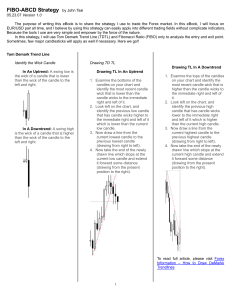
Memory & Problem Solving Chapter 10 Acquiring, Processing, and Retaining Information
advertisement

Memory & Problem Solving Chapter 10 Acquiring, Processing, and Retaining Information 3 Steps Input: Information people receive from their senses. Central Processing: Storing (Memory) and sorting (thought) the information. Output: Ideas and actions that result. Taking Information In 2 processes (steps) help people narrow sensory inputs to a manageable number. SELECTIVE ATTENTION The ability to choose among the various available inputs. “Cocktail-Party Phenomenon” TOP-PRIORITY Hunger Strange Interest FEATURE EXTRACTION Locating the outstanding characteristics of incoming information. Experience helps! The identification of anything. Aoccdrnig to a rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtsy, it deosn’t mttaer waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmaotnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a total mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit a porbelm. STORING INFORMATION Memory 3 types 1. Sensory Storage Your senses holds information for an instant. Ex. Movie Frames Experiment - cover lens! T D R S R N F Z K 2. SHORT–TERM MEMORY Keeps information in mind about 20 seconds. Rehearsal: Repeating information to self (Ex. Paying close attention). Chunking: Limited capacity of 7 bits of information. Ex. 5556794 = 555-6794 or 555-67-94 3. LONG-TERM MEMORY Store information for future use. Involves all sensory processes. Declarative memory Semantic: A network and associations of facts, concepts and skills. Language, rules words and meanings. Episodic: Concrete information, personal experiences. Memories of ones life. Procedural: Concrete, executable procedures stored in memory, Learned skills RECOGNITION Human memory is organized to make recognition easy. Single item is under several headings. Ex. WWSHS, Multiple choice test, Mug shot or Line up. RECALL The active reconstruction of information. Knowledge, attitudes and expectations Essay test, Police sketch. EIDETIC MEMORY Photographic memory. Usually Children. How many white stripes on the cats tail? Proactive Interference An early memory blocks out a more recent memory. 2013 v. 2014 Retroactive Memory A Recent memory blocks out an older memory. Ex. New locker combo. CONFABULATION *Remembering information not stored in memory. *Categorical intrusion. Bed, rest, tired, wake, night, dream, eat, comfort, awake, sound, slumber, snore. “Sleep” 50% to 75% will recall – but, not on list. THINKING Changing and reorganizing information stored in memory to create new information. Different units of thought include images, symbols, concepts, prototypes, and rules. DIRECTED THINKING A systematic and logical attempt to reach a specific goal. Symbols, concepts and rules. Ex. Math, crosswords. NONDIRECTED THINKING Free flow of thoughts with no goal or plan. “Creativity is the residue of time wasted.” Images Ex. Daydreaming, Brainstorming. PROBLEM SOLVING Strategies: Specific methods for approaching problems. Set: Useful strategies become cemented into the problem solving process. Rigidity:When a set interferes with problem solving. CREATIVITY The ability to use information in such a way that the result is somehow NEW, ORIGINAL and MEANINGFUL. Can you Solve this? A man in Wheaton, IL has married 20 women. All of the women are still alive, and none of them is divorced. The man has broken no laws. Who is the man? Can you Solve this? People were given a candle, matches and a box of tacks and asked to attach the candle to a corkboard wall so that the candle would burn without dripping wax on the floor. 3 components FLEXIBILITY: The ability to overcome rigidity. RECOMBINATION: A new mental rearrangement of the elements. INSIGHT: “Aha experience” The sudden emergence of a solution by the recombination of the elements.