AP Chemistry Schrodinger Wave Equation – The Highlights Schrodinger Wave Equation (SWE):

AP Chemistry Schrodinger Wave Equation – The Highlights
Schrodinger Wave Equation (SWE):
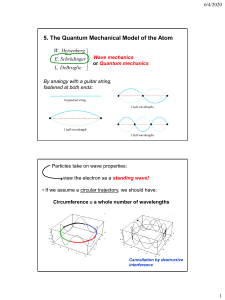
A very complex differential equation that describes the behavior of an electron in the atom as wave-like.
Solutions to the SWE are themselves equations, referred to as wave functions ( , psi).
Each unique electron has its own wave function , thus theoretically there are 110 (?) current possible solutions to the SWE.
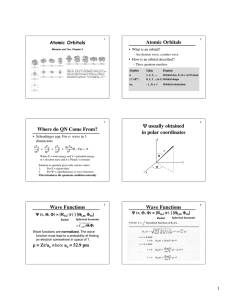
describes the state of an electron by providing information about it, doing so in the form of Quantum
Numbers. Thus, provides QUANTUM NUMBERS (n, l, m l
) describing the behavior of the electron.
If one squares ( 2 ), a function describing the probability of finding the electron about the nucleus is formed. This function is what we call an ORBITAL and is best represented graphically below. Thus, 2
provides ORBITALS describing the probability of finding the electron in the atom.
(a) 2
1s
(the 1s orbital for hydrogen)
(b) The Radial probability graph for the 1s orbital of hydrogen. max. away from nucleus
As the electron increases in energy, its 2 distributions increase in complexity, giving rise to orbitals of different shapes and an increase of zero probability regions (nodes) in the orbital
90% boundary:
Inside this lies
90% of the probability nodes


![6) cobalt [Ar] 4s 2 3d 7](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009918562_1-1950b3428f2f6bf78209e86f923b4abf-300x300.png)