisting colleagues to do the same to ensure that all students learn. b. are knowledgeable, articulate, and think critically about educational practice, policy, and issues on national and international levels. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 12 of 53 11/18/2005 c. understand, respond to, and influence the larger political, social, economic, legal, and cultural contexts in matters related to education. d. are knowledgeable about the factors contributing to safe physical environments for education. e. develop, articulate, implement, and steward a vision of learning supported by the school community. 2. Demonstrate leadership as agents for change, collaboration, and collegiality. Candidates a. understand the complexity of schools and the ambiguous nature of educational issues. b. act in concert with and/or on behalf of colleagues to improve teaching and learning in the classroom as supported by effective school-district and state-level policies and operations. c. facilitate shared-decision making and teamwork. d. improve teaching and learning by intentionally and systematically building networks of influence at local, state, national, and international arenas. e. impact student learning for all and assist other educators to do the same by effectively working within the structures and culture of schools, families, and communities. f. support the teaching and learning process by soliciting all sources of funding and educational resources. 3. Demonstrate leadership as mentors. Candidates a. support and guide teachers to improve teaching and learning for all. b. are committed to improving student learning by improving teaching and the learning environment. c. model consistent, intentional, and effective use of technology while mentoring and encouraging others to do the same. 4. Demonstrate leadership as expert teachers and instructional leaders. Candidates a. are creative and flexible in their thinking and in seeking solutions to educational challenges. b. are knowledgeable of assessment, evaluation, and accountability practices and critically synthesize and utilize the data to improve student learning. c. are master teachers and instructional leaders, possessing and demonstrating content and pedagogical expertise who are able to make international comparisons in both areas. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 13 of 53 11/18/2005 d. develop and/or support appropriate, meaningful curricula that positively impact student learning for all and assist others to do the same. e. facilitate and support curricular design, instructional strategies, and learning environments that integrate appropriate technologies to maximize teaching and learning. f. use technology to collect and analyze data, interpret results, and communicate findings to improve instructional practice and student learning. 5. Demonstrate leadership as models of professionalism. Candidates a. effectively design and conduct educational research that positively influences educational practice or policy. b. exhibit ethical behavior in all professional and personal interactions. c. respect others, value differences, and are open to feedback. d. believe that for every problem there is a solution and actualize that belief when engaging colleagues, students, families, and community partners. e. seek out responsibility and are accountable for their actions. f. maintain currency of current knowledge and best practices through continued professional development. 6. Demonstrate leadership in meeting the needs of diverse constituents. Candidates a. value and recognize the strength, power, and meaningfulness of diversity. b. incorporate global perspectives and cultural richness in curriculum planning and decision making c. address exceptionalities in planning, teaching, and assessment and respond to diverse community interests and needs by mobilizing community resources. d. proactively and intentionally advocate for and work to build educational environments that are inclusive and supportive of diverse students, families, and colleagues. III JUSTIFICATION AND NEED FOR THE PROGRAM In the field of education, what has always been done has not always worked. Recent research and position statements of the American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education have leveled indictments against doctoral degrees in education (Levine, 2005). However, the EdD in Teacher and Administrator Leadership is unique in its development, design, and delivery. From the beginning, the task force developing this degree has worked to transform traditional educational leader training into a powerful force with the specific goal of positively impacting student learning for all in P-12 Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 14 of 53 11/18/2005 classrooms. With the influence of the No Child Left Behind Act of 2001, school districts have been even more anxious to find highly qualified leaders who can impact student learning at all levels and who can serve in distributed leadership roles to lead schools to achieve high levels of learning for all students. Unfortunately, doctoral degrees in education have often been considered to be of poor quality and Levine (2005) goes further to suggest that most doctoral degrees in education do little to prepare educational leaders who can positively impact student learning. Clearly, the Kennesaw State University EdD in Teacher and Administrator Leadership stands out as distinctive in its focus of assisting professional educators to become leaders of learning. The Bagwell College of Education accepts, welcomes, and embraces this emphasis area as a primary mission. More recently, the task force has recognized the Distributed Leadership models of the USGBOR as being particularly salient in shaping our thinking about the uniqueness and distinctiveness of this program. Ironically, for more than two years, the faculty and administrators charged with designing the EdD have envisioned school leadership as being shared or distributed throughout the development of this program. As a result, this program is emerging at a particularly critical time since it is one of if not the first programs in education which links explicitly with the USGBOR Distributed Leadership initiatives. The core requirements of the EdD are 27 hours of common courses in which candidates from all concentrations will be engaged in collaborative problem-solving, requiring them to tackle the amorphous, often ambiguous problems in P-12 schools. The core courses are as follows: KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 EDL Advanced Study of Learning (3) 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Not only will candidates be engaged in collaborative, case-based problem solving in these core courses, but faculty from across departments will deliver the courses collaboratively, sharing expertise and modeling collaborative problem-solving. No longer can we envision professional educators working in isolation to solve problems. Only when educational leaders from multiple Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 15 of 53 11/18/2005 perspectives work collaboratively on real-life problems will real and workable answers to educational problems be found. Furthermore, the reality of schooling today demands that leaders for learning possess the knowledge, skills, and dispositions to work across boundaries and to build networks of influence within and outside of their own areas of expertise. Solving complex problems in schools requires this kind of expertise. Graduates of the EdD in Teacher and Administrator Leadership will be prepared to function effectively in these distributed leadership roles. Kennesaw’s regional and national reputation for quality in undergraduate and graduate education combined with demonstrated success at the entry level of graduate studies has generated a need for additional graduate degree opportunities through the doctoral degree. Each department is maintaining waiting lists of candidates desiring to work on advanced graduate degrees in education specifically at KSU range as high as 150 across the seven concentration areas. Some of these potential candidates are turning to out-of-state public and private institutions that are conducting cohort activities in KSU’s immediate service area or to distance-learning options that are readily available. Unfortunately, as Levine (2005) has suggested, many such programs are of questionable quality and do not prepare educational leaders who possess the knowledge, skills or dispositions to bring all students to high levels of achievement. Kennesaw’s Doctorate of Education provides teachers and administrators an opportunity to obtain a degree of distinction- one that prepares them to be leaders of learning, making a strong positive impact on learning in Georgia’s P-12 classrooms. From the perspective of a state-wide need, KSU is rapidly developing as a key institution in the internationalization of its offerings. The attention to diversity and multiculturalism and the emerging ESOL field of study further strengthen this dimension of the proposed program. As previously noted, statewide needs as outlined in the Double Double plan will be met by preparing teachers to be leaders of learning in Adolescent Education (mathematics and reading), Early Childhood and Elementary Education, and Special Education. These teacher leaders will be prepared to assist, support, inspire, and mentor new teachers, thereby reducing teacher attrition rates. This Doctor of Education Program, housed in the Bagwell College of Education, will prepare top leaders for learning in education, utilizing a collaborative, problem-based, field-based approach. Graduates will be prepared to effectively assume distributed leadership roles in P-12 schools. This field-based approach will enhance participant learning and interaction through all levels of educational leadership. KSU recognizes that many academic programs are frequently so specialized and technically oriented to the details and culture of a particular discipline that graduates are not prepared for interaction outside their own area of expertise. This unique Doctor of Education Program will meet the high demand for educational leaders with advanced degrees who can guide educational organizations in