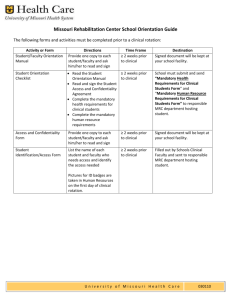
COMMUNITY UNIT SCHOOL DISTRICT 200 Social Studies Curriculum
advertisement

COMMUNITY UNIT SCHOOL DISTRICT 200 Social Studies Curriculum We believe that through Social Studies education, every child can learn the role of responsible citizenship in a culturally diverse society in a democratic world. Students will be able to access information which will help them be curious lifelong learners capable of making informed and reasoned decisions for the public good. Grade 6 1. Subject Expectation (State Goal 14) The student will understand political systems, with an emphasis on the United States. Essential Learning 1 (Learning Standard A) Understand and explain basic principles of the United States government Critical Content a. identify different world governments and compare them to the United States and local governments feudalism monarchy empires theocracy b. explain the principles of government expressed in the Magna Carta c. give examples of how political systems/governments provided for the needs and wants of the people, established order and security, and managed conflict d. identify who had the authority to make decisions in the world civilizations or empires 14.A.3 14.A.3 14.A.3 14.A.3 Essential Learning 2 (Learning Standard B) Understand the structures and functions of the political systems of Illinois, the United States and other nations Critical Content a. examine the roles and responsibilities of world political systems and compare them to our own within the social hierarchy of the existing governments such as tribal organization theocracy monarchy dictatorship aristocracy republic city-state bureaucracy b. explain the role and need for authority in societies 14.B.3 14.B.3 NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 1 Essential Learning 3 (Learning Standard C) Understand election processes and responsibilities of citizens Critical Content a. recognize the need for authority figures in society b. identify the processes by which leaders emerge in world civilizations and compare them to our own election process and personal freedoms such as dynasties military takeovers societal influence 14.C.3 14.C.3 Essential Learning 4 (Learning Standard D) Critical Content 14.D.3 14.D.3 14.D.3 14.D.3 Understand the roles and influences of individuals and interest groups in the political systems of Illinois, the United States and other nations of the years between AD 476 and AD1700 a. explain the effects of interest groups within the political system and how these groups can bring about changes (religious, cultural and economic) such as state-sponsored religions trade-guilds political factions b. explain the causes, purposes, and/or motivations that cause cooperation or conflict between and among cultures c. identify how the various cultures influenced the development of political ideas in other cultures d. identify treaties and alliances between political entities Essential Learning 5 (Learning Standard E) Understand United States foreign policy as it relates to other nations and international issues Critical Content a. examine the interests and relationships within political entities and between cultures conquest alliance b. explain the influence of one civilization on another (cultural diffusion) 14.E.3 14.E.3 Essential Learning 6 (Learning Standard F) Understand the development of United States political ideas and traditions Critical Content a. analyze historical influences on the development of political ideas and practices in other cultures as well as the United States such as wars religious events technology b. understand the development of the rule of law and personal freedoms as demonstrated in the Magna Carta and other cultural ideals 14.F.3a 14.F.3b NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 2 Essential Learning 7 * Formulate and defend reasoned judgments and evaluate those of others regarding political topics Critical Content * a. examine and evaluate persistent issues throughout the civilizations and identify the pros and cons such as succession of power use and abuse of power b. demonstrate an understanding that different people may describe the same event or situation in diverse ways but must provide reasons or evidence for their views c. explain and apply concepts such as power, justice and equity to situations in world history between AD 476 and AD 1700 d. apply the following skills and strategies to formulate and defend ideas relative to civilizations between AD 476 and AD 1700 distinguish fact from opinion interpret point of view in primary sources deduce causes and effects of historical events analyze information provided in illustrations, maps, charts, and graphs in fiction and nonfiction history readings including primary sources distinguish primary from secondary sources interpret the meaning of political cartoons criticize decisions made throughout history and justify criticisms with evidence infer motivations for decisions made throughout history hypothesize solutions to problems using factual evidence from history and current events justify predictions using historical evidence e. interpret quotes of famous people from various periods of history * * * * Essential Learning 8 * Use reading and writing strategies to comprehend expository materials Critical Content * a. activate background information using pre-reading strategies such as brainstorming previewing predicting surveying using skimming and scanning setting a purpose b. recognize the organizing principles of a text in order to aid comprehension and recall format features within a text - identify heading to determine the ordinance