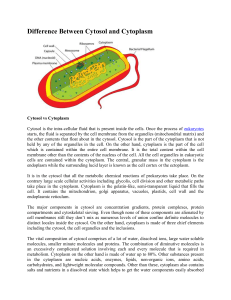
Cells
advertisement

Cells Robert Hooke -1665 • In his book, entitled Micrographia, Hooke was the first to use the term cell • From the Latin “cella” meaning “small chamber” Anton van Leeuwenhoek1675 • A Dutch cloth merchant who became interested in studying cells • Was the first to see and describe bacteria, sperm cells and protista • Theodor Schwann (1838) – all animals are composed of cells • Matthias Schleiden (1838) – all plants are composed of cells • Rudolf Virchow (1856) “Omnis cellula e cellula” • “where a cell arises, there a cell must previously have existed” Modern Cell Theory • All organisms are composed of cells. • Cell come from other cells. • Cells are the smallest unit of structure and function in living organisms. Prokaryotic Cells • Lack a true nucleus • Size: 1-10 microns • Include bacteria Basic Bacterial Cell Examples of Prokaryotes Eukaryotic Cells • Have a true nucleus • Size: 10-100+ microns • Include plants, animals, fungi and protista • • • • Cell Membrane – surrounds the cell Cytosol – “cell liquid” Organelles – “little organs” Nucleus- control center Cell Membrane • Regulates the passage into and out of the cell • Provides protection • Helps in cellular recognition of molecules Cytosol/Cytoplasm • Cytosol: the liquid portion inside the cell membrane • Cytoplasm: the cytosol and organelles, but not the nucleus Nucleus Nucleus • Contains DNA • The cell’s “brain” or CPU • DNA codes for protein production • Surrounded by the nuclear envelope Cytoplasm • Contains the cytosol and organelles • • • • • • Ribosomes Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi bodies or complex Lysosomes Mitochondria Chloroplasts Ribosomes Ribosomes • Are the cell’s protein factories • Read mRNA code as seen on the right • Maybe free in the cytoplasm • Or bound to the ER Endoplasmic Reticulum • Comes from the Greek Endo = “within” Latin reticulum = “network.” • A membrane network within the cytoplasm • Two types: Rough – with ribosomes attached (RER) • Or Smooth – with no ribosomes (SER) Rough ER • Helps the ribosomes in the formation of proteins • Used to transport proteins to other parts of the cell Smooth ER • Functions include synthesis of membrane lipids & detoxification of drugs • Liver cells contain large amounts of smooth ER Golgi Body Golgi Body • Modify, sort, and package proteins from the ER for storage in the cell & secretion out of the cell Lysosomes Lysosomes • Digestive sacs filled with enzymes • Breakdown lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into a form that can be used by the cell • Digest worn out organelles • Helps to recycle cellular structures • Sometimes called “suicide sacs” • Involved in rheumatoid arthritis • Example… Mitochondria • Converts chemical energy stored in food into compounds that the cell can use (cellular respiration) • Contain their own DNA Chloroplasts • Site of photosynthesis • Contains the green pigment chlorophyll • Helps to convert light energy, water, and carbon dioxide into sugars • Also contain genetic information Endosymbiotic Theory • States mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free living prokaryotic cells • First proposed in the 1890s, but not supported until 1981 with the discovery of mitochondrial DNA • Explanation… Vacuole • Storage area for water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates • Many plants have a large central vacuole filled with liquid to support the plant Cell Wall • The cell wall is a rigid structure that is found in plants, fungi, and bacteria cells • It supports and maintains the shape of the cell. It is extremely strong.