Georgia to higher levels of student achievement. The shortage of education leaders who have received advanced training is parallel to the shortage of teachers. This shortage of education leaders in Georgia is currently under consideration by the Professional Standards Commission on Educational Leadership Task Force of which Dr. Yiping Wan, Dean of the Bagwell College of Education, serves as Co-Chair and the Georgia Board of Regent’s Leadership Institute for School Improvement. The high demand for Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 16 of 53 11/18/2005 educational leaders can also be seen through a survey conducted of the graduates of the MEd and Add-on programs in Educational Leadership at KSU. Results showed that over 70% of the graduates plan to pursue advanced graduate study in education and prefer to seek their advanced graduate degree at Kennesaw State University. In addition, KSU has received many phone calls and e-mails from perspective EdD and EdS students expressing their great interest in the proposed program. In fact, many departments of BCOE have developed long waiting lists of potential candidates who intend to pursue their EdS and EdD studies at Kennesaw State University. The EdD program will help keep the best educators in schools by upgrading their certification and salary. Educators are underpaid in comparison to other professionals and corporate leaders. In essence, the EdD program not only provides our candidates with advanced professional preparation that will enable them to profoundly impact student learning, but also provides them an opportunity to increase their salary and expand their professional opportunities in education. Currently, few doctor of education programs maintain an appropriate balance between academics and professional practice. Individuals wishing to pursue doctoral studies in education are likely to enroll in a program that is either too theory-oriented or too practice-centered. KSU’s proposed program will balance theory and practice. The program will provide the candidates with knowledge and skills that will further prepare them to assume important leadership positions in their fields, and, at the same time, prepare them to pursue an academic career in higher education. The proposed EdD. Program at Kennesaw State University is both professionally rewarding and academically challenging. The Doctor of Education Program in Teacher and Administrator Leadership will prepare leaders with an advanced degree that will allow them to expand their employment opportunities and influence in public or private P-12 schools, educational agencies, and higher education as in positions such as: Superintendents Central Office Administrators Principals Curriculum Supervisors Technology Directors Technology Instructional Specialists Lead Teachers Department Chairs Department of Education staff or consultants Community college or university faculty Appropriate specialization The program is designed to prepare all candidates to become leaders of learning. Common core courses are designed to increase candidates’ knowledge, skills, and dispositions for meeting the demands of distributed leadership roles in P-12 schools. Courses in the concentration areas deepen and broaden the candidates’ knowledge, skills, and dispositions for these roles so that graduates can profoundly impact teaching and learning in P-12 schools. Program graduates will be ready to Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 17 of 53 11/18/2005 assume leadership responsibilities both in public and private schools and in state educational agencies. At the same time, program candidates are fully prepared academically to pursue a career track in higher education, specifically in teacher education or educational leadership. Candidates for the EdD or EdS degree in the Teacher or Administrator Leadership fields of study may select from five different concentrations with their related tracks. The rationale and description for each of these concentrations or specializations are provided below. Adolescent Education & Advocacy (Mathematics, Reading): The EdD/EdS in Teacher Leadership- Adolescent Education & Advocacy is designed for middle and secondary school educators. Graduates of the EdD/EdS in Teacher Leadership- Adolescent Education & Advocacy program are leaders for learning because they possess the knowledge, skills and dispositions necessary to serve in a variety of distributed leadership roles in P-12 schools. The program is aligned with NCATE and PSC standards, as well as with the specialty area content standards of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics and the International Reading Association. Consistent with the Bagwell College of Education’s Conceptual Framework, the Collaborative Development of Expertise in Teaching, Learning and Leadership, graduates of the EdD/EdS program in Adolescent Education are prepared to serve as collaborative experts and to be effective advocates, agents, mentors and models. As advocates for education and students, they are knowledgeable; think critically; and speak and write articulately about educational policy and issues. They understand, design and use research findings on best practice to “take a stand for what is right” for students and to assist others to do the same. They challenge the status quo by raising student voices. As agents for change, collaboration and collegiality, they understand the complexity of schools and the ambiguous nature of educational issues. They act in concert with and/or on behalf of colleagues to improve teaching and learning at the school, district, regional or state level. They provide leadership by facilitating shared decisionmaking and teamwork. They span boundaries, working within and across school structures to influence teaching and learning. They build and nurture networks of influence while navigating the structures and culture of schools to create a positive impact on student learning for all, and they assist others to do the same. As mentors, they are trusted and known for their pedagogical and content expertise by novice and advanced teachers and administrators alike. They provide support and guidance to teachers in all stages of their careers. As models of professionalism and expert teaching and learning, they are knowledgeable of professional and national standards in their content areas. They are master-teachers and instructional leaders who develop appropriate and meaningful curriculum consistent with national standards. They are dedicated to improving teaching in all classrooms in order to have a positive impact on all student learning, and they help others to do the same. They exhibit the highest standards of ethical behavior in all of their professional and personal interactions. They seek out responsibility and are accountable for their actions. They are respectful of others, value differences and are open to feedback. They are optimistic and hopeful about education and the influence they can have on teaching and learning. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 18 of 53 11/18/2005 Elementary and Early Childhood Education: Teacher Advocate. While teachers in the Elementary and Early Childhood profession are perceived as having gentleness, compassion, and a nurturing demeanor to effectively teach young children, it is the purpose of this program to allow these teachers to also develop into leaders in their schools. What better ways to make lasting changes in our schools, than to empower the classroom teachers to have a role in educational change. Their various roles in distributed leadership will enable them to be teacher advocates for curriculum improvement while specializing in the art and craft of teaching. Through a thorough theoretical base of curriculum development, understanding of global education issues, and an appreciation for the philosophical inquiry and ethical issues in education, our graduates will be leaders in learning. Understanding, implementing and evaluating the Georgia Performance Standards while addressing the requirements of No Child Left Behind will be an interwoven aspect of all the ECE courses. The Teacher Advocate will become the change agent of tomorrow’s schools. Elementary and Early Childhood Education : Reading. The reading program is designed to meet the specific needs of our students at the EdS and EdD levels. The courses that are planned cover the spectrum from theory to practice. One course was chosen for the core because it provides an advanced analysis of reading development and instruction as an emergent literacy course. (EDRD 8470, Analysis of Literacy Development and Reading Instruction). Our courses for advanced diagnosis and assessment, (EDRD 8430, Analysis of Reading Diagnosis and Assessment) our practicum for strategic reading across the content areas (ECRD 8460, Practicum for Strategic Reading in the Content Areas) and our advance children’s literature courses (EDRD 8440, Analysis of Children’s Literature) are designed to give students opportunities to practice effective reading pedagogy with students. The courses Advanced Reading in the content Areas (ERRD 8450) and our research courses (EDRD 8410, Curriculum in Reading: Theory and Research and EDRD 8420, Reading Theory and Research; Advanced Theories and Models of Reading) provide ED S and Ed D students with more in-depth opportunities for research and exploration of reading theory. This array of reading courses assure the extensive study of the reading processes, application and understanding of the Georgia Performance Standards as well as the International Reading Association standards. These courses are designed to develop instructional leaders with the distributed leadership skills to ultimately meet the needs of the children of our region and the state of Georgia. Elementary and Early Childhood Education: Teacher Educator. Teaching at the college or university level, while having different requirements than teaching in the Elementary and Early Childhood schools, is not a time to forget effective pedagogy. It is a time to model best practice, a time to continue personal academic growth through research, reading, and publications as well as collaborative endeavors through the university, college, department and local school systems. The courses in