Cell Division
advertisement

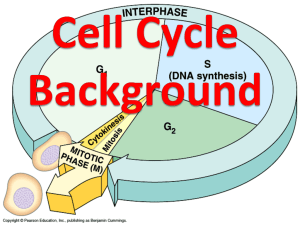
Cell Division CHAPTER 3 SECTION 5 I can… explain the process of cell division Did you write down your homework? Warm Up: According to the cell theory, where do all cells come from? Wrap Up: What two parts of the cell cycle are not technically part of the process of Mitosis? Cell Cycle The regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo Cell grows Prepares for division Divides into two new cells, “daughter cells” Three main stages: Interphase Mitosis cytokinesis Stage 1: Interphase Period before cell division The cell grows to full size Replicates Makes an EXACT copy of its DNA in its nucleus Each daughter cell must have a complete set of DNA to survive End of replication, cell contains two identical sets of DNA Prepares to divide Stage 2: Mitosis Mitosis The second stage of the cell cycle Cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei One copy of the DNA is distributed into each of the two daughter cells 4 Parts of Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 4 Parts of Mitosis Prophase Threadlike chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form double-rod structure called chromosomes Each chromosome has two rods, due to replication Each identical rod in a chromosome is called a chromatid Two chromatids are held together by a centromere 4 Parts of Mitosis Metaphase The chromosomes line up at the center of the cell Each chromosome attaches to a spindle fiber at its centromere 4 Parts of Mitosis Anaphase The centromeres split The chromatids separate by spindle fibers (go to opposite ends of the cell) 4 Parts of Mitosis Telophase Chromosomes begin to stretch out, lose rodlike appearance Nuclear envelope forms around each region of chromosomes Stage 3: Cytokinesis Cytokinesis Final stage of the cell cycle The cytoplasm divides Organelles are distributed into each of the two new cells The cell will then enter interphase… and the cycle begins again. Cytokinesis in Animal Cells: cell membrane squeezes together Cytokinesis in Plant Cells: cell wall cannot squeeze together, a cell plate forms that gradually will develop into the cell membrane The Structure of DNA Looks like a twisted ladder, or spiral staircase The sides of the ladder are made up of Deoxyribose (sugar) Phosphate Each rung of the ladder is made up of a pair of molecules called nitrogen bases Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) The Replication Process The two sides of the DNA molecule unzip and separate Nitrogen bases floating in nucleus pair up with the bases on each half of the DNA molecule New bases attach, two new DNA molecules form