hierarchy of ideas - discern where a section of text starts and stops using organizational visual cues * NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 3 * * * * - distinguish headings from boldfaced vocabulary words - identify features unusual to the specific text *skill pages *captions *review section *adjunct pages of information *charts *graphs - use the front and end matter of text *glossary *table of contents knowledge of the interrelationship among ideas - enumeration (listing) - time order (chronology) - comparison/contrast - cause/effects - problem/solutions c. adjust one’s reading rate to the reading task skimming scanning retelling d. develop and apply appropriate strategies during reading to understand expository text use metacognitive strategies - confirming or rejecting previous predictions - revise/formulate predictions - develop questions as one reads - self-monitoring - rereading use vocabulary strategies to determine text meaning - context clues - word recognition strategies - glossary usage e. check for understanding of expository text after reading using various strategies such as summarize information in internal, oral or written formats paraphrase information in oral or written formats make generalizations from text in oral or written formats form reasoned arguments/judgments from text in oral or written formats decide what’s important information in a text f. produce written products for a variety of purposes and audiences such as note taking outlining summarizing research reports NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 4 expository essays persuasive essays narrative essays journaling illustrating formulate answers to open-ended questions Essential Learning 9 * Access, use and evaluate information from a variety of sources Critical Content * * a. self-select appropriate research materials b. recognize and understand the function of parts of a book and use appropriately such as table of contents index glossary gazetteer atlas timeline c. locate and organize information using a variety of resources such as encyclopedia periodicals atlas almanac non-fiction books computer technology videos newspaper approved Internet sites historical fiction community resources such as speakers and museums * NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 5 2. Subject Expectation (State Goal 15) The student will understand economic systems, with an emphasis on the United States. Essential Learning 1 (Learning Standard A) Define the principles of the economic systems used by world cultures between the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the 1700’s Critical Content 15.A.2a, 15.A.3a 15.A.3a 15.A.3b 15.A.3c 15.A.3d * * Essential Learning 2 (Learning Standard B) Critical Content 15.B.3a 15.B.3b 15.A.2a 15.B.3a a. define the principles of the economic systems used by early civilizations such as exchange (trade, barter, use of currency) production (agriculture, culture, crafts) distribution (local markets, trade routes) consumption of goods and services b. explain how market prices signal producers about what, how and how much to produce c. explain the relationship between productivity and wages d. describe the relationship between consumer purchases and businesses paying for productive resources e. describe the causes of unemployment (e.g., seasonal fluctuation in demand, changing jobs, changing skill requirements, national spending) f. explain the economic reasons for immigration and migration worldwide throughout history g. make connections between the economic systems of the world civilizations to that of the U.S. Understand that scarcity necessitates choices by consumers a. describe the “market clearing price” of a good or service relative to world cultures b. explain the effects of choice and competition on individuals and the economy as a whole c. analyze the relationship between a civilization’s geography and its economic development d. explain the following concepts scarcity surplus supply and demand NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 6 15.A.2a * e. explain how technological advancements affected the economies of civilizations between AD 476 and AD 1700 such as tools plow writing paper the printing press in Europe mathematics calendar irrigation transportation construction techniques maritime technology military technology farming techniques f. make connections between technological advancements of a world civilization to that of the U.S. Essential Learning 3 (Learning Standard C) Understand that scarcity necessitates choices by producers Critical Content a. identify and explain the effects of various incentives to 15.C.3 formulate a good or service b. explain the effects of choices c. explain why different cultures had different or various goods Essential Learning 4 (Learning Standard D) Understand trade as an exchange of goods or services Critical Content a. explain the effects of increasing and declining imports and exports to an individual and to the nation’s economy as a whole with an emphasis on: foreign trade age of exploration b. explain how comparative advantage forms the basis for specialization and trade among nations including gold and salt trade in Africa c. explain how workers can affect their productivity through training and by using tools, machinery and technology such as printing press better farming and irrigation technologies d. explain how trade among cultures created various degrees of interdependence e. explain how trade within a culture created various degrees of interdependence 15.D.3a 15.D.3b 15.D.3c 15.D.3b 15.D.3b NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 7 