this program have been developed to introduce future college and university teachers into the world of teaching at the college and university level. Through a detailed exploration of, critical issues in Elementary Education, and theories of instructional design EDS and EdD students will gain a global understanding of the knowledge they need to address the content of courses they might teach at the college level to future teachers. The course in post secondary education, assessment in post secondary education, instructional methods and internship will provide future college and university teachers the skills needed to effectively present new and challenging information to college and university students. Through these courses the circle of teacher leader development will have gone full circle. Professors who teach future teacher leaders Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 19 of 53 11/18/2005 must experience what it means to be a teacher leader. They need to know the certifying entities of higher education, NCATE, SACS, ACEI and numerous SPA organizations. Diversity (Literacy, Special Education Administration): The fields of study offered by the Department of Special Education emerged as a result of collaborative dialogue among faculty members in the department, the P-12 school community, and members of the PTEU. The ideas articulated in this collaborative effort guided the development of the proposed concentrations in Diversity. The overarching goal of this advanced preparation is to increase the academic and social achievement of students with disabilities and those who are English language learners in the stateapproved curriculum. To be successful educator must first, and foremost, have a clear understanding of diversity that guides their leadership of others and brings them to a better understanding of the various constituency groups in their schools. Second, school leaders must demonstrate the ability to foster learning environments that are culturally responsive, inclusive, caring and accepting of all individuals. Research suggests that when schools succeed with culturally and linguistically diverse students, there exists a powerful belief system of high expectations that rejects deficit assumptions about students, their cultures, abilities and life circumstances (Williams, 2005). Simply stated, students make greater academic and social gains when their teachers use quality research-based pedagogy; that is pedagogically responsive to the learning, emotional and social needs of culturally and linguistically diverse students. The advanced preparation concentration in Diversity attempts to prepare such individuals. The concentrations in the area of Diversity were carefully crafted in concert with the conceptual framework that was originally developed and adopted by the PTEU in 2003. However, the original theme of the conceptual framework, Collaborative Development of Teaching and Learning, was expanded to include the concept of Leadership. As noted in the conceptual framework, candidates in Advanced Programs develop as leaders by (a) refining expertise in content knowledge and effective instruction; (b) defining new professional roles and responsibilities; and (c) contributing towards more effective schools by providing professional support and direction for colleagues, parents, and community members. To successfully move the field of teacher education beyond the fragmented and superficial treatment of diversity that currently prevails, teacher educators must articulate a vision of teaching and learning in a diverse society and use that vision to systematically guide the infusion of multicultural issues throughout the curriculum. The proposed concentrations in Diversity emphasize eight essential components of preparation including: (a) recognition of one’s own ethnocentrism; (b) knowledge of students’ cultural backgrounds; (c) understanding of the broader social, economic and political context; (d) ability and willingness to use culturally appropriate management strategies; (e) commitment to building caring classrooms that provide equitable access for all students to the state-approved standards; (f) understanding and use of research-based practices in general education environments; (g) the ability to analyze school wide, complex problems and resolve issues such that all teachers, students and parents are supported and successful; and (h) an understanding of global issues in education and how they translate into the education of students in the United States. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 20 of 53 11/18/2005 The EdS/EdD in Diversity is offered through the Department of Special Education, but consistent with the umbrella format of the EdS/EdD, the required courses offered through a variety of departments within the BCOE and the PTEU, as well as universities in Spain, Mexico and China. Graduates of the EdD/EdS in Administration will demonstrate the knowledge, skills and dispositions to serve in a variety of distributed leadership roles in the P-12 schools, state and federal governmental agencies, and/or private not-for-profit agencies. Similarly, graduates in Teacher Leadership will demonstrate the knowledge, skills and dispositions to teach in universities, conduct research for private agencies or serve as master (mentor) teachers and instructional leaders in P-12 settings. The programs are aligned with NCATE and PSC standards as well as those of the Council for Exceptional Children and National Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Languages. Instructional Technology: The EdS/EdD program with an Instructional Technology concentration prepares elementary, secondary and middle grades teachers to be leaders in the use of technology for standards-based instruction and assessment. The program will prepare teachers to model best practices the use of instructional technologies and to provide high-quality professional learning experiences for other educators. This course of study is designed to meet the Georgia Professional Standards Commission (GPSC) standards for receipt of a T -6 (EdS) and an T-7 (EdD) certificate . The program is aligned to the “advanced levels” of the Technology Facilitation standards developed by National Council of Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE) and the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE). These standards are designed to help candidates “exhibit knowledge, skills, and dispositions equipping them to teach technology applications; demonstrate effective use of technology to support student learning of content; and provide professional development, mentoring, and basic technical assistance for other teachers who require support in their efforts to apply technology to support student learning” (ISTE/NCATE, 2002). Students will address these performance standards in the context of collaborative inquiry with peers and faculty during class discussions and course assignments. Course assignments will focus on promoting the development of high-quality, technology-based curriculum resources and facilitating the effective uses of technology for standards-based instruction and assessment of student learning. Assignments will also build candidates’ understanding of how to design and implement high-quality professional learning for educators and to navigate the change process connected with introducing a technological innovation into a learning environment. Courses will also require candidates to interact with a broader community of researchers and practitioners through the review of published literature in the field and the participation in professional learning organizations. Admission to the EdS/EdD program in Instructional Technology requires a current State of Georgia T-5 certificate and the successful completion of a master’s level program aligned to ISTE/NCATE’s Technology Facilitation (TF) Standards, such as the M.Ed. in Educational Leadership with a Technology Concentration at Kennesaw State University. Prior to admission, students who have not completed an approved course of study aligned to the Technology Facilitation Standards must demonstrate that they are currently proficient in the “meets” category of the TF standards through their individual professional practices, other courses of study, and/or their own independent study. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 21 of 53 11/18/2005 This demonstration of competency may be submitted in the form of a portfolio or another approved assessment method as approved by the department. Technology Leadership: The EdS/EdD program with a Technology Leadership concentration is designed to prepare and develop candidates to serve as technology directors, coordinators, or specialists at district, regional, and/or state levels. It is also designed to enhance the ability of other practicing school administrators to leverage the use of modern technologies for educational improvement. The program is aligned to the Technology Leadership standards developed by the National Council of Accreditation of Teacher Education (NCATE) and the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE). The program is also designed to help candidates understand how technology is related to the eight roles of educational leaders as defined by Georgia’s Leadership Institute for School Improvement (GLISI). Performance standards addressed in the course of study are related to computing systems, facilities planning and management, instructional program development, professional learning, and other advanced applications of technology to support student learning and assessment. Students will address these performance standards in the context of collaborative inquiry with peers and faculty during class discussions and course assignments. Candidates will also interact with a broader community of researchers and practitioners through the review of published literature in the field and the participation in professional learning organizations. Admission to the EdS/EdD program in Technology Leadership requires a current State of Georgia L-5 certificate or current enrollment in an add-on certification program and the successful completion of a master’s level program aligned to ISTE/NCATE’s Technology Facilitation Standards, such as the M.Ed. in