AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
advertisement

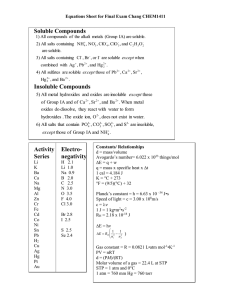
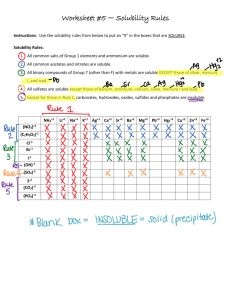
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment Welcome to AP Chemistry! I am looking forward to our school year together! AP Chemistry is a difficult course. It is not all about memorization; however, having these following items as rote memory is essential for success in learning the concepts covered in the course. These should be review from your Honors Chemistry course. Make flashcards, have your friends and family quiz you, take the lists with you on vacation, or do whatever it takes to get this information firmly planted in your head. We will have a test on this information within the first few weeks of school. Topics to Review: Physical vs chemical properties and changes—describe, identify, and apply Atoms, elements, mixtures (heterogeneous & homogeneous), and compounds—contrast, identify, and apply Scientific notation—use appropriately and apply Metric system—apply and use appropriately Significant figures—use appropriately Temperature conversions, especially between Kelvin and Celsius scales Atomic theory—describe Atomic structure—identify subatomic particles, their locations, and their charges and describe how the structure has changed over time Isotopes, including calculating average atomic mass—describe and identify Molecule—describe and identify Ion & types—describe and identify Periodic Table—describe, including main characteristics, and identify: o Metals o Nonmetals o Metalloids o Families/Groups o Ionic charge o Number of valence electrons Name compounds & write chemical formulas for ionic, covalent, and acidic compounds and hydrates Write & balance chemical equations—5 main types Percent Composition—describe and complete applicable calculations Empirical & Molecular Formulas, including hydrates—contrast, complete applicable calculations, and identify Stoichiometry—complete applicable calculations of all types: moles, mass, number of particles, and volume Molarity & Dilutions—describe and complete appropriate calculations Limiting Reactants, Excess Reactants, & Percent Yield—contrast, describe, and complete appropriate calculations Aqueous—describe and identify Electrolyte, including types—describe and identify Net Ionic Equations—describe and be able to write from overall molecular equation Acid vs Base & relative strengths—contrast, including main characteristics Neutralization—describe, identify, and balance appropriate reactions Titration—describe, know when the technique is used, and complete appropriate calculations Reduction, Oxidation, reducing agent, oxidizing agent, and oxidation numbers—contrast and apply Balance redox reactions, in both acidic and basic solutions Polyatomic ions—KNOW THEM ! Name Ammonium Acetate Tartrate Arsenate Bromate Borate Thiocyanate Formula & Charge NH4+ CH3COO- or C2H3O2C4H4O6-2 AsO4-3 BrO3BO3-3 SCN- Cyanide Cyanate Permanganate Hydroxide Iodate Nitrite Nitrate Hypochlorite Chlorite CNCNOMnO4OHIO3NO2NO3ClOClO2- Name Chlorate Perchlorate Oxalate Selenate Silicate Carbonate Hydrogen Carbonate (Bicarbonate) Chromate Dichromate Thiosulfate Sulfate Hydrogen Sulfate (Bisulfate) Sulfite Hydrogen Sulfite (Bisulfite) Phosphite Phosphate Dihydrogen Phosphate Formula & Charge ClO3ClO4C2O4-2 SeO4-2 SiO3-2 CO3-2 HCO3CrO4-2 Cr2O7-2 S2O3-2 SO4-2 HSO4SO3-2 HSO3PO3-3 PO4-3 H2PO4- Solubility Guidelines— KNOW THEM ! One of the options below may be helpful: Option 1: o o All ammonium and Group 1 compounds are soluble. For halogens: o All chlorides are soluble except those of silver, mercury, and lead. Lead (II) chloride is soluble in hot water. o All bromides are soluble except those of silver, mercury, and lead. o All iodides are soluble except those of silver, mercury, and lead. o All fluorides are insoluble except ammonium & group 1 compounds. o o o o o o o Chlorates, acetates, nitrates, nitrites, and perchlorates are soluble. Sulfates are soluble except those of calcium, strontium, barium, mercury, radium, lead, and silver. Phosphates, chromates, carbonates, borates, sulfites, and silicates are insoluble except ammonium and Group 1 compounds. All metallic oxides are insoluble except those of ammonium and Group 1 compounds. All metallic hydroxides are insoluble except those of ammonium, Group 1, and Group 2 below calcium. All sulfides are insoluble except those of ammonium, Group 1, and Group 2. Most silver salts are insoluble except those of silver nitrate and silver acetate. Option 2: https://www.google.com/search?q=visual+solubility+table&espv=2&biw=1024&bih=643&tbm=isch&imgil=XTrfB eYlurjfoM%253A%253BQc3i9jT0y_VdOM%253Bhttps%25253A%25252F%25252Fwww.teacherspayteachers. com%25252FProduct%25252FVisual-Solubility-Table1026650&source=iu&pf=m&fir=XTrfBeYlurjfoM%253A%252CQc3i9jT0y_VdOM%252C_&usg=__0CZ5qEUrGy 051dzz8pN95Ydepqg%3D&ved=0CCkQyjc&ei=7FMVcnQDIibyATCq4HgBg&safe=active&ssui=on#imgrc=XTrfBeYlurjfoM%253A%3BQc3i9jT0y_VdOM%3Bhtt ps%253A%252F%252Fmcdn1.teacherspayteachers.com%252Fthumbitem%252FVisual-Solubility-Table054522200-1387500259%252Foriginal-10266501.jpg%3Bhttps%253A%252F%252Fwww.teacherspayteachers.com%252FProduct%252FVisual-SolubilityTable-1026650%3B350%3B270 Option 3: Solubility Rules Made Easy - An acronym: “CASH N’ Gia.” All these things are soluble unless they are found with certain elements. - A list of bullet points if you do not like the acronym. The best way to remember these is pure memorization. There is no short cut! All Soluble Except With Chlorates Acetates Sulfates Halogens CaBaSr HgAgPb (CBS HAPpy) HgAgPb (HAPpy) N’itrates Group (IA) i a Option 4: Simple Solubility Rules: Nitrate (NO3-) salts are soluble. Alkali (group 1) salts and NH4+ are soluble. Cl-, Br-, and I- salts are soluble (NOT Ag+, Pb2+, Hg22+) -Sulfate salts are soluble (NOT BaSO4, PbSO4, HgSO4, CaSO4) -OH− salts are only slightly soluble (NaOH, KOH are soluble, Ba(OH)2,Ca(OH)2 are marginally soluble) -S2−, CO32−, CrO42−, PO43− salts are insoluble.