Essential Learning 5 (Learning Standard E) Understand the impact of government policies and decisions on production and consumption in the economy Critical Content a. identify the types of taxes levied by differing levels of governments (e.g. income tax, sales tax, property tax) religious taxes import/export taxes b. explain how laws and government policies (e.g. property rights, contract enforcement, standard weights/measurements) establish rules that help a market economy function effectively 15.E.3a 15.E.3b Essential Learning 6 * Formulate and defend reasoned judgments and evaluate those of others regarding relevant economic topics Critical Content * a. examine and evaluate persistent economic issues throughout the civilizations and identify the pros and cons such as values and beliefs influencing different economic decisions including uneven distribution of wealth b. demonstrate an understanding that different people may describe the same event or situation in diverse ways but must provide reasons or evidence for their views c. use economic concepts to help explain historical and current developments and issues in local, national, or global contexts d. apply the following skills and strategies to formulate and defend ideas relative to civilizations between AD 476 and AD 1700 distinguish fact from opinion interpret point of view in primary sources deduce causes and effects of historical events analyze information provided in illustrations, maps, charts, and graphs in fiction and nonfiction history readings including primary sources distinguish primary from secondary sources interpret the meaning of political cartoons criticize decisions made throughout history and justify criticisms with evidence infer motivations for decisions made throughout history hypothesize solutions to problems using factual evidence from history and current events justify predictions using historical evidence * * * Essential Learning 7 * Use reading and writing strategies to comprehend expository materials Critical Content * Same as Subject Expectation 1, Essential Learning 8 Essential Learning 8 * Access, use and evaluate information from a variety of sources Critical Content * Same as Subject Expectation 1, Essential Learning 9 NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 8 3. Subject Expectation (State Goal 16) The student will understand events, trends, individuals and movements shaping the history of Illinois, the United States and other nations. Essential Learning 1 (Learning Standard A) Apply the skills of historical analysis and interpretation Critical Content a. apply the models historians have used for organizing historical interpretation biographies political events issues conflicts b. interpret and/or complete data presented in timeline format c. make inferences and analyze data about historical events and eras using historical sources historical maps charts/graphs primary source documents images d. compare and contrast historical fact and interpretation e. identify and describe selected historical periods and patterns of change within and across cultures with a focus on the cultural universals 16.A.3a 16.A.3b 16.A.3b 16.A.3c 16.A.3b Essential Learning 2 (Learning Standard B) Understand the development of significant political events Critical Content a. compare the political characteristics of different world civilizations between the years of A.D. 476 and A.D. 1700 including Muslim Empires (Umayyad, Abbasid, Muslim Spain) African Empires (Ghana, Mali, Songhai, Zimbabwe, Kongo) Asian Civilizations (China, Japan) Europe (feudal kingdoms of the medieval period, monarchies and republics/city-states of the postmedieval period) Early American Civilizations (Maya, Aztec and Inca) b. investigate and analyze the causes and effects of major world political events such as the growth of Islam the development of feudalism the effects of exploration c. identify turning points in world political history 16.B.3a (W) 16.B.3b (W) 16.B.3b (W) NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 9 16.B.3b (W) d. identify causes and effects of the decline of major world empires and political events including 16.B.3c (W) 16.B.3d (W) Islamic Empires Kingdoms of West and East Africa Chinese Dynasties Japanese Feudalism Feudal kingdoms into monarchies Civilizations of the Americas e. investigate and analyze the causes and effects of European feudalism and the emergence of nation states between 500CE and 1500CE f. analyze political effects of European exploration and expansion on the Americas, Asia, and Africa after 1500 CE Essential Learning 3 (Learning Standard C) Understand the development of economic systems Critical Content a. survey major economic trends from 476 A.D. to 1700 A.D. including long distance trade, banking, specialization of labor, commercialization, urbanization, technological and scientific progress b. explain the economic systems and trade patterns of Central and South America before the encounter with the Europeans c. describe the impact of technology in different parts of the world including weaponry printing transportation farming technology d. describe basic economic changes that led to and resulted from the development of agricultural system such as division of labor surplus trade 16.C.3a (W) 16.C.3b (W) 16.C.3c (W) 16.C.2c(W) Essential Learning 4 (Learning Standard D) Understand Illinois, United States and world social history Critical Content a. identify the origins and analyze consequences of events that have shaped world social history including famines, migrations, plagues, slave trading 16.D.3 (W) Essential Learning 5 (Learning Standard E) Understand Illinois, United