Educational Leadership with a Technology Concentration at Kennesaw State University. Prior to admission, students who have not completed an approved course of study aligned to the Technology Facilitation Standards must demonstrate that they are currently proficient in the “meets” category of the TF standards through their individual professional practices, other courses of study, and/or their own independent study. This demonstration of competency may be submitted in the form of a portfolio or another approved assessment method as approved by the department. Preference for program admission will be given to candidates who are currently holding administrative, instructional technology specialist, or professional learning positions in private or public schools, regional service agencies, university systems, or state government. Educational Leadership and Policy: The Doctor of Education in Administrator Leadership- Educational Leadership and Policy program is designed for individuals who are interested in pursuing an advanced program in educational leadership and policy. While the Master of Educational Leadership program is focused on the preparation of school level administrators, the Doctor of Education program aims at providing practical training for district level administrators who play key roles in policy development and implementation. The program will start with advanced level coursework in specific content areas to solidify candidates’ understanding of knowledge, skill, and disposition in educational leadership. Candidates having completed this phase of the program will be awarded an Education Specialist degree and be permitted to continue with the second phase of the doctoral program. Intensive and extensive interaction with current issues in educational policy studies will provide challenges to candidates in the second phase of the program. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 22 of 53 11/18/2005 The Doctor of Education in Educational Leadership Program is committed to shape knowledgeable, skillful, and ethical educational leaders who dare to accept responsible positions at the district level. Productivity Both levels of the program will operate with a cohort format. At the EdS level, cohorts will be limited to 25 students who will be completing 33 hours of graduate courses over five semesters. Two academic courses will be delivered each semester (.50 FTE faculty) along with a need for cohort coordination, advisement and supervision of field experience (.25 FTE) establishing a .75 FTE for faculty support per cohort. The EdS will be offered at the regular graduate tuition and fee rates. It is felt that tuition and fee income and formulae funding flow through dollars will support the EdS program and possibly produce some excess revenue. Based upon our understanding of funding of the total operating budge at KSU, about 45% comes from student tuition and about 45% from state appropriations (formula funding) with the remaining 10% from all other sources. With 25 students in each cohort taking 33 credit hours (embedded EdS) over a five-semester period, each cohort will generate $100,650 in tuition. With a reduction of $20,000 for one summer session, the tuition income would be in the neighborhood of $80,000. The state appropriation, based upon the above understandings, should be around the same figure. Therefore, the tuition income and the state appropriation should be adequate to cover all of the instructional costs of the EdS cohort program. We understand that state appropriations are two year in arrears, but KSU will underwrite the startup costs in the first two years. Similar calculations for the 42-credit hours in the doctoral component of the program would produce similar revenues even at regular funding rates. The doctoral component (the last 42 hours) will also operate in a cohort model over 6 semesters with an upper limit of 20 students per cohort. The lower class sizes in concentration/track course will necessitate a need for 1.0 FTE faculty per cohort with an additional need for .50 FTE support for doctoral committee participation and dissertation direction. These projections give consideration to the reduction of academic assignments for doctoral faculty to enhance their scholarly activities. The costs of the doctoral component, particularly faculty support as described will need to be supported at a “premium pricing” level. Programs of this Student Credit Hours (SCH) potential will obviously generate greater staff support and operational costs as they develop. It is estimated that an additional staff support person will be needed in each program area with increased supply and operational funds needed as well. It is anticipated that such needs will be manageable with increases in formulae driven allocations from the USG. Partnering Bagwell College of Education will continue its excellent tradition of working with public school systems, the Regional Educational Support Agencies, the USG Board of Regents, the Georgia Department of Education, state universities in Georgia, and international partnerships in the enrichment of educational experiences of program participants. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 23 of 53 11/18/2005 Placement The program will be housed in the Bagwell College of Education, specifically in the departments of Educational Leadership, Secondary and Middle Grades Education, Elementary and Early Childhood Education, and Special Education. The program coordinators and support personnel will reside in these respective departments. Candidate advisement files and advisors will be located in their respective departments. IV. PROCEDURES USED TO DEVELOP THE PROGRAM Kennesaw State University first became aware of the need for educational leaders prepared to serve as leaders for learning through professional contacts with Kennesaw State University’s partner school districts. In 2001, surveys regarding preparation of educational leaders were conducted to solicit input from area school superintendents. All respondents identified the need for quality school leaders of different levels in their school districts and pledged their strong support for graduate programs at KSU designed to prepare leaders who had the knowledge, skills, and dispositions to positively impact student learning. From the beginning, the task force charged with developing this proposal has been committed to designing a program that builds on our collaborative approach and mission at KSU. Faculty and administrators from departments and colleges across the university have worked to design and develop a program that engages the candidates in real-life, problem-based learning. In addition, through a well-established system of advisory boards, professional colleagues in P-12 schools have provided feedback and input to the task force. We have envisioned learning experiences delivered by faculty who model collaborative collegiality and team work. These experiences will be delivered through a core of nine courses taken by candidates in all concentrations and taught by faculty across all departments. Candidates’ knowledges, skills, and dispositions to serve effectively as leaders of learning are further developed by carefully designed learning experiences in five unique concentrations and their respective specialty areas. Dr. Yiping Wan, Dean of the Bagwell College of Education, has encouraged and supported the faculty of all departments in the development of a quality program of advanced educational studies to meet the needs of the market. The faculty met and discussed intensively the issues and challenges of the EdD program and decided to go forward with the development of the comprehensive EdD with an embedded EdS. At the same time, Education Specialist and Doctor of Education Programs of the following universities in Georgia were carefully reviewed: University of Georgia Georgia State University Georgia Southern University Valdosta State University Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 24 of 53 11/18/2005 State University of West Georgia The task force decided that the Doctor of Education Program at KSU would bear orientations both from the practicing and academic standpoints. The program is designed to meet the need of the market for educational leaders of advanced level training. At the same time, the program places a vigorous demand for academic performance to prepare graduates for an academic career in higher education. It was with these basic understandings in mind that the Doctor of Education in Teacher and Administrator Leadership program was developed. V. CURRICULUM: DEGREE PROGRAM REQUIREMENTS The EdD Teacher and Administrator Leadership is primarily designed for experience educators who hold an L-5, T-5, L-6, or T-6 certificate. It allows experienced educational professionals to earn an EdD degree with EdS coursework embedded as the first 33 credit hours. Upon completion of the first 33 hours, candidates may apply for admission to the doctoral program and complete a minimum of 42 hours to obtain the EdD. The program will be delivered in cohorts offered through a combination of on campus, on-site, and on-line learning experiences specifically designed so that candidates maximize collaboration with professional colleagues and peers. The proposed program will be offered through the use of modules, direct instruction, cohort planning, and individual projects based on personal development plans formulated jointly by the participants and the faculty. At the EdS level, participants will develop a school-based leadership research project to be implemented and completed as part of the program requirements. Practicum experiences are required and will be arranged through Kennesaw State University’s partnership schools and universities. At the EdD level, participants will work under the direction of a doctoral committee to complete the dissertation for graduation. At the conclusion of the program, participants will posses the knowledge, skills, and dispositions necessary to lead schools to higher levels of achievement for all students. Program Admission/Residency Requirements: Admission Requirements First level of review: Graduate Admissions Candidate for admission to the Doctor of Education (EdD) 1. Official transcripts for all college-level coursework, graduate and undergraduate 2. Evidence of completion of Master degree or its equivalent. 