Five Essential Components in Reading Bingo
advertisement

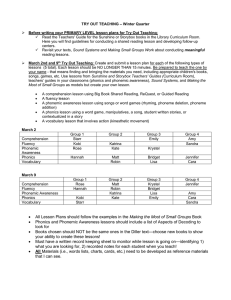
Five Essential Components in Reading Bingo Directions For each of the five essential components the following elements will be presented: definition, examples (activities), high priority skills, and instructional research. After each slide, mark the appropriate spot on your Bingo card until you make a Bingo. Blending two and three sounds to make words. Segmenting spoken words into individual Sounds. Phonemic Awareness High priority skills in kindergarten In small groups, the students list as many meanings as they can think of for the word, main. Vocabulary Example Keep the end in mind. Have students apply phonics skills daily in reading and writing activities. Phonics Instructional research Reads 110 words correct in a minute with phrasing and appropriate expression. Fluency High priority skill for third grade Before reading an information passage, the teacher has students make predictions about that they think they will learn. Comprehension Example Teacher places three picture on the board. She says three individual sounds out loud that represent the name of one of the pictures. Students listen and say the word. Phonemic Awareness Example Blends sounds in printed words together and reads words as a whole accurately. Phonics High priority skill in first grade Teacher models reading of a passage explicitly teaching smooth reading and pausing at punctuation. Fluency Example Learns and uses unfamiliar words introduced in stories and informational text. Vocabulary High priority skill for all grade levels. Retell the main idea of stories or informational text. Answers literal, inferential and evaluative questions about a passage. Comprehension High priority skill for first - sixth grade The teacher tells the students that -dge and -ge both stand for /j/ at the end of words. Students then sort a group of twenty -ge and -dge words to determine when the -dge spelling is used. Students read the words once they are sorted. Phonics Example Students move three chips into sound boxes as they say single sounds of the word /h/ /ou/ /se/ (house). Phonemic Awareness Example During reading, students stop and discuss at predetermined spots in the passage what the gist of that section is: Who or what is the passage mostly about? What is important about the who or what? Tell me that in a main idea statement. Comprehension Example Use relatively brief sessions (15-20 minutes) with texts that students are reading with 90-95% accuracy. Fluency Instructional research Students attempt to define the word burden by reading this sentence: the pilgrim’s burden weighed heavily on his shoulders as he ascended the steep mountain trail. Vocabulary Example Understanding that words are made up of letters, sounds are connected to letters, and can use these letter and letter combinations to read and spell unfamiliar words. Phonics Definition Children pair up and do repeated reading of a passage to improve automaticity and phrasing. Fluency Example Complex process of listening/reading and reacting to spoken/written text in a meaningful way Comprehension Definition Make sure students know meanings of words that are used in sound blending and sound segmenting activities. Phonemic Awareness Instructional research Understanding and use of words to acquire and convey meaning (mental dictionary). Vocabulary Definition Explicitly teach rather than mention or assess. Teaching students to be strategic will take time. Comprehension Instructional research The teacher points to the written word matador and asks how many syllables are in the word. Phonics Example Ability to read words in grade level text accurately with automaticity and with proper expression. Fluency Definition Awareness that spoken words are made up of individual sounds. Phonemic Awareness Definition Repetitions and multiple exposures (4-12) to word in a variety of contexts. Vocabulary Instructional research