AP Chemistry Rate Law from Data Example O
advertisement
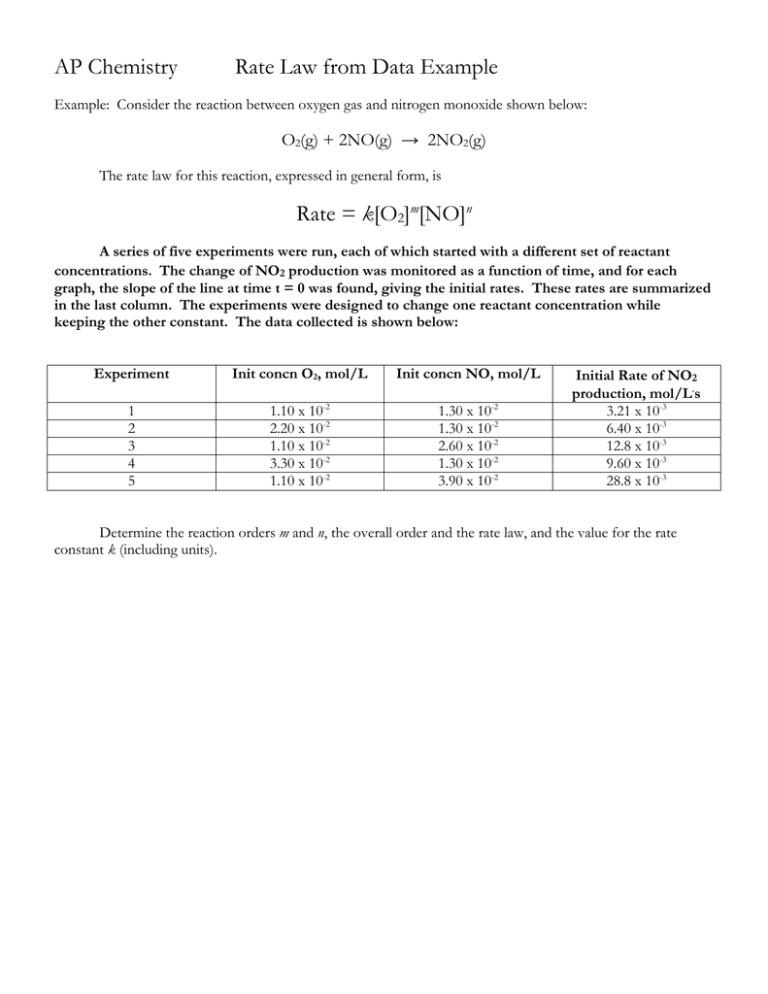
AP Chemistry Rate Law from Data Example Example: Consider the reaction between oxygen gas and nitrogen monoxide shown below: O2(g) + 2NO(g) → 2NO2(g) The rate law for this reaction, expressed in general form, is Rate = k[O2]m[NO]n A series of five experiments were run, each of which started with a different set of reactant concentrations. The change of NO2 production was monitored as a function of time, and for each graph, the slope of the line at time t = 0 was found, giving the initial rates. These rates are summarized in the last column. The experiments were designed to change one reactant concentration while keeping the other constant. The data collected is shown below: Experiment Init concn O2, mol/L Init concn NO, mol/L 1 2 3 4 5 1.10 x 10-2 2.20 x 10-2 1.10 x 10-2 3.30 x 10-2 1.10 x 10-2 1.30 x 10-2 1.30 x 10-2 2.60 x 10-2 1.30 x 10-2 3.90 x 10-2 Initial Rate of NO2 production, mol/L.s 3.21 x 10-3 6.40 x 10-3 12.8 x 10-3 9.60 x 10-3 28.8 x 10-3 Determine the reaction orders m and n, the overall order and the rate law, and the value for the rate constant k (including units).