3. Scores on the General Test of the Graduate Record Exam Candidates will pass this initial level of review by having an Index Score of 3500 minimum for consideration for admission to the EdD. The analytical writing score of the GRE will Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 25 of 53 11/18/2005 also be required and will be considered in evaluating the candidates qualifications and potential for success in the program. The index score is calculated in the following way. Index Score = (GRE Quant + GRE Verbal) X Graduate GPA 4. Professional resume or vita 5. Goals statement: A 1-2 page narrative of one’s prior professional experiences and professional goals as they relate to the selected program of study. Candidate for admission to the Education Specialist (EdS) 1. Official transcripts for all college-level coursework, graduate and undergraduate. 2. Evidence of completion of Master degree or its equivalent. 3. Scores on the General Test of the Graduate Record Exam Candidates will pass this initial level of review by having an Index Score of 3000 minimum for consideration for admission to the EdD. The analytical writing score of the GRE will also be required and will be considered in evaluating the candidates qualifications and potential for success in the program. Index Score = (GRE Quant + GRE Verbal) X Graduate GPA 4. Professional resume or vita 5. Goals statement: A 1-2 page narrative of one’s prior professional experiences and professional goals as they relate to the selected program of study. Second level of review: Program Level Admissions Committee Each program will draft additional admission requirements that will be used at the program level to identify qualified candidates who successfully passed the first level of review. Possible additional requirements could include but are not limited to the following: 1. A Master degree in related field (to be specified by the program level committee) 2. Letters of recommendation 3. Portfolio of previous work 4. Interview with program admissions committee Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 26 of 53 11/18/2005 5. Extemporaneous written responses 6. Scores on specified exams (such as Praxis II) AND/OR minimum scores on sections of exams (such as minimal scores on each of the sections of the GRE) 7. Teaching or administrative experience 8. Minimum number of hours in a content area (such as English, math, science, reading) Admissions review process The Bagwell College of Education will implement a graduate admissions review process. The purpose of the process is to help ensure equity and fairness in graduate admission decisions across programs. The review committee shall consist of a representative from the Bagwell College of Education Graduate Admissions office and faculty representatives from each department. Students who are not recommended for admission may initiate a review of their admission documents. Students must contact the program coordinator of the program to which they applied OR the BCOE graduate admissions coordinator in writing to request a review of their admission file. Residency Requirements Candidates for the Doctor of Education degree must complete 21 hours in the concentration at Kennesaw State University prior to enrolling in the Doctoral Seminar. Course Offering Schedule and Plan-of-Study The initial scheduling of course offerings is planned to span five consecutive semesters for a total of 33 hours. At the completion of these first 33 hours, candidates will have met the requirements for the EdS. At that time, the candidates will be awarded the Education Specialist Degree and endorsed for L-6 or T-6 Certificate in the State of Georgia. Candidates who wish to continue their study and who met the requirements for admission to the EdD program will complete a minimum of additional 42 hours of course work to complete the EdD. Candidates satisfying all EdD. program requirements will be awarded the Doctor of Education Degree and endorsed for L-7 and T-7 Certification in the State of Georgia. As described in section one of this document, the comprehensive Doctor of Education Program at Kennesaw State University consists of two fields of study with ten concentration areas and their respective specialty tracks, as follows: Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 27 of 53 11/18/2005 Fields of Study : I. Administrator Leadership Concentrations: A. Educational Leadership & Policy B. Diversity: Track: Special Education Administration C. Technology Leadership II. Teacher Leadership Concentrations: A. Adolescent Education Tracks: Mathematics Reading (Future additional tracks in science, English/Language Arts) B. Diversity Track: Literacy C. Elementary and Early Childhood Tracks: Teacher Advocate Teacher Education Reading D. Instructional Technology Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 28 of 53 11/18/2005 Doctor of Education (EdD) (Umbrella Proposal) 27 hr Core + 27 hrs Concentration + 12 hrs electives + 9 hrs dissertation A D M I N I S T R A T O R L E A D E R S H I P Educational Leadership & Policy COMMON CORE (27 hrs) Applied Quan, Qual Research (3) Field Research (3) Adv. Qual. Research (3) L E A D E R S H I P Adv. Quan. Research (3) Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) Advanced Study of Learning (3) Leadership for Systemic Change (3) Diversit Literac Doctoral Seminar (3) Comparative International Education (3) Technology Leadership Instructional Technology the Early Childhood and Elementary Education: Teacher Advocate, Teacher Education, Reading Diversity: Special Education Administration Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 T E A C H E R Page 29 of 53 Adolescent Education: Mathematics Reading 11/14/2005 The course of study in each of the concentrations are listed below. Degree: Field of Study: Concentration: Track: EdS/EdD Administrator Leadership Educational Leadership and Policy N/A KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Concentration (27 Hours) EDL 8450 EDL 8725 EDL 8730 EDL 8825 EDL 8980 Educational Evaluation School Finance Advanced School Law Educational Facilities Field Experiences EDL 9100 EDL 9260 EDL 9325 EDL 9480 Educational Planning School Policies and Practices Politics of Education Executive Leadership in Education Guided Electives (12 hours) Must be outside of department and at least 6 outside of the Bagwell College of Education. Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 30 of 53 11/14/2005 Degree: Field of Study: Concentration: Track: EdS/EdD Administrator Leadership Diversity Special Education Administration KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Concentration (27 Hours) EXC 8300 EXC 8310 EDL/EXC EDL/EXC Inclusive Policies & Practices in Special Education Supervision, Mentoring and Collegial Coaching in Special Education Elective in Administration Elective in Administration EXC 8325 EXC 8359 EXC 8370 EXC 8375 EDRD 8360 Creating Culturally Responsive Schools Creating Culturally Responsive Classrooms Planning, Implementing & Assessing Instruction for Diverse Students Increasing Achievement of Diverse Learners through Practical Application Literacy Instruction for English Language Learners Guided Electives (12 hours) Must be outside of department and at least 6 outside of the Bagwell College of Education. EDL 6740 Multicultural and International Education (3) Offerings by University of Spain, University of Monterey (Mexico) or Nanjing Normal University (China) (6) Additional hours with advisor approval (3) Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 31 of 53 11/14/2005 Degree: Field of Study: Concentration: EdS/EdD Administrator Leadership Technology Leadership KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Concentration (27 Hours) EDL 8500 Technology & School Improvement EDL 8510 Research and Best Practices in Curriculum, Instruction, and Technology Integration EDL 8520 Adult Learning and Development EDL 8530 Strategic Planning for Educational Technology Programs EDL 8540 21st Century Facilities and Finance EDL 9500 Research and Theory in Educational Technology EDL 9510 Leadership in Educational Technology EDL 9520 Evaluation of K-12 Technology Programs EDL 9530 Principles and Practices of Online Learning Guided Electives (12 hours) Must be outside of department and at least 6 outside of the Bagwell College of Education. Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Total Hours for EdD = 75 minimum Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 32 of 53 11/14/2005 Degree: Field of Study: Concentration: Track: EdD Teacher Leadership Adolescent Education Mathematics COURSES: KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDL 9000 The Organization of School Transformation (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Adolescent Education Core (12 hours) EDAD 8100 Curriculum Theory & Practice in Middle & Secondary Schools (3) EDAD 8200 Supervision, Mentoring & Advocacy in Mid & Sec Schools (3) EDAD 8300 Critical Analysis of Educational Policy for Teacher Leaders (3) EDAD 8400 Internship in Teacher Development or Teacher Education (3) Content Area Core (15 hours) Select from the following: MATH 7700 Elementary Set Theory MATH 7712 Discrete Mathematics MATH 7713 Statistics & Data Analysis MATH 7714 Geometry from Multiple Perspectives MATH 7717 Number Theory MATH 7718 Functions & Analytic Techniques MATH 7900 Special Topics MATH 7950 Directed Study MAED 7701 History of Mathematics MAED 7715 Mathematical Problem Solving MAED 7716 Math Studies MAED 7719 Technology & Mathematics MAED 7751 Survey of Mathematics Teaching & Learning MAED 7900 Special Topics MAED 7950 Directed Study MAED 8890 Research Methods & Critique in Mathematics Education Guided Electives (12 hours) Choose any combination of courses with advisor guidance Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 33 of 53 11/14/2005 Degree: EdD Field of Study: Teacher Leadership Concentration: Adolescent Education Track: Reading COURSES: KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Adolescent Education Core (12 hours) EDAD 8100 Curriculum Theory & Practice in Middle & Secondary Schools (3) EDAD 8200 Supervision, Mentoring & Advocacy in Mid & Sec Schools (3) EDAD 8300 Critical Analysis of Educational Policy for Teacher Leaders (3) EDAD 8400 Internship in Teacher Development or Teacher Education (3) Content Area Core (15 hours *) Reading Core (ECE/Sec.