States and world environmental history Critical Content a. summarize how people around the world use and adapt to environmental resources to form successful civilizations (e.g. water, natural resources, landforms) such as Middle East-desert Africa-desert, rainforest 16.E.3a (W) NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 10 16.E.3b (W) 16.E.3b (W) b. draw a conclusion to demonstrate how contact between cultures had an environmental impact transfer of disease exploration foreign trade c. explain how expanded European and Asian contacts affected the environment of both continents, 476AD-1500AD Essential Learning 6 * Formulate and defend reasoned judgments and evaluate those of others regarding historical topics Critical Content a. identify and use key concepts such as chronology, causality, change, conflict and complexity to explain, analyze and show connections among patterns of historical change and continuity b. apply the following skills and strategies to formulate and defend ideas relative to civilizations between AD 476 and AD * * 1700 distinguish fact from opinion interpret point of view in primary sources deduce causes and effects of historical events analyze information provided in illustrations, maps, charts, and graphs in fiction and nonfiction history readings including primary sources distinguish primary from secondary sources interpret the meaning of political cartoons criticize decisions made throughout history and justify criticisms with evidence infer motivations for decisions made throughout history hypothesize solutions to problems using factual evidence from history and current events justify predictions using historical evidence Essential Learning 7 * Use reading and writing strategies to comprehend expository materials Critical Content Same as Subject Expectation 1, Essential Learning 8 * Essential Learning 8 * Access, use and evaluate information from a variety of sources Critical Content Same as Subject Expectation 1, Essential Learning 9 * NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 11 4. Subject Expectation (State Goal 17) The student will understand world geography and the effects of geography on society, with an emphasis on the United States. Essential Learning 1 (Learning Standard A) Locate, describe and explain places, regions and features on the Earth Critical Content a. explain how people use geographic markers and boundaries to analyze and navigate the Earth such as hemispheres, meridians, continents, bodies of water locate and identify the continents, major climates, major bodies of water, specific rivers, and natural resources in the geographical regions studied b. identify land formations and bodies of water which are characteristic of the geographical regions studied and explain their relationship to the ecosystem - mountain - desert - river - coastline - ocean - sea - continent - peninsula - sea level - delta - plain - strait - lake - land bridge c. locate civilizations between AD 476 and AD 1700 and their corresponding modern day countries using latitude longitude hemisphere cardinal directions intermediate directions d. interpret a variety of maps using a key to estimate distances and calculate scale a scale other graphic representations legends e. explain how to make and use geographic representations to provide and enhance spatial information including maps, graphs, charts, models, aerial photographs and satellite images 17.A.3a 17.A.3a 17.A.3a 17.A.3b 17.A.3b Essential Learning 2 (Learning Standard B) Analyze and explain characteristics and interactions of the Earth’s physical systems Critical Content a. explain how physical processes including climate, plate tectonics, erosion, soil formation, water cycle, and circulation patterns in the ocean shape patterns in the environment and influence availability and quality of natural resources such as desertification of Sahara migration of African Civilizations migration of hunter-gatherers in Americas 17.B.3a NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 12 17.B.3b b. explain how changes in components of an ecosystem affect the system overall such as famines plagues farming techniques Essential Learning 3 (Learning Standard C) Understand relationships between geographic factors and society Critical Content a. explain how human activity is affected by geographic factors (deserts, climate, mountains, bodies of water) such as Middle East- desert and nomads Africa-multiple climates Asia-sea as a natural resource Europe-trade routes on water Americas-hunter and gatherers to settlers b. explain how natural resources are used in various world cultures such as trade between cultures use of resources for cultural uses salt and gold trade different building materials conflict between cultures accessibility of various civilizations c. analyze how human processes influence settlement patterns including migration and population growth such as transportation technology exploration 17.C.3a 17.B.3b 17.C.3c Essential Learning 4 (Learning Standard D) Understand the historical significance of geography Critical Content a. explain how and why spatial patterns of settlement change over time desertification location of urban and rural centers migration conquests b. show how interactions of geographic factors have shaped present conditions such as monsoons, deserts, growing seasons, agricultural modifications 17.D.3a 17.D.3b NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 13 Essential Learning 5 * Formulate and defend reasoned judgments and evaluate those of others regarding geographical topics Critical Content * a. identify and use key concepts such as chronology, causality, change and conflict to explain, analyze and show connections among patterns of change and continuity relative to geography observe and speculate about social and economic effects of environmental changes and crises resulting from phenomena such as floods, storms and drought b. demonstrate an understanding that different people may describe the same event or situation in diverse ways but must provide reasons or evidence for their views c. apply the following skills and strategies to formulate and defend ideas relative to ancient civilizations identify the main idea identify facts from opinions determine causes and results of issues and conflicts identify multiple perspectives of individual society members summarize key events leading up to conflict between cultures judge the significance and advantages of certain geographical locations * * Essential Learning 6 * Use reading and writing strategies to comprehend expository materials Critical Content * Same as Subject Expectation 1, Essential Learning 8 Essential Learning 7 * Access, use and evaluate information from a variety of sources Critical Content * Same as Subject Expectation 1, Essential Learning 9 NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 14 5. Subject Expectation (State Goal 18) The student will understand social systems, with an emphasis on the United States. Essential Learning 1 (Learning Standard A) Compare characteristics of culture as reflected in language, literature, the arts, traditions and institutions Critical Content a. determine how language, literature, the arts, architecture and traditions contribute to the development and transmission of culture such as poetry and tales places of worship universities b. recognize the use of both written and oral language to communicate such as to increase cooperation to transmit values and history of the culture c. explain and compare how writing was used in various cultures such as recording business transactions through the use of a scribe recording laws religious beliefs literature determine social class d. recognize the literary, artistic and architectural contribution of world civilizations e. recognize the scientific, mathematical and philosophical contributions of world civilizations f. recognize the importance of artifacts found by archeologists to our understanding of the lives of the people of world civilizations g. give an example of ethnocentrism 18.A.3 18.A.3 18.A.3 18.A.3 18.A.3 18.A.3 18.A.3 Essential Learning 2 (Learning Standard B) Understand the roles and interactions of individual and groups in society Critical Content a. analyze how individuals and groups interact with and within institutions (e.g. educational, military, hierarchies, religious groups, guilds) b. demonstrate an understanding of how social institutions contribute to the development and exchange of cultural ideas such as universities and schools religious groups c. describe personal connections to community, nation, and world d. describe ways family, gender, ethnicity, nationality, and institutional affiliations contribute to personal identity 18.B.3a 18.A.3b 18.B.3a 18.B.3a NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 15 18.A.3b 18.A.3b 18.B.3a e. demonstrate an understanding of concepts such as role, status, and social class in describing the interactions of individuals and social groups f. apply knowledge of how groups and institutions work to meet individual needs and promote the common good g. explain the causes and the effects of conflicts between groups and/or institutions such as crusades Essential Learning 3 (Learning Standard C) Understand how social systems form and develop over time Critical Content a. describe ways in which diverse populations have interacted to form a common cultures (empires) such as common religious beliefs monetary systems languages b. analyze group and institutional influences on people, events, and elements of culture c. describe the role of institutions in furthering both continuity and change 18.C.3a 18.C.3a 18.C.3a Essential Learning 4 * Formulate and defend reasoned judgments and evaluate those of others regarding social topics Critical Content a. identify and interpret examples of stereotyping and conformity b. identify and analyze examples of tensions between expressions of individuality and group or institutional efforts to promote social conformity c. apply the following skills and strategies to formulate and defend ideas relative to civilizations distinguish fact from opinion interpret point of view in primary sources deduce causes and effects of historical events analyze information provided in illustrations, maps, charts, and graphs in fiction and nonfiction history readings including primary sources distinguish primary from secondary sources interpret the meaning of political cartoons criticize decisions made throughout history and justify criticisms with evidence infer motivations for decisions made throughout history hypothesize solutions to problems using factual evidence from history and current events justify predictions using historical evidence * * * NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 16 Essential Learning 5 * Use reading and writing strategies to comprehend expository materials Critical Content Same as Subject Expectation 1, Essential Learning 8 * Essential Learning 6 * Access, use and evaluate information from a variety of sources Critical Content Same as Subject Expectation 1, Essential Learning 9 * NOTE: such as = an example used for clarification, but not a mandatory concept including= a mandatory concept * = exceeds state standards Grade 6 Board Approved 1-23-08 17