& Middle) EDRD 8300 Literacy-Based Instruction for English Language Learners or EDRD 8310 Literacy-Based Instruction for Students with Disabilities EDRD 8470 Analysis of Literacy Development and Reading Instruction EDRD 8580 Supervision of School Literacy Programs Candidates select remaining hours from the following EDRD 8530 Critical Media Literacy EDRD 8540 Problems, Issues & Trends in Teaching YA Literature EDRD 8550 Communities of Discourse EDRD 9580 Supervision of School Literacy Programs EDRD 9590 Critique of Reading Research EDRD 8300 Literacy-Based Instruction for English Language Learners or EDRD 8310 Literacy-Based Instruction for Students with Disabilities *NOTE: Candidates who do not hold a reading endorsement must take the following courses to obtain the reading endorsement prior to enrolling in EDRD 8000 level courses Guided elective hours may be used: EDRD 7715 Theory & Pedagogy in the Study of Reading EDRD 7717 Reading Assessment & Instruction EDRD 7718 Content Area Reading Guided Electives (12 hours) Choose any combination of courses with advisor guidance Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 34 of 53 11/14/2005 Degree: Field of Study: Concentration: Track: EdS/EdD Teacher Leadership Diversity Literacy KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Concentration (27 Hours) EDRD 8365 Literacy Instruction for Students with Disabilities (3) EDRD 8360 Literacy Instruction for English Language Learners (3) EDRD 7765 Teaching Content Area Reading to Diverse Learners (3) (Or its equivalent) EDRD 9580 Supervision of School Literacy Programs EDRD 8540 Problems, Issues & Trends in Teaching YA Literature EXC EXC EXC EXC 8325 8350 8370 8375 Creating Culturally Responsive Schools (3) Creating Culturally Responsive Classrooms (3) Planning, Implementing & Assessing Instruction for Diverse Students (3) Increasing Achievement of Diverse Learners through Practical Application (3) Guided Electives (12 hours) Must be outside of department and at least 6 outside of the Bagwell College of Education. 6 Hours from offerings by University of Spain, University of Monterey (Mexico) or Nanjing Normal University (China) (3) EDL 6740 Multicultural and International Education (3) ENGL 7731 Language Studies in English (3) Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 35 of 53 11/14/2005 Degree: Field of Study: Concentration: Track: EdD Teacher Leadership Elementary and Early Childhood Education Teacher Advocate COURSES: KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Elementary and Early Childhood Education core (12 hours) ECE 8110 Global Education: Issues and Perspectives (3) ECE 8130 Curriculum Inquiry ECE 8120 Advanced Educational Technology (3) ECE 9110 Philosophic Inquiry in Education (3) ECE 9120 Ethics and Excellence in the Elementary Classroom Teacher Advocate Track (15 hours) ECE 8320 School Reform through Classroom Practice (grades K – 5th) or ECE 8321 School Reform through Classroom Practice (Birth through 8 years) ECE 8340 The Classroom Community ECE 9310 Authentic Assessment in Content Areas (3 hrs) ECE 9320 Linking Traditional Assessment to Instruction ECE 9330 Cognitive Processes and Educational Practice ECE 9340 Stand Up and be Counted: Teacher as Decision Maker Guided Electives (12 hours) Must be outside of the concentration or department and at least 6 outside of the Bagwell College of Education Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Total Hours for EdD = 75 minimum Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 36 of 53 11/14/2005 Degree: Field of Study: Concentration: Track: EdD Teacher Leadership Elementary and Early Childhood Education Teacher Educator COURSES: KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Elementary and Early Childhood Education core (12 hours) COURSES: ECE 8110 Global Education: Issues and Perspectives (3) ECE 8130 Curriculum Inquiry ECE 8120 Advanced Educational Technology (3) ECE 9110 Philosophic Inquiry in Education (3) ECE 9120 Ethics and Excellence in the Elementary Classroom Teacher Educator Track (15 hours) ECE 8210 Issues in Post Secondary Teacher Education (3 hrs) ECE 8220 Current Critical Issues in Elementary Education ECE 8230 Applied Theories of Instructional Design–(3 hrs) ECE 9210 Assessment in Post Secondary Teacher Education (3 hrs) ECE 9220 Post-Secondary Instructional Methods and Internship (3 hrs) Guided Electives (12 hours) Must be outside of the concentration or department and at least 6 outside of the Bagwell College of Education Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Total Hours for EdD = 75 minimum Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 37 of 53 11/14/2005 Degree: Field of Study: Concentration: Track: EdD Teacher Leadership Elementary and Early Childhood Education Reading COURSES: KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Elementary and Early Childhood Education Core (12 hours) COURSES: ECE 8110 Global Education: Issues and Perspectives (3) ECE 8120 Advanced Educational Technology (3) ECE 8130 Curriculum Inquiry ECE 9110 Philosophic Inquiry in Education (3) ECE 9120 Ethics and Excellence in the Elementary Classroom Reading Track Prerequisite: Reading Endorsement Reading Core Courses: EDRD 8470 Analysis of Literacy Development and Reading Instruction EDRD 8380 Supervision of School Literacy Programs EDRD 8300 Literacy-Based Instruction for English Language Learners Or EDRD 8310 Literacy-Based Instruction for Students with Disabilities Prerequisite: Reading Core courses EDRD 8410 Curriculum in Reading: Theory and Research EDRD 8420 Advanced Theories and Models of Reading EDRD 8430 Analysis of Reading Diagnosis and Assessment EDRD 8440 Analysis of Children’s Literature EDRD 8450 Advanced Reading Across the Curriculum EDRD 8460 Practicum for Strategic Reading Across the Curriculum Guided Electives (12 hours) Must be outside of the concentration or department and at least 6 outside of the Bagwell College of Education Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Total Hours for EdD = 75 minimum Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 38 of 53 11/14/2005 Degree: Field of Study: Concentration: EdS/EdD Teacher Leadership Instructional Technology KSU Core (27 Hours) EDUC 8100 Advanced Study of Learning (3) EDL 8000 Leadership for Systemic Change (3) EDRS 8000 Applied Quantitative & Qualitative Research (3) EDRS 8900 Field Research (3) EDL 9000 Advanced Study of School Transformation (3) EDRS 9100 Advanced Qualitative Research Methods (3) EDRS 9200 Advanced Quantitative Research Methods (3) EDUC 9300 Comparative International Education (3) EDUC 9500 Doctoral Seminar (3) Concentration (27 Hours) ITEC 8400 Evaluating K-12 Technologies ITEC 8410 Theories and Application of Instructional Design ITEC 8420 Facilitating Professional Learning and Change ITEC 8430 Planning and Implementing Instructional Technology Programs ITEC 8440 Technology and Student Assessment ITEC 9400 Research and Theory in Instructional Technology ITEC 9410 Instructional Leadership and Technology Facilitation ITEC 9420 Designing and Facilitating Online Learning ITEC 9430 Evaluating Professional Learning Programs Guided Electives (12 hours) Must be outside of department and at least 6 outside of the Bagwell College of Education. Dissertation (9 hours minimum) Total Hours for EdD = 75 minimum Growth and Flexibility As the Doctor of Education Program continues to grow, each program area will need to assess its resources and capabilities for possible expansion to meet the demands of the market. Opportunities may arise to meet school district requests to tailor a cohort of candidates to suit their particular needs. International demands may call for the initiation of a special cohort to prepare their educational leaders. Additional concentrations are already under development and will be added as programs can support them. These concentrations include but are not limited to Adolescent Education Science and Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 39 of 53 11/14/2005 Adolescent Education English, Counselor Education and Higher Education/Community College. VI INVENTORY OF FACULTY DIRECTLY INVOLVED Course/instructor support The present faculty has a diversity of educational backgrounds and experiences to support the course instruction of the proposed Doctor of Education Program. See Part I: Staffing and Enrollment for discussion on faculty expertise. In addition, faculty in all departments maintain and demonstrate sustained scholarship activity and agendas consistent with expectations of faculty working in professional doctoral programs. Some of the most prominent journals in which faculty publish are listed below. Journals in Which Faculty Regularly Publish Teacher Education and Special Education Exceptional Children Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Languages American Teacher Educators Bilingual Educator Remedial and Special Education The Standard Journal of Learning Disabilities Behavior Disorders National Association of Multicultural Education Journal Contemporary Educational Psychology Science Teacher Principal Leadership American School Board Journal School Business Affairs Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 40 of 53 11/14/2005 Journal of School Public Relations Principal Educational Planning Asia-Pacific Journal of Teacher Education & Development Educational Research and Development Georgia Educational Researcher Educational and Psychological Measurement Journal of Liberal Arts and Sciences Education Week Chronicle of Higher Education Current Issues in Middle Level Education The Teacher Educator The Journal of General Education American School Board Journal American Teacher Educators Behavior Disorders Current Issues in Middle Level Education Education Week Educational and Psychological Measurement Exceptional Children Journal of Learning Disabilities Journal of Liberal Arts and Sciences National Association of Multicultural Education Journal Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 41 of 53 11/14/2005 Principal Principal Leadership Conferences at Which Faculty Regularly Present and Attend Council for Exceptional Children Teacher Education Division of CEC Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Languages National Association of Multicultural Education American Education Research Association American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education National Middle School Association National Science Teachers Association American Association of Higher Education Association of Teacher Education American Association of School Administrators National Council for Professors of Educational Administration International Society of Educational Planning Association of School Business Officials International National Association of Multicultural Education Southern Regional Council for Educational Administration American Educational Research Association Georgia Educational Research Association Georgia Association of Teacher Educators Georgia Association of Multicultural Education Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 42 of 53 11/14/2005 Georgia Educational Technology Conference American Association for Colleges of Teacher Education International Conference on Education Faculty Development The faculty maintains active membership and provides leadership in major professional organizations that relate to the area of teacher and administrative leadership. Travel funds are available for faculty to participate in significant educational conferences at the state, national, and international levels. Aside from departmental and college- level support for travel, the KSU Foundation, Office of Graduate Studies, and the International Office have supplemented faculty travel funds for professional endeavors. Faculty Research and Scholarship: Faculty members from each department have traveled internationally to share professional educational expertise and to gain knowledge of educational practices around the world and to establish partnerships with international peers. Specifically, in the last five years faculty from the college of education have traveled on professional exchanges to Nigeria, China, Britain, Russia, Belize, and Spain. During these exchanges, faculty members have presented papers at conferences, visited schools and colleges, and worked with educational colleagues on common research interests. VII. OUTSTANDING PROGRAMS OF THIS NATURE AT OTHER INSTITUTIONS Survey and comparative analysis There are no similar programs to this distinctively designed EdD in Teacher and Administrator Leadership offered at the state level or regionally. In fact, in surveying doctoral degrees in education nationwide, none were found that were comparable to the collaborative model and distributed leadership focus of the proposed degree. It is unique and distinctive. Although there are several doctor of education programs offered in the University System of Georgia, a comparison of the proposed Doctor of Education Program to the doctor of education programs offered at the following institutions revealed that the program proposed by Kennesaw State University is uniquely designed and will be delivered through a collaborative process which that engages the candidates for the degree in problem-based learning experiences with professionals from diverse perspectives. Institutions used in the comparison were Georgia State University, State University of West Georgia, Valdosta State University, University of Georgia, and Georgia Southern University. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 43 of 53 11/14/2005 Unique Features of KSU’s program As outlined in Part I: Program Description: Unique Aspects of Program, the KSU EdD in Teacher and Administrator Leadership is distinctive, unique, and stands apart from other EdD programs in the state, region, and perhaps even nationally. A few of the unique features of KSU’s Doctor of Education Program in Teacher and Administrative Leadership are highlighted below. Collaborative development, design and delivery across departments, colleges, and with stakeholders in P-12 schools. Collaborative learning experiences which that bring professional educators from diverse backgrounds together to solve ambiguous and difficult problems in schools. Focused on preparing educational professionals to effectively fill distributed leadership roles in schools. Utilizes the best practices of cohort dynamics. Prepares candidates for higher levels of academic challenges. Prepares leaders for public, private, and non-profit organizations in the education arena. Widens candidates’ diverse academic horizons. Prepares candidates to meet the needs for international challenges. Delivered both on campus, on-site and on-line. VIII. INVENTORY OF PERTINENT LIBRARY RESOURCES Sturgis Library resources are at least equivalent to resources at other doctoral degreegranting institutions in the state. The library has GALILEO, the state library database, plus 240 other full-text databases across the curriculum, including ProQuest, ERIC, and Lexis/Nexis. The GALILEO service also provides access to World Wide Web resources such as the Library of Congress, full-text journal titles, and newspapers. In addition to these resources, the library has fourteen thousand full-text electronic books, all cataloged and available on-line. Total holdings are more than 600,000 books and periodicals. There are more than 1,500,000 government documents, more than 3,300 serial publications, and well over 1,000,000 pieces of microfiche The library makes use of both the University System and the ARCHE (Atlanta Regional Consortium for Higher Education) interlibrary Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 44 of 53 11/14/2005 use systems. These include interlibrary loans and individual borrowing from more than 8 million unique titles. The collections have been expanded over the last five years to support KSU graduate programs, and the library continues to build resources and programs for further graduate degree offerings. The library is the only institution in Georgia to provide Early English Titles Online (a full-text database of 110,000 books from 1450-1701) to support and enhance the curriculum. With the interlibrary use resources, which are provided to the users at no charge, the library can comfortably support further graduate program expansion. The Sturgis Library’s hours of operation are only two fewer than those at UGA and are longer than those at GSU and West Georgia. Library staff will provide instruction to program participants on resources, materials, and service on a regular basis. Program participants will receive an overview of library resources (printed and electronic), and private instruction and demonstrations will be available by appointment. The Bagwell College of Education has a representative on the university Library Committee. Should resources not contained in the library be needed, these representatives will work with the Library Committee to obtain them. The office of the CIO, to which the library reports, has provided the latest in technology, including laptop computers that can be borrowed for library use and the use of wireless technology. Information Technology Services and Administrative Computer Systems constantly refine, improve, expand, and advance the computing resources available to students, faculty, and staff at KSU. They provide network and desktop support for the more than 18,000 members of the KSU community. Information Technology Services coordinates computing services for KSU candidates and supports over 2,700 personal computers, LANs and connections to many different computing locations. Students, as well as faculty and staff, are eligible for computer accounts affording access to services such as the Internet, KSU’s library system, an active jobs database, a current scholarship database, electronic mail, Archie, Veronica, FTP, Telnet, and KSU’s web site server. IX. FACILITIES The Bagwell COE is located in a 60,000 square foot area of Kennesaw Hall, which was completed in the summer of 1999. The facility-- including the technology areas, support services, and the model classrooms –are available to all educator preparation programs. It The facility was designed to provide ample space for each faculty member to have his or her own office that is spacious, pre-wired for technology, and equipped with needed bookcases, file cabinets, etc and other furnishings. There is also adequate room for the secretary’s office, a workroom, student assistant space, and conference facilities. As the program continues to grow, the demand for space has obviously outgrown the extent of the building capacity. Additional classrooms, office spaces, and conference areas will be needed. The rental space at Town Pointe Center has helped to relieve some crowding conditions in the Bagwell College of Education. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 45 of 53 11/14/2005 Kennesaw Hall also houses workrooms, seminar rooms, storage, and two completely upto-date demonstration classrooms. Participants will also have available the Teacher Resource and Activity Center (TRAC) located within the building TRAC has a large collection of books, journals, and other appropriate resources. Shelves are stocked with textbooks, professional books, kits and videotapes available for checkout, and state-ofthe-art equipment for creating a variety of documents and instructional materials. TRAC also frequently offers workshops on topics of interest and expressed needs. Kennesaw Hall contains rooms equipped with presentation technology for use by students and faculty student and faculty use during classes. An example of this use might involve having the entire cohort work with a specific class scheduling software that is utilized in real world settings. In addition to classroom technology, program participants will have access to computers at several convenient locations in Kennesaw Hall and across campus. There are facilities the participants can use for preparing PowerPoint presentations, setting up web sites, and various other technology applications. Participants who need to acquire additional technology skills can take courses and/or workshops in the Educational Technology Training Center (ETTC). This center offers technology training to KSU’s faculty, staff, and students, as well as to public school personnel. Both Windows and MacIntosh equipment is available for participants’ use. Education partners also make facilities available to further participant learning. Schools within the service area are well-equipped with technology. They also provide a real setting to complete learning activities that can best be accomplished in a school. The proposed program has adequate resources to prepare participants to meet standards for educational leaders. There are ample resources to develop and implement the proposed program’s assessment plan, and technology to support faculty and program participants. Both faculty and students have access to sufficient, current library and curricular resources and to electronic information. Significant enhancements and upgrades have occurred in the technology support area as a result of increased allocations, much of which came from special funding sources through the University’s Office of Information Technology Services (ITS) for additional personnel, equipment, software, model classrooms, computer labs, and instructional resources. Each college/school is assigned through ITS a full-time Information Technology Specialist to support the technology needs of faculty and staff. The specialist assists in the installation of new hardware and software, diagnoses computer or other technology problems and makes minor repairs when possible, and maintains special instructional equipment, including overhead and data projectors, laptops and cameras. The Bagwell College of Education Learning Technology Lab (LTL), created in 1995 to provide hands-on learning to assist all candidates in integrating technology into the classroom environment, acquired 24 Windows98 desktop machines, two I-Macs, two laser printers, one color printer, one scanner, and a teaching station connected to an LCD data projector upon relocation to the new Kennesaw Hall. The lab is open daily for use by students and faculty. .Likewise, when ETTC moved into Kennesaw Hall, its new Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 46 of 53 11/14/2005 acquisitions enabled the center to expand into a far greater physical space than before with state-of-the-art hardware/software/networking capabilities. In fact, a third lab was created, giving the center a total of one MacIntosh and two Windows labs with access to other technology such as digital cameras, scanners, laser and ink jet printers, and still video. A fourth lab used as a network training center is located at the KSU Center. X. ADMINISTRATION The program will be administered under the supervision of the Chair of each of the academic departments with coordinating support by the Associate Dean of Graduate Studies for the Bagwell College of Education. Program coordinators will be assigned to manage of omit the daily administrative responsibilities. The program coordinators will have the overall responsibilities of student recruitment, placement, retention, and assessment. The staff of the Teacher Education Advisory Center as well as the KSU Graduate Admissions Director, and the Office of the Dean of Graduate Studies will provide admission support for the program. The curriculum of the program will be planned by the entire faculty and implemented by the program coordinators. XI. ASSESSMENT Consistent with accrediting agencies such as NCATE and SACS, the assessment of the EdD in Teacher and Administrator Leadership program will include but will not be limited to the following: 1) Program assessment that will utilize longitudinal surveys and focus groups to gauge and document the impact of the program’s graduates on P-12 schools and student learning. And, 2) Candidate Knowledge, Skills, and Dispositions and assessment of candidate and student learning. The task force has identified four particular transition points at which candidates’ knowledge skills and dispositions will be assessed. They are as follows: 1. Admission 2. Capstone experience to EdS (Applied Field Research Course) 3. Admission to candidacy (Doctoral Seminar) 4. Final defense and completion of dissertation. The assessment plan of the program will be consistent with the Professional Teacher Education Unit’s NCATE Standard 2 (Unit Assessment Plan) and will comply with all requirements therein. Unit-wide rubrics, aligned with the appropriate standards and KSDs, will be designed by faculty across programs. In addition, the program will also provide evidence that it is meeting Kennesaw State University’s Assurance of Learning Council’s assessment of student learning as required by SACS. Finally, an annual Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 47 of 53 11/14/2005 assessment report will be filed with the Board of Regents. XII. ACCREDITATION The program will be accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools, and the National Council for the Accreditation of Teacher Education. The program will meet all requirements of the Georgia Professional Standards Commission for leadership certification at the L-6, T-6, L-7, and T-7 levels. XIII. AFFIRMATIVE ACTION IMPACT The program will be in full compliance with the requirements of Affirmative Action. Participants of this program will be admitted irrespective of race, gender, age, religion, and ethnicity. XIV. DEGREE INSCRIPTION Participants satisfying all program requirements at the Preliminary Level will be awarded the Education Specialist Degree. Participants satisfying all program requirements at the Advanced Level will be awarded the Doctor of Education Degree. XV. FISCAL AND ENROLLMENT IMPACT, AND ESTIMATED BUDGET Enrollment Projections It is projected that, once the program is in place, marketing will draw the attention of many educational practitioners from both the public and private sectors. The initial plan is to accommodate a cohort of 25-30 candidates per concentration each year. However, it is anticipated that the rising demand will justify the admission of additional cohorts each year. Costs The umbrella format was intentionally designed to influence the overall cost structure of the doctoral program through the designations of core courses offered at nearly every level. For example, all students must enroll in the 27-hour doctoral core, then depending upon the concentration; students enroll in another core (9-15 hours) in the cognate area. In addition, at least two concentrations interface with the college-wide specialization in literacy that is offered by the BCOE Reading Institute. The development of this structure increases the cost effectiveness of the doctoral program by enhancing the utilization of faculty, streamlining procedures for scheduling of classes (space), and reducing the need for support staff. Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 48 of 53 11/14/2005 A. Personnel (reassigned or existing positions) All members of the faculty will participate in teaching in their areas of specialization in the EdS. omit period and EdD. omit period Programs. B. Personnel (new positions) It is anticipated that, with the additional teaching load, at least one additional faculty line is justified for each department. If two cohorts are admitted each year, then, omit comma two additional faculty lines are needed to support the program. C. One-Time Startup costs Startup costs will include program- omit hyphen marketing expenses in printing, mailing, telephoning, faxing, and traveling. Office setup expenses will include budgeting for furniture, equipment, and supplies. D. Operating Costs Operating costs will include the salaries and benefits of additional faculty and office assistants. Office overheads, books, supplies, and faculty traveling expenses will be included. E. Revenue Sources Revenue sources are the program candidates and from the Board of Regents. Budget PROGRAM DESCRIPTION A Cohort of 25 (EdD Level) Program Length (EdS. Level) 5 Semesters 5 semesters (EdS & EdD) (20 months) Total Program Credit Hours 33 Total program tuition/fees per person *$4,698.00 Total number of students per cohort 25 BUDGET FOR PROGRAM EXPENDITURES Personal Services Full-Time Faculty Part-Time Faculty Support Staff Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 **$106,200.00 ***$12,000.00 ****$16,667.00 Page 49 of 53 10 semesters (20 months) (36-40 months) 39 72 See note below See note below 11/14/2005 Fringe Benefits (30% of salary) Subtotal Personal Services Operating Expenses Regular Operating Expenses Faculty Travel Distinguished Practitioner Faculty per diem Other: Books, Subscriptions Orientation/Retreats Office setup Subtotal Operating Expenses Others: Administrative Expenses, international travels, and assistantship/fellowship $36,860.00 $171,727.00 Total Expenditures $194,227.00 REVENUE Fund Sources State Appropriation Sponsored Tuition Revenue Total Revenue $8,000.00 $3,000.00 $1,500.00 $1,500.00 $1,500.00 $7,000.00 $22,500.00 $76,777.00 $117,450.00 $194,227.00 * Per person fee will cover all tuition fees and student activity fees for 5 semesters. EdS program is based on $122 per credit hour plus $168 per semester. EdD funding is still under consideration as a potential “premium priced” program. ** Calculation is based on one full-time faculty at $60,000.00 per year (9 month contract). $136,200 is derived from the one faculty’s salary of 4 full semesters and 1 summer sessions. $106,200 is derived from the one faculty’s salary of 3 full semesters and 1 summer sessions. The cost of fringe benefits has not been added. *** Calculation is based on paying $3,000 for one adjunct faculty per course per semester. **** Calculation is based on one half-time secretary at $25,000 per year (12 months). Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 50 of 53 11/14/2005 APPENDIX A Distributed School Leadership (Adapted from USGBOR at http://www.usg.edu/p16/lq/ga-edl/) Data Analysis Leader Performance Leader Master Teacher Peer Teacher/ Coach Curriculum, Instruction & Assessment Leader Relationship Development Leader TEACHER Process Improvement Leader Operations Leader Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 51 of 53 Change Leader Learning and Development Leader LEAD PRINCIPAL 11/14/2005 Appendix B KSDs linked to Distributed Leadership Roles, NCATEE & PSC standards Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 52 of 53 11/14/2005 Appendix C Survey Data on Faculty Qualifications Title: Doctor of Education Description; Program Proposal Date: November 2005 